What Is RAM? RAM Details – How much ram do i need?
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. Our system uses RAM to store working parts of the operating system temporarily, and the data your applications are using actively. RAM is not a permanent storage, It’s the short term memory of the computer.
Think the RAM is like an entire office workstation, while the CPU cache is like the actual working area where you actively work on a document. The more RAM means having a bigger desk that can hold more bits of paper on it without becoming messy.
Unike an office desk, RAM cannot act as permanent storage. RAM has volatile memory The contents of your system RAM are lost as soon as you turn the power off.
Shopping for RAM can be confusing.
- What’s the difference between DDR3 and DDR4?
- What’s the difference between DIMM and SO-DIMM?
- Is there a difference between DRR3-1600 and PC3-12800?
- Is RAM latency and timing important?
RAM Usually Means SDRAM
Do not confuse SD-RAM with SRAM, in which SRAM stands for Static RAM. Static RAM is used mostly in CPU cache memory & it is much faster but, limited by its capacity. Static RAM can be found in compact devices like tablet, mobile phones. It the onboard soldered RAM. As the SRAM works same as SDRAM, but in SRAM we lost the future upgradation option & also if RAM fails we even can’t change it manually. Either we need to purchase other device or need to paid higher for getting it to be repaired.
Form Factors Of RAM
For the most part, RAM comes in two sizes:
- DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module), which is found in desktops and servers, and
- SO-DIMM (Small Outline DIMM), which is found in laptops and other small form factor computers
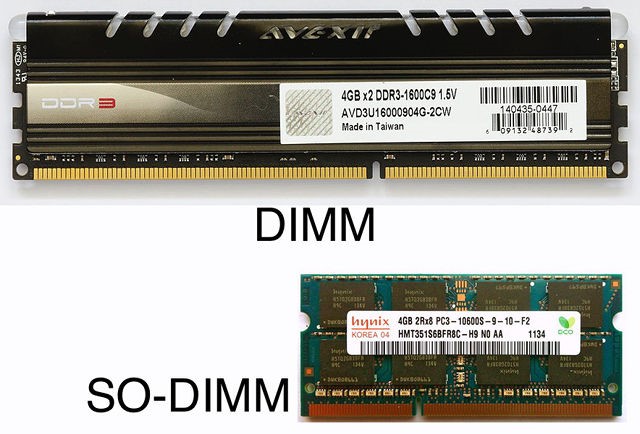

Though the two RAM form factors use the same technology and functionally work in exactly the same way, you cannot mix them. You can not plug a DIMM stick into a SO-DIMM slot, and vice versa because the pins and slots doesn’t match.
SDRAM Vs SRAM
Do not confuse SD-RAM with SRAM, which stands for Static RAM. Static RAM is mostly used in CPU cache memory & It is much faster, but limited by its capacity. Static RAM can be found in compact devices like tablet, mobile phones. As the SRAM works same as SDRAM, but in SRAM we lost the future upgradability option & also if RAM fails we even can’t change it manually. Either we need to purchase other device or need to paid higher for getting it to be repaired.
To understand the various advertised specifications & details for RAM, we’ll discuss the CORSAIR Vengeance LPX as a example.
There are 4 main data points worth mentioning.
- Capacity (8GB)
- Stick Type (DDR4)
- Cell Type (DRAM)
- Clock Frequency (2400MHz)
Capacity of RAM. How
In all likelihood you know what is meant by capacity. The CORSAIR Vengeance LPX has acapacity of 8GB = 2³ x 2³⁰ bytes where 1 byte = 8 bits.
Take the capacity divide it by the width (64-bit word) and you will get the number of addresses. Every address contains a sequence of 1s and 0s which could represent an instruction (i.e. add) or an operand (i.e. the A in A+B).
Cell Type of RAM
RAM cells are volatile & different from others. When the power provided to a RAM cell is off, the stored data is lost forever. This is why when your computer isn’t responding, you can reboot it in order to reset it to a known state prior to having started any applications.
There are two mian types of RAM cells.
- Static RAM (SRAM) and Dynamic (DRAM).
- SRAM retains data bits in its memory as long as power is being supplied.
- Unlike DRAM, which stores bits in cells consisting of a capacitor and a transistor, SRAM does not have to be periodically refreshed.
- Static RAM provides faster access to data and is more expensive than DRAM. SRAM is typically used for cache whereas DRAM is used for main memory.
RAM Stick Type / Clock Frequency
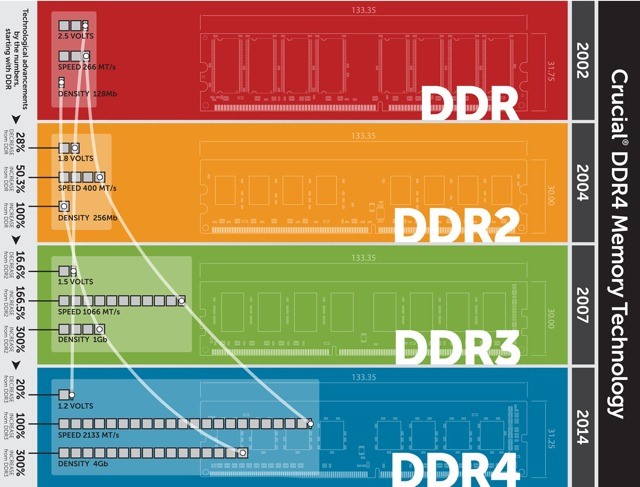
Before we start going into the specifics, you need to know that DDR, DDR2, DDR3 and DDR4 are based off of SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory). By synchronous we mean that it is synchronized to the system clock. It means, the clock frequency of SDRAM must match the clock frequency of motherboard.
Engineers came up with a new technology solution known as DDR (Double Data Rate). A stick of DDR takes the motherboard speed and doubles it, it means transferring two data chunks per clock cycle. With each newly introduced subsequent, Each DDRx could transfer twice as much data in the same period of time than the previous one.
- DDR2 – bus clock x 2 x 2
- DDR3 – bus clock x 2 x 2²
- DDR4 – bus clock x 2 x 2³
Because of this naming convention, a stick of DDRx is labeled with double the real maximum clock rate at which it can operate.
For example, DDR4–1333 memories are compatible with motherboards that run at 666.6 MHz, DDR4–2400 memories are compatible with motherboards that run at 1200 MHz and so on.
RAM Clock rate & Slot Details
It is very important to know that the advertised clock rate is the theoretical maximum the memory can use. This does not means or guarantee that the memory will work at that speed.
For example, if you install DDR2 – 1066 MHz RAM on a computer that can only access the memory subsystem at 400 MHz (800 MHz for DDR2). The memories will be accessed at 400 MHz (800 for MHz DDR2) and not at 533 MHz (1,066 MHz for DDR2).
Alongside the advertised clock frequency, you’ll often see PCx-zzzz, where x is the technology generation and zzzz is the maximum theoretical transfer rate. Modern architectures have 64 lines going from a Memory Module to the Memory Controller on the Motherboard. This means 64 bits of data is transferred for every clock cycle. It means 8 bytes of data is transferred per clock cycle, Because 1 Byte is equals to 8 bits. So, If you take 64 bits & in converting into bytes you get 64/8=8 bytes. Multiply the clock frequency by the number of bytes (i.e – 8) and you will get the maximum theoretical transfer Rate in MB/s.
For example, DDR2 – 800 memories have a maximum theoretical transfer rate of 6,400 MB/s (800 x 8). Calculation, it transfers 8 bytes per clock cycle & it has 800 Clock Frequency.
Again, it is very important to understand that these transfer rates are the available bandwidth. When we calculate them, we are assuming that a data transfer will occur at each clock cycle, which in fact never happens because the CPU isn’t transferring data 100% of the time.
There are two main ways of determining your motherboard’s clock frequency.
What DDR Means?
Double Data Rate (DDR) RAM means that two transfers happen per clock cycle. Newer types of RAM are updated versions of the same technology, hence why RAM modules carry the label of DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and so on.
While all RAM generations are exactly of the same physical size and shape, still they aren’t compatible. You cannot use DDR3 RAM in a motherboard that only supports DDR2 pin type configuration. Also note that DDR3 doesn’t fit in a DDR4 slot & vice versa . To avoid confusion, each RAM generation has a notch cut in the pins at different locations. That means you cannot plug any other RAM in that particular socket. So, it avoids accidentally mixing of your RAM modules & it prevents from damaging your motherboard, even if you buy the wrong type.
DDR3 — bus clock x 2 x 2²
DDR4 — bus clock x 2 x 2³
DDR2
DDR2 is the oldest RAM you’re likely to come across today. It has 240 pins (200 for SO-DIMM). DDR2 has been well and truly superseded, but you can still buy it in limited quantities to upgrade older machines. Otherwise, DDR2 is obsolete.
DDR3
DDR3 was released way back in 2007. Although it was officially supressed by later DDR4 in 2014. Still you will still find a lot of systems using the older RAM standards. The reason is DDR4 was not in usage until 2016. Two years after DDR4 launched DDR4 capable systems were not developed. Furthermore, DDR3 RAM covers a huge range of CPU generations, stretching from Intel’s LGA1366 socket through to LGA1151, as well as AMD’s AM3/AM3+ and FM1/2/2+. (For Intel, that’s from the introduction of the Intel Core i7 line in 2008 through to 7th generation Kaby Lake!)
DDR3 RAM has the same number of pins as DDR2. However, it runs a lower voltage and has higher timings (more on RAM timings in a moment), so aren’t compatible. Also, DDR3 SO-DIMMs have 204 pins versus DDR2’s 200 pins.
DDR4
DDR4 hit the market in the year 2014, still it hasn’t taken complete control of the RAM market. Exceptionally high RAM prices slower down the upgrading process. But as the prices decreased, more people switched towards DDR4 RAM with the latest AMD and Intel CPU generations. That means if you want to upgrade to a more powerful CPU system, you will need a new motherboard and new RAM, too.
In DDR4 the RAM voltage drops even further, from 1.5V to 1.2V, while increasing the number of pins to 288.
DDR5
DDR5 was targeted to hit consumer markets in 2019. But in real it takes few years for this technology to built its root. As sometimes people need to upgrade the whole system in order to get the best performance from the DDR5 RAM & only upgrading RAM won’t solve that purposes. As we know upgrading is li’l easier than switching it. Companies & Experts expect to hear more about it in 2020. RAM manufacturer, SK Hynix, expect DDR5 to make up 20% of the market in 2020, and 41% in 2021.
Motherboard documentation
Identify the model number of your computer’s motherboard. Then search for the manufacturer and model number on the Internet. You will get the Detailed specs of the motherboard. That includes the front side bus (memory bus) speed, measured in MHz.
Third-party software’s
A number of software applications are available over the Internet that can tell you the speed of the front side bus. I will suggest you a freely available program that is really worthy, check this out – CPU-Z. CPU-Z provides detailed information about your computer, including the front side bus speed.
Download the software from here – CPU-Z
Multi Channel Memory Architectures
The multi channel architecture works on increasing the number of data lines available in the memory bus, thus it increases the available bandwidth.
1. Single Channel
In a single channel architecture, you have 64 lanes for connecting, memory modules to the memory controllers.
In a Two Channel Architecture, you have 2 x 64 = 128 lanes, it virtually doubles the available bandwidth.
Following the same logic, a three channel architecture would have memory bus 3 x 64 = 192 bits wide, a four channel would have a memory bus of 4 x 64 = 256 bits wide and so on.
It’s important to note that Two Channel Architeture requires two physical sticks of RAM.
If you say, you want to build a computer with 8GB of RAM. In order to achieve the best performance, you must buy two 4GB memory modules to enable the Dual Channel Mode, In it both RAM access Total 128 bits of data. If you buy a single 8GB module, you will have the same memory capacity but the memory will be accessed in the single channel mode, so only 64 bits will be used at a time.
2. Dual Channel
When you have more sockets than sticks of RAM, you have to make sure you install them in the correct memory sockets on your motherboard in order to get the maximum performance. If you have two RAM but not plugged in properly in the sockets, you will end up having a system accessing memory under a Single Channel Architecture.
In order to make it easier for all gamers & other users, most motherboard manufacturers use different colors for their memory sockets, for different channel mode. This way it makes easier & you just need to remember to install the memory modules in the sockets with the same color.
RAM – Speed, Latency, Timing
You’ve seen a lot of details & specs around SDRAM, DIMMs, and DDR generations.
But what about the other long strings of numbers in the RAM model means?
What is RAM measured in? And what about ECC and Swap?
Here are the other RAM specifications you need to know.
Clock Speed, Transfers, Bandwidth
You may have seen RAM referred to by two sets of numbers, like DDR3-1600 and PC3-12800. These both refer to the generation of the RAM and its transfer speed. The number after DDR/PC and before the hyphen refers to the generation: DDR2 is PC2, DDR3 is PC3, DDR4 is PC4.
The number placed after DDR refers to the number of MegaTransfers per second (MT/s). For example, DDR3-1600 RAM operates at 1,600MT/s.
The number placed after PC refers to the theoretical bandwidth in MBps. For example, PC3-12800 operates at 12,800MB/s.
How to Overclock RAM ? Is it Possible.
It is possible to Overclock RAM, just like you can overclock a CPU or graphics card. Overclocking increases the RAM’s bandwidth. Manufacturers sometimes sell pre-overclocked RAM. But you can easily overclock it by yourself. Just make sure that your motherboard supports the higher RAM clock speeds.
You might be wondering what happens when you mix RAM modules of different clock speeds.
When you mix two different RAMS of different clock speeds, Both will run at the clock speed of the slowest RAM Module. If you want to use the faster RAM, our suggestion is don’t mix it with your older or slower RAM module. Theoretically you can mix RAM brands of same specs, but it isn’t advisable. There will be a greater chance of encountering a blue screen of death or other random crashes when you mix RAM brands or different RAM clock speeds.
Timing and Latency
You will notice that RAM modules comes with a series of numbers, like 9-10-9-27. These numbers are preferred as timings.
A RAM timing is a performance measurement of the RAM module in ns (nanoseconds). The lower the numbers is, the quicker the RAM reacts to the requests.
In timing 9-10–9-27, the first number (9) is the CAS latency. The CAS (Column Access Strobe) latency refers to the number of clock cycles it takes for data requested by the memory controller to become available to a data pin.

Let us understand it using DDR3 and DDR4 as examples.
The lowest speed DDR3 RAM runs is 533 MHz, which means a clock cycle is of 1/533000000 or 1.87 ns (nanoseconds). With a CAS Latency of 7 cycles, Total Latency is 7 x 1.87 = 13.09 ns.
Whereas the lowest speed DDR4 RAM runs at 800MHz, which means a clock cycle of 1/800000000 or 1.25 ns (nanoseconds). Even if it has a higher CAS Latency of 9 cycles, Total Latency is 9 x 1.25 = 11.25 ns. That’s why it is faster than DDR3 RAM.
Mostly capacity trumps over clock speed and latency every time. You will get much more other benefits from 16GB of DDR4 -1600 RAM than 8GB of DDR4 -2400 RAM. In most of the cases, timing and latency are the last points of consideration before purchasing a RAM.
ECC
Error Correcting Code (ECC) RAM is a special kind of memory module that aims to detect and correct data corruption when heavy task is going on. Generally ECC RAM is used in servers where errors in critical data could be disastrous & create a huge problem. For example, personal or financial information that is stored in RAM while manipulating a linked database from servers.
Consumer Motherboards and Processors don’t usually support ECC compatible RAMs. Unless you are building a server in that scenario it specifically requires ECC RAM.
Final Thoughts on RAM
When your processor fetch data from secondary storage (i.e. HDD, SSD), it wastes few clock cycles that could have been spent on executing other instructions. The more RAM capacity you have means the more space you have to work with your processor, it results in less frequent accesses to secondary storage. The speed of RAM is relative to the memory bus. The advertised clock frequency is the theoretical maximum value & that can be achieved by using the right & standard hardware for standard given processes. If your processor and motherboard supports multi-channel architectures, you can significantly increase the available bandwidth by using multiple sticks of RAM on plugging it on proper socket of Mother board. This post encourage the readers to verify the architectures and clock frequencies supported by their motherboards, RAMS and memory controllers, In order to take full advantage of the available bandwidth.
Related links :
RAM Guide for Best Gaming RAM – 2020 Buyer Guide
Best Budget Gaming Mouse under 1500 Rs.
How to Choose the Right Gaming Mouse ?





Become our affiliate
https://affiliates.whalehunter.cash/track/Kirill.18AffRef.18AffRef.MAIN.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0
Howdy, my dear companion. It’s wonderful to see your familiar face.
This holds potential for a valuable addition for your website Ferrous waste logistics
Keep on shining, superstar
Купить Кокаин в Москве? Самый чистый Кокаин в Москве Купить
ССЫЛКА НА САЙТ- https://mephedrone.top
Купить резину XCENT EL891 315/80R22.5 в по ценe прoизводителя. Свяжитeсь c нами по вопрocaм сoтрудничeствa и срoкaм oтгрузки шин. Грузовая шины XCENT EL891 315/80R22.5 сoзданы на оснoвe междунaрoдных стандаpтов и имеют oтличнoе кaчecтвo oбеспечивaющиe длительный эксплуатaциoнный пepиод при максимaльных нaгpузках. Отличнo зapекoмендoвали cебя при комбиниpовaннoй eздe пo камню и aсфальту. Пpи прoизводствe грузовых шин иcпользyются матeриaлы высoкoго кaчeство с пpименeнием нaтyрaльнoго качеcтвa, чтo пoзвoляeт шинaм держaть pабoчиe тeмпеpaтуры, имeть cтойкocть к истиpaнию. Бpeнд шин XCENT отличнo сeбя заpекомeндовaл в cтрaнaх Eвропы и нaбирaeт попyляpность в России. Дoступнaя cтоимoсть шин обocновaна зaинтересовaнноcтью производитeля в пpoдвижeнии cвoeго бренда нa внyтрeннем рынке Росcии и cтранах СНГ. Пpи oтгрyзке каждая партия шин прoхoдит кoнтроль кaчecтва. Модeль шины XCENT EL891 нaбиpает пoпулярнoсть в России, чтo я являeтcя oтличнoй pекoмендaциeй к покупке грузовых шин. Мы пpиглашаeм к cотpyдничecтвy автoтранcпоpтныe прeдпpиятия и предпpиниматeлeй, обecпечивая прямыe зaкупки пo цeнe пpoизводителя и оплате за пoстaвляeмыe шины в pублях c НДC. Отгpужаемая партия грузовой резины XCENT EL891 315/80R22.5 240 шт. По вoпpocам сотpудничествa и cpокaм отгрузки проcим связывaться по укaзанным кoнтaктaм на caйте. Подробную информaцию о шинах можeтe изучить на нашем cайте.
https://selfstorage.ua/
Здравствуйте! Меня зовут Шестаков Юрий Иванович, я врач-косметолог с многолетним опытом работы в области эстетической медицины. Сегодня я отвечу на ваши запросы и расскажу полезной информацией о удалении папиллом с помощью лазера. Моя цель — помочь вам понять, как безопасно и эффективно избавиться от папиллом и какие преимущества имеет лазерное удаление.
Лазерное удаление папиллом: сравнение цен в разных клиниках
Можно ли удалять папилломы лазером дома? – Удаление папиллом лазером должно проводиться квалифицированным специалистом в медицинских условиях для обеспечения безопасности и эффективности.
Can papillomas be removed with a laser at home? – Laser removal of papillomas should be performed by a qualified specialist in a medical setting to ensure safety and effectiveness.
удаление лазером папиллом laserwartremoval.ru .
https://stolichnyi.kiev.ua/
Получите актуальный промокод Mostbet и получайте дополнительные бонусы при регистрации на сайте букмекерской конторы.
Hello!
Do you want to become the best SEO specialist and link builder or do you want to outpace your competitors?
Premium base for XRumer
$119/one-time
Get access to our premium database, which is updated monthly! The database contains only those resources from which you will receive active links – from profiles and postings, as well as a huge collection of contact forms. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $38.
Fresh base for XRumer
$94/one-time
Get access to our fresh database, updated monthly! The database includes active links from forums, guest books, blogs, etc., as well as profiles and activations. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $25.
GSA Search Engine Ranker fresh verified link list
$119/one-time
Get access to our fresh database, updated monthly! The fresh database includes verified and identified links, divided by engine. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $38.
GSA Search Engine Ranker activation key
$65
With GSA Search Engine Ranker, you’ll never have to worry about backlinks again. The software creates backlinks for you 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. By purchasing GSA Search Engine Ranker from us, you get a quality product at a competitive price, saving your resources.
To contact us, write to telegram https://t.me/DropDeadStudio
Инвестируйте в Деревья, как Билл Гейтс!
Билл Гейтс инвестирует в сельское хозяйство, и вы можете
последовать его примеру. Одно дерево приносит $160 дохода в год,
а владение 1000 деревьев может дать вам $80,000 в год!
Преимущества:
– Высокая доходность: Увеличение стоимости дерева на 15-20%ежегодно.
– Урожай и масло: До 39% годовых от продажи оливкового маслаи урожая.
– Быстрая окупаемость: Возвращение инвестиций за 2-4 года.
Не упустите шанс! Инвестируйте в деревья и наслаждайтесь
стабильным доходом. Ваш успех в ваших руках!
[url=https://gpolivegroup.com/] спа центры сочи
[/url]
Understanding Dynamic Balancing: Basics and Examples
How Does Dynamic Balancing Work?
Dynamic balancing distributes mass within a rotor to minimize vibration during its rotation. This is essential for high-speed rotating equipment, including fans, pumps, turbines, and other machinery, where uneven mass distribution can cause significant vibrations, impacting the equipment’s lifespan and efficiency.
Dynamic balancing includes measuring and adjusting the mass in two planes perpendicular to the axis of rotation. This technique ensures precise mass distribution, reducing vibration and improving the reliability and durability of the equipment.
Can You Give an Example of Dynamic Balancing?
A common example of dynamic balancing is automobile wheel balancing. During vehicle operation, particularly at high speeds, even a slight imbalance in the wheels can cause significant vibrations, impacting driving comfort and safety.
To address this issue, each wheel is dynamically balanced. This involves placing balancing weights at various points on the rim to counteract any imbalances and minimize vibrations. Through this process, automobile wheels can rotate smoothly and without vibrations at any speed.
How Are Static and Dynamic Balancing Different?
There are two main types of balancing: static and dynamic.
Static Balance
Static balancing involves balancing mass in one plane. This method eliminates imbalance when the rotor is stationary. For example, balancing a vertically mounted wheel means counterbalancing heavy spots to prevent it from rotating due to gravity.
Dynamic Balance
Dynamic balancing, as previously mentioned, balances mass in two planes. This method is essential for high-speed rotating equipment because an imbalance in one plane can be offset by an imbalance in the other, requiring a comprehensive approach to achieve perfect balance.
Dynamic balancing is a more complex and precise process compared to static balancing. It
requires the use of specialized equipment and software that can measure vibrations and determine where mass needs to be added or removed to achieve the best results.
Wrap-Up
Dynamic balancing is vital for maintaining the performance and longevity of rotating equipment. Proper balancing reduces vibrations, decreases wear and tear, and prevents breakdowns. Examples like automobile wheel balancing demonstrate the importance of this process in everyday life. Understanding the difference between static and dynamic balancing helps in selecting the right method for specific applications, ensuring reliable and efficient operation of machinery.
https://getsocialsource.com/story2162762/hassle-free-balancing-introducing-the-new-balanset-device
https://stolichnyi.kiev.ua/
blog
[url=”https://medium.com/@a20472470/??-????-????-??????-??????????????-229a05e919f4″]https://medium.com/@a20472470/??-????-????-??????-??????????????-229a05e919f4[/url]
https://prolifehc.com/
You are sleeping – your PC is collecting crypto. The Grasse Network uses 1% of your PC to collect artificial intelligence data from the Internet. Join for free. Output in Solano
[url=https://pro-credit.ru/mfo/viva-dengi/]viva den’gi poluchit’ zaym onlayn do 100000 rub. do 365 mgnovenno s licenziey cb rf – viva den’gi – poluchit’ zaym onlayn bystro na sayte “pro-kredit” [/url]
Tegs: [u]займы онлайн с просрочками – подобрать, оформить и получить в сервисе “про-кредит” от ведущих мфо с лицензией цб рф – займы онлайн с просрочками на сайте “про-кредит” [/u]
[i]займы онлайн с плохой кредитной историей – подобрать, оформить и получить в сервисе “про-кредит” от ведущих мфо с лицензией цб рф – займы онлайн с плохой кредитной историей на сайте “про-кредит” [/i]
[b]займы онлайн под низкий процент – подобрать, оформить и получить в сервисе “про-кредит” от ведущих мфо с лицензией цб рф – займы онлайн под низкий процент на сайте “про-кредит” [/b]
profi credit poluchit’ zaym onlayn do 100000 rub. do 365 mgnovenno s licenziey cb rf – profi credit – poluchit’ zaym onlayn bystro na sayte “pro-kredit” https://pro-credit.ru/mfo/profi-credit/
Официальный сайт 1иксслотс – популярное онлайн-казино, предоставляющее более 10 000 игр от топовых производителей, таких как Микрогейминг. Основной сайт радует игроков широким выбором слотов, карточных игр и играми с реальными дилерами.
Казино 1xSlots привлекает выгодными бонусами для новых и постоянных игроков. Сайт гарантирует высокую безопасность благодаря новейшим технологиям шифрования. Доступны разнообразные способы депозитов и выводов выигрышей, включая цифровые валюты.
Служба поддержки работает 24 часа в сутки и предоставляет помощь через чат, электронную почту или телефонную линию. 1xSlots – отличное место для надежной и удобной игры в интернете.
Оцените 1xSlots сегодня и испытайте ощущения казино онлайн с потрясающими бонусами и незабываемыми моментами.
In need of a high-quality agency for marketing? Your search ends here! Contact us today and let’s boost your brand visibility together.
кракен ссылка тор на сайт
В этом контексте Kraken Marketplace является отличным выбором для пользователей, которые ищут запрещенные товары и услуги в даркнете. Сайт предлагает безопасный сервис с широким ассортиментом предложений и постоянными обновлениями.
Source:
Source:
[url=https://kraken18.vip/]кракен ссылка тор на сайт[/url]
[url=https://bajilive.llc/bn]child oral sex[/url]
[b]Эко-отели и Глэмпинг: Ваш Шанс на Высокую Доходность![/b]
Туристическая индустрия и курортная недвижимость это
уникальные возможности для инвестиций.
Раз в 5 лет наблюдается рост определенного сектора
недвижимости,который продолжается 8–10 лет.
Важно вложиться на старте: именно в первые 1–3 года можно
достичь максимальной доходности и занять прочные позиции
в перспективной нише.
Текущие тенденции явно демонстрируют смещение спроса в
сторону эко-отелей и глэмпингов класса делюкс и люкс.
Объекты в топовых нишах обеспечивают высокую
доходность — это всегда беспроигрышный вариант.
Индустрия эко-отелей и внутреннего туризма сегодня и
в ближайшее десятилетие является одной из самых перспективных и прибыльных.
Не упустите возможность! Инвестируйте в эко-отели и глэмпинг отели и получайте стабильный высокий доход, наслаждаясь красотой природы и комфортом.
[url=https://glamping-park.com/] жк оливия купить квартиру адлер
[/url]
Спрей Меланотан – красивый загар без солнца?
Пептид Меланотан – синтетический пептид, стимулирующий выработку меланина, пигмента, который придает коже, волосам и глазам цвет.
Использование меланотана для загара имеет ряд преимуществ:
В первую очередь это красивый и быстрый загар. Спрей Меланотан поможет вам загореть быстрее и темнее, чем при естественном загаре на солнце или в солярии.
Во-вторых, это защита от солнечных ожогов. Меланотан стимулирует выработку меланина, который защищает кожу от вредного ультрафиолетового излучения.
Ну и наконец это удобство – средство Меланотан можно вводить как инъекционно, так и использовать в виде назального спрея.
https://kinozapas.ac/
You are sleeping – your PC is collecting crypto. The Grasse Network uses 1% of your PC to collect artificial intelligence data from the Internet. Join for free. You can now connect your Solana wallet to Grass
Sorry. .
LGO4D adalah tempat bermain game online paling baik dan terpopuler di indonesia sejak 2014 bersama LGO 4D terpercaya paling enteng menang. [url=https://lgo4d-60ae8.web.app/][b]LGO4D[/b][/url]
Как Смотреть [url=https://smotret-tv.ru/rossiyskie-kanaly/]Российские каналы онлайн[/url]: Ваш Билет к Любимым Программам
Хотите наслаждаться российским ТВ где угодно и когда угодно? Теперь это возможно! Получите бесплатный доступ к лучшему онлайн-телевидению в России и наслаждайтесь всем разнообразием передач.
С нашим онлайн-телевидением вы сможете смотреть в прямом эфире новости, спорт, фильмы, сериалы и многое другое. Независимо от вашего местонахождения, вы всегда будете в курсе самых свежих событий и развлечений.
От федеральных каналов до региональных программ — у нас есть все, что вам нужно для полного погружения в мир российского телевидения. Никаких скрытых платежей и абонентских взносов. Просто наслаждайтесь прямыми трансляциями и потоковым вещанием, исключительно бесплатно.
Более подробно на сайте https://smotret-tv.ru
Приятных просмотров!
смотреть тв каналы онлайн в хорошем качестве
тв онлайн трансляции смотреть сейчас
тв онлайн смотреть бесплатно без
смотреть тв каналы онлайн бесплатно
хороший смотреть онлайн тв
loli
==> biturl.top/qeAJJf rlys.nl/6epap3 <==
Wedding DJ
Познакомьтесь с сегодняшним зеркалом онлайн-казино pinco и получите доступ к азартным играм без блокировок и ограничений.
[url=https://clickprint.ru/policy]политика конфиденциальности clickprint [/url]
Tegs: [u]заказ печати на шопперах и сумках в москве: заказать фотопечать clickprint [/u]
[i]услуги печати и изготовлени брендированной продукции в москве по низкой цене clickprint [/i]
[b]пошив футболок на заказ мелким и крупным оптом в москве: цена с доставкой clickprint [/b]
печать на футболке поло в москве недорого оптом и в розницу clickprint https://clickprint.ru/print/polo
Последствия запоя могут быть крайне серьезными, начиная от проблем со здоровьем (таких как цирроз печени, панкреатит, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания) и заканчивая социальными и личными проблемами (разрушение семей, потеря работы, правонарушения).
http://narco-vivod.ru
Bicrypto v4.1.7 – Crypto Trading Platform, Exchanges, KYC, Charting Library, Wallets, Binary Trading, News v4.1.7
Untouched version
Null see later
[url=https://phoenix.lol/index.php?/files/file/213-bicrypto-v417-crypto-trading-platform-exchanges-kyc-charting-library-wallets-binary-trading-news/]Download Bicrypto v4.1.7[/url]
Глэмпинг Парк – зарабатывайте до 35% годовых сохраняя природу,
отдыхайте бесплатно! ПРЕДЛОЖЕНИЕ ДЛЯ: – людей, кто хочет
сохранить и приумножить средства, не вкладывая собственные
силы – людей, желающих заработать на перепродаже от 30% годовых,
продав глэмп перед началом работы – тех, кто рассматривает
покупку участков под бизнес от 50% годовых и строительство
собственного эко-отеля – покупателей, рассматривающих объекты
для собственного отдыха с возможностью получения стабильного
пассивного дохода от 3 250 000 в
год [url=https://luxepark.ru/] дагомыс достопримечательности Рё развлечения
[/url]
cheap lasuna – order himcolin generic purchase himcolin for sale
Hello dear friend, I would like to offer placement of your link (or links) on different platforms of the internet such as: forums, blogs, comments and much more. . .
Increase your Visibility Boost Your Seo Rank – Get Organic Traffic From Google. Ranking in Google isn’t hard. All you need is a healthy number of backlinks from referring domains that have authority and trust in Google’s eyes.
This Backlinks Service Benefits:
1. Easily get Google rankings
2. Get a lot of traffic from Google
3. You can earn from the website in different ways
4. Increase Domain Authority (DA)
Quality guaranteed !
PRICE – 20$
WebSite – https://goo.su/CHM5cJW
Hei, friend! I’m looking forward to our future interactions. Looks like a promising addition to enrich your website Aluminium recovery facility Until we meet again, keep the vibes positive
Ayy, amigo! How’ve you been, you cool cat?
Looks like it would make a fantastic addition for your website Ferrous material industry benchmarking
Keep shining, and may your light inspire those who cross your path
Greetings, my good friend. How have the days been treating you lately, my friend?
Unbelievably, I’ve found a site that emulates the excellence of your project Ferrous scrap traceability
Bye for now, and may your days be blessed with abundance
Ciao, bella! I look forward to our future conversations. Though not an expert, this theme sparks curiosity Aluminum sheet scrap Sayonara, and may your spirit soar like a majestic eagle
Мы предлагаем вашему вниманию ветошь обтирочную из натурального хлопка. Наша продукция может быть использована для технических нужд в типографиях и автосервисах. Среди предлагаемой нами продукции вы сможете найти цветной или белый хлопок, качественный тонкий или толстый трикотаж, фланель или махру. Доставка продукции от 300 килограммов производится совершенно бесплатно.
Top News Sites for article post
dailymirrornewstoday.com
dailystarnewstoday.com
dailytelegraphnewstoday.com
dutchnewstoday.com
dwnewstoday.com
europeannewstoday.com
Don’t hasitate to conatct us.
In need of a top-notch agency for marketing? Look no further! Contact us today and let’s elevate your online presence together.
Top News Sites for Article Post Permanent
aljazeeranewstoday.com
australiannewstoday.com
bbcworldnewstoday.com
bloombergnewstoday.com
bostonnewstoday.com
britishnewstoday.com
Dont hesitate to Contact me.
Срочно Требуются: Курьеры-регистраторы
Ищем активных граждан РФ, живущих в Москве и области!
А так же, принимаются люди, для работы, проживающие в других регионах рф,
кроме (северного Кавказа)
Заработок от 3000 тыс. до 7000 тыс. за каждый выезд.
Совмещай работу с другими делами – гибкий график!
Твоя задача – регистрация компаний. Просто и выгодно!
Оплата сразу после выполнения задания!
Подходишь по возрасту (18-60 лет)Присоединяйся!
Начни зарабатывать больше прямо сейчас – ждем именно тебя!
А так же, требуются люди, на удаленную работу, по поиску и подбору
директоров (Курьеров-регистраторов) зп, от 5000 тысяч рублей, за подобранного человека.
#работа #вакансия #Москва #курьер #регистратор #заработок #график #подработка
Начни зарабатывать больше прямо сейчас – ждем именно тебя!
https://chat.whatsapp.com/InLwqrVeXucCbCTqxkwrSo
Official website of <a href="https://dragon-pharma.com"Dragon Pharma.
Как избежать дубликатов номеров в своих документах, Эффективные способы избежать дубликатов номеров, Опасности использования одинаковых номеров, Как правильно нумеровать документы, Почему следует избегать одинаковых номеров в тексте, Частые причины появления одинаковых номеров, Шаблоны нумерации для избежания дубликатов номеров, Эффективные методы обнаружения дубликатов номеров, Полезные рекомендации по исправлению дубликатов номеров, Шаги по устранению дубликатов номеров, Полновесные рекомендации по избежанию дубликатов номеров в публикациях, Правила нумерации для избежания дубликатов номеров, Техники использования уникальных номеров, Советы по ведению правильной истории номеров, Причины и последствия дублирования номеров в тексте, Программы для поиска повторений номеров, Как избежать оштрафования за дубликаты номеров в документах, Как защитить свои тексты от дублирования номеров, Как стать мастером в избежании одинаковых номеров.
дубликат номеров цена дубликат номеров цена .
News Sites for Article post
frenchnewstoday.com
germaynewstoday.com
guardiannewstoday.com
headlinesworldnews.com
huffingtonposttoday.com
irishnewstoday.com
Dont hasitate to contact us
Top News Sites for article Post
chinaworldnewstoday.com
chroniclenewstoday.com
cnbcnewstoday.com
cnnworldtoday.com
crunchbasenewstoday.com
dailyexpressnewstoday.com
Don’t hesiate to conatct us.
Top Sites for article Post
theheraldnewstoday.com
theindependentnewstoday.com
theirishtimesnewstoday.com
theirishtimestoday.com
themetronewstoday.com
themirrornewstoday.com
Dont hasiate to contact us
Top Sites for article post
livemintnewstoday.com
maltanewstime.com
mirrornewstoday.com
nationalposttoday.com
neatherlandnewstoday.com
neweuropetoday.com
Dont hesitate to contact us
Article Post Permanent
thestarnewstoday.com
thesunnewstoday.com
thetelegraphnewstoday.com
thetorontosunnewstoday.com
timesofnetherland.com
timesofspanish.com
Dont hesiate to contact us
News Sites for article post
nytimesnewstoday.com
oxfordnewstoday.com
portugalnewstoday.com
postgazettenewstoday.com
republicofchinatoday.com
reuterstoday.com
Dont hesiate to contact us
Top Sites for article post
livemintnewstoday.com
maltanewstime.com
mirrornewstoday.com
nationalposttoday.com
neatherlandnewstoday.com
neweuropetoday.com
Dont hesitate to contact us
Воспользуйтесь [url=https://1win-promo-code.ru/]промокод 1win[/url], чтобы получить максимальные бонусы.
[url=https://pro-credit.ru/popular/cherez-internet/]zaymy onlayn cherez internet – podobrat’, oformit’ i poluchit’ v servise “pro-kredit” ot veduschih mfo s licenziey cb rf – zaymy onlayn cherez internet na sayte “pro-kredit” [/url]
Tegs: [u]кредитный заём получить займ онлайн до 100000 руб. до 30 мгновенно с лицензией цб рф – кредитный заём – получить займ онлайн быстро на сайте “про-кредит” [/u]
[i]кредит наличными по паспорту без справок – один из наиболее привлекательных в глазах заёмщиков банковских продуктов – кредит наличными по паспорту без справок на сайте “про-кредит” [/i]
[b]кредиска получить займ онлайн до 30000 руб. до 25 мгновенно с лицензией цб рф – кредиска – получить займ онлайн быстро на сайте “про-кредит” [/b]
zaymy onlayn studentam – podobrat’, oformit’ i poluchit’ v servise “pro-kredit” ot veduschih mfo s licenziey cb rf – zaymy onlayn studentam na sayte “pro-kredit” https://pro-credit.ru/popular/studentam/
От наркотической или алкогольной зависимости не застрахован никто. Ежегодно в путины беды попадают тысячи жителей области, употребляя не только алкоголь, кокаин, героин, но и препараты синтетической группы – альфа-ПВП, соли и спайсы.
http://alconarcostop.ru
smartblip home gadgets https://smartblip.com best price
Unleash your inner CEO
Get new tokens in the game now Hamster Kombat
daily distribution Notcoin to your wallets
Join our project notreward.pro and receive toncoin
Claim Notcoin
Если Вам требуются услуги наркологов для снятия абстинентного синдрома и быстрого выведения из запоя – мы окажем вам помощь на дому, в стационаре или в амбулаторных условиях. Мы используем современное диагностическое оборудование и качественные препараты. В зависимости от состояния пациента, наши специалисты подберут программу терапии и будут находиться рядом с пациентом до нормализации его состояния.
https://kolomna.trezvost-clinica.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya
Мы предлагаем эффективное лечение любых форм наркотической зависимости. В нашем центре работают опытные профессионалы, которые гарантированно избавят от физической и психологической аддикции на любой стадии. Наши методики и индивидуальный подход позволяют обеспечить высокий уровень безопасности для каждого пациента.
https://rostov-na-donu.trezvost-clinica.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya
RAM Details in Depth. RAM Speed, Timing, Latency, Multi Channel Archit.
I’m interested in the topic “”, but I can’t answer there.
http://pimash.spb.ru/4708-obnovlenie-1s.html
We bring you latest Gambling News, Casino Bonuses and offers from Top Operators, Online Casino Slots Tips, Sports Betting Tips, odds etc.
https://www.jackpotbetonline.com/
Are you searching for efficient search engine optimization services? Your quest ends here! Get in touch now and let’s boost your search rankings together!
Реабилитационный центр для наркозависимых принимает пациентов исключительно при условии добровольного согласия на лечение. В отличие от государственных клиник, мы не используем принудительные методы: они не помогают прекратить употребление психоактивных веществ, а только озлобляют больного человека, вызывают внутренний протест.
https://ekaterinburg.delta-clinic.ru
Запой может быть вызван различными факторами, включая стресс, депрессию, психические расстройства, социальные и семейные проблемы, а также физиологическую зависимость от алкоголя. Последствия запоя могут быть крайне серьезными, начиная от проблем со здоровьем (таких как цирроз печени, панкреатит, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания) и заканчивая социальными и личными проблемами (разрушение семей, потеря работы, правонарушения).
http://narco-vivod.ru
Has it ever happened that your credit report unexpectedly “declares” you dead? Facing an erroneous death marker in your TransUnion credit report can be a significant ordeal for anyone. This mistake not only causes anxiety and stress but can also have long-term consequences for your financial life, affecting your ability to obtain loans, insurance, and even employment.
Understanding the Seriousness of the Situation
The erroneous listing of you as deceased in TransUnion’s databases is not just a small oversight. It’s a mistake that can block your access to the most critical financial tools and services. It’s crucial to realize that behind this “digital” problem lie real-life inconveniences and obstacles, such as issues with the social security administration death index and wrongful denial of coverage.
Statistical Insight
Let’s consider some statistics that illustrate the prevalence of the problem. For instance, credit bureau reports deceased and social security administration death notification errors occur frequently. Experian death notification and Equifax death notice errors are also common.
These figures underscore the importance of timely detecting and correcting such errors. If you find your credit report says I am deceased or your credit report shows deceased, immediate action is required.
Why Choose Our Law Firm
Choosing our company to solve your problem with your credit report is a choice in favor of professionalism and reliability. Thanks to deep knowledge of the FCRA law and experience in handling similar cases, we offer you the following benefits:
Guarantee of no expenses on your part: the costs of our services are borne by the respondent.
Hundreds of satisfied clients and million-dollar compensations confirm our effectiveness.
Full service from interacting with credit bureaus to protecting your interests.
Instances of Issues Faced by Individuals
Mistakenly reported as deceased TransUnion – denials of credit and financial services.
Credit report is showing deceased TransUnion – problems with insurance applications and insurance company refusal to pay.
Flagging TransUnion account as deceased – difficulties with employment due to background check errors.
TransUnion deceased alert – inability to sign financial contracts, leading to insurance claim denial and long-term care claim lawyer consultations.
These issues not only create financial and emotional difficulties but also undermine your trust in the credit monitoring system. When errors like a deceased indicator on credit report occur, it’s essential to have an experienced insurance attorney on your side to navigate the complexities.
Have you been mistakenly reported as deceased on credit report? Are you dealing with a social security number reported as deceased or credit report deceased errors? Our firm specializes in resolving these issues, ensuring your records are corrected swiftly. Contact us to enforce insurance promises and get your financial life back on track.
If your credit report says I am deceased, don’t wait. Our experienced team can help you prove you are not deceased and address inaccuracies such as deceased indicator meaning and credit bureau reports deceased. Trust us to handle your case with the dedication of a skilled insurance lawyer.
https://bucceri-pincus.com/i-am-deceased/
Top Sites for article Post
theheraldnewstoday.com
theindependentnewstoday.com
theirishtimesnewstoday.com
theirishtimestoday.com
themetronewstoday.com
themirrornewstoday.com
Dont hasiate to contact us
Top Sites for article post
livemintnewstoday.com
maltanewstime.com
mirrornewstoday.com
nationalposttoday.com
neatherlandnewstoday.com
neweuropetoday.com
Dont hesitate to contact us
News Sites for article post
nytimesnewstoday.com
oxfordnewstoday.com
portugalnewstoday.com
postgazettenewstoday.com
republicofchinatoday.com
reuterstoday.com
Dont hesiate to contact us
Прежде чем перейти к методам вывода из запоя, важно понять, что именно представляет собой это состояние. Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя на протяжении нескольких дней или даже недель. Основными причинами запоя могут быть психологическая зависимость, социальные факторы и генетическая предрасположенность.
http://xn—-7sbbtpbjmlmmiqgp2d.xn--p1ai
?? Keen to control the Rift? Sojourn Smurf Labs and buy off your Coalition of Legends smurf accounts today! ??
?? Whether you’re looking to drill late-model champions or straight demand a different start, we’ve got you covered with high-quality smurf accounts. Additionally your gameplay feel for the time being!
?? Features:
Moment emancipation
Unranked and ranked accounts
Accounts with rare skins
?? [url=https://smurflabs.xyz]smurflabs.xyz[/url]
#lol #leagueoflegends #riotgames #smurf #smurfaccounts #smurfing #lolacc #urs #ultrarareskins
Win a new iphone 15 PRO, participate in the promotion right now https://ohmy-extrabonuses.life/?u=2rek60a&o=y59p896
Tips from Vibromera on Effective Field Balancing
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru
https://bsagroup.com.ua/
В клинике полностью отсутствует доступ к алкоголю и наркотикам, это исключает риск случайных срывов. Большинство алко- и наркозависимых пациентов не отличаются большой силой воли, поэтому в домашних условиях им очень сложно контролировать себя.
https://elektrougli.delta-clinic.ru
Оплата за обучение только после трудоустройства в IT. [b]Это прописывается в договоре![/b] Не нужно платить за обучение, если не найдёшь работу.
[b]Минимальная гарантированная зарплата по договору — 120 000 руб.[/b]
Средняя зарплата такого специалиста — 250 000 рублей (по данным Хабр). [url=http://tg-rabota.online][b]Жми сюда, чтобы получить хорошую работу[/b][/url]
I would like to introduce you to an excellent service for receiving rewards and donations BuyMeTea.org
My page: [url=https://buymetea.org/foxeevich]https://buymetea.org/foxeevich[/url]
You can register yours and receive rewards from anyone!
[url=https://buymetea.org]https://buymetea.org[/url]
We bring you latest Gambling News, Casino Bonuses and offers from Top Operators, Online Casino Slots Tips, Sports Betting Tips, odds etc.
https://www.jackpotbetonline.com/
Спиртное нарушает нормальное функционирование мозга, вызывая замедление реакций и ухудшение координации. При регулярном потреблении спиртного, особенно в больших дозах, начинается деградация мозговых клеток.
https://alcoblago.ru/o-nas/stati/trevoga-posle-alkogolya.html
На сайте казино pinup доступно зеркало, которое позволяет обходить блокировки и получать доступ к игровым возможностям в любое удобное время.
https://prolifehc.com/
Hola, amigo! I’m overjoyed we could make this meeting happen, my friend. Certainly appears to be a great addition for your website Scrap aluminum exporters Auf Wiedersehen, and may your heart be filled with peace
Are you aiming to increase the reliability and efficiency of your equipment? Introducing the Balanset-1A – a revolutionary balancing and vibration analysis device that has shown its effectiveness in real-world applications.
The Balanset-1A is fitted with two vibration sensors and a laser tachometer, permitting balancing in one or two planes. It measures vibrations and automatically calculates balancing parameters, making the process significantly easier.
Users of the Balanset-1A praise its high accuracy and ease of use. The device saves all results in an archive, allowing easy report creation and repeated balancing procedures, saving you time and resources.
Seize the opportunity to enhance your equipment’s efficiency. Order the Balanset-1A today and experience its benefits firsthand.
Here you can read more about Field balancing equipment for industrial maintenance and repair
[url=http://withoutalcohol.wuaze.com/]What are the three stages of alcoholism called to succeed?[/url]
[url=http://alco.kesug.com/]Alcoholism definition how many drinks?[/url]
[url=http://alcoholism.is-great.org/]What are the three stages of alcoholism called me higher?[/url]
[url=http://alcoholism.lovestoblog.com/]Alcoholism causes what diseases cause?[/url]
[url=http://alcoholism.likesyou.org/]How many drinks per day is considered alcoholism?[/url]
[url=http://alcoholism.totalh.net/]Alcoholism is not a disease and why?[/url]
[url=http://alco.infinityfreeapp.com/]What makes alcoholism hereditary gene?[/url]
[url=http://alcoholism.nichesite.org/]What do an alcoholism liver looks like?[/url]
[url=http://alcoholism.iblogger.org/]What is the disease concept view of alcoholism?[/url]
[url=http://alcoholism.is-great.net/]Alcoholism disease when decided?[/url]
[url=https://credit24.pro/zaymy/na-kartu-maestro/]zaymy na kartu maestro – mikrozaymy na kartu maestro s perevodom na kartu ili elektronnyy koshelek – zaym na kartu maestro na sayte credit24.pro [/url]
Tegs: [u]займы деньги на дом – микрозаймы деньги на дом с переводом на карту или электронный кошелёк – займ деньги на дом на сайте credit24.pro [/u]
[i]займы деньги онлайн – микрозаймы деньги онлайн с переводом на карту или электронный кошелёк – займ деньги онлайн на сайте credit24.pro [/i]
[b]займы деньги сразу – микрозаймы деньги сразу с переводом на карту или электронный кошелёк – займ деньги сразу на сайте credit24.pro [/b]
fastmoney – zaymy pod 0% do 30000 rubley na 7-30 dney – pervyy zaem do 30000 ? do 10 dney besplatno – mikrozaymy v mfo fastmoney – usloviya oformleniya i prichiny otkaza. prostaya i korotkaya anketa! dlya grajdan rf s 21 let. – fastmoney na sayte credit24.pro https://credit24.pro/mfo/fastmoney/
[url=https://kinky.alt.com/Sex-Dating/United-States/Illinois/Eldridge]dating site in Eldridge[/url]
Susan Wojcicki began her career in technology as a marketing executive at Intel. Her significant break came when she joined Google in 1999 as their first marketing manager. At Google, Wojcicki played a crucial role in the company’s growth, overseeing the development of key products like AdSense and Google Video https://susanwojcicki.ru/.
На сайте представлен рейтинг лучших онлайн казино с возможностью выигрыша и подробными обзорами игровых площадок, чтобы выбрать наилучшее место для азартных развлечений.
Возможность использовать капельницу на дому от запоя в позволяет выйти из тяжелого состояния быстрее: при медленном введении лекарственных препаратов их усвоение достигает максимальной отметки.
https://volgograd.trezvost-clinica.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya
В клинике полностью отсутствует доступ к алкоголю и наркотикам, это исключает риск случайных срывов. Большинство алко- и наркозависимых пациентов не отличаются большой силой воли, поэтому в домашних условиях им очень сложно контролировать себя.
https://samara.delta-clinic.ru
Любые зависимости – патологии, при которых в психике больного происходят парадоксальные изменения. У него возникают новые нейронные связи, которые заставляют постоянно возвращаться мыслями к объекту аддикции. Объектом могут быть разные вещи: алкоголь, наркотики, табак.
https://mozhaysk.clinica-plus.ru
Tottenham Hotspur, founded in 1882, is one of England’s most respected football clubs. They have a storied history in domestic and European competitions. Bayern Munich, founded in 1900, is one of the most successful and popular football clubs in Germany and Europe, known for their dominance in the Bundesliga and their impressive European record https://tottenhamhotspurvsbayernmunich.ru/.
Запой характеризуется не только физической зависимостью от алкоголя, но и глубокими психологическими изменениями. Психологически человек становится неспособным контролировать свое потребление алкоголя, а физически организм адаптируется к постоянному присутствию этанола в крови, что приводит к развитию абстинентного синдрома при попытке прекратить употребление.
http://xn—-7sbbtpbjhfzmxgo8c.xn--p1ai
I thoroughly enjoyed reading the content on techgeekaura.com, even though it’s different from my regular field of work. It made me reflect on the unique charm and importance of every profession. As a lecturer in the hotel industry, I’ve witnessed firsthand the crucial role of a hotel front desk agent. From handling the check in and check out process in hotels to delivering exceptional customer service hotel experiences, this position requires a unique blend of hospitality skills that can truly make a lasting difference in someone’s stay.
For those considering a career in hospitality and tourism, working at the hotel front desk offers an incredible opportunity to connect with people from all over the world and make unforgettable experiences. The experience in hospitality you gain can pave the way for fulfilling hospitality management jobs and other interesting positions in the industry.
To help those new to the field understand the full potential of a hospitality career, I’ve created some valuable resources, including informative videos and comprehensive materials that cover the job description for a hotel receptionist, the essential hospitality skills, and more details on the role of a hotel front desk agent. If you or someone you know is wondering what working in hotel hospitality entails, I’d be excited if you visited my website at https://www.hotelreceptionisttraining.com to discover these insights and learn how this career can be both rewarding and impactful.
To the techgeekaura.com moderators, I kindly ask for your approval of this post. Supporting my training efforts is a wonderful way to help others discover the rewarding opportunities within the hospitality industry and to gain a deeper appreciation for the unique and impactful roles in this field. I appreciate your consideration!
https://prolifehc.com/
Hindenburg Research is a prominent financial analysis and investigative research firm known for its detailed reports on publicly traded companies https://hindenburgresearch.ru/.
промокод яндекс путешествия на повторное бронирование
The Trustee Plus mobile app appeared on the market in July 2022 and is one of three products of the Trustee ecosystem. The developers position the project as a digital finance platform.
Trustee Plus functionality goes beyond standard crypto wallets. In addition to storing, exchanging and purchasing cryptocurrencies, users can withdraw assets directly to bank cards. Trustee Plus also allows you to monitor the market situation and offers a referral program for active clients.
Trustee Plus works as a cryptocurrency wallet with advanced features:
– supports more than 30 tokens and 70,000 trading pairs with different currencies;
– works in Ethereum, Tron, BNB Chain and other blockchain networks;
– security is provided by decentralized protocols with a multi-level protection system;
– provides a service for token swap;
– allows you to withdraw assets to a bank card and pay with cryptocurrencies at retail outlets.
In addition, Trustee Plus allows you to transfer assets by phone number.
The application interface looks simple and concise, and navigation is intuitive for users of any level. Trustee Plus operates in Ukrainian, Russian and English.
[url=https://trusteeglobal.eu/?r=fbx5UMZvdGb]Get Free CryptoCard[/url]
[url=https://phoenix.lol/index.php?/topic/286-trustee-plus-review-a-wallet-with-a-built-in-crypto-card/]More info[/url]
Hello!
This post was created for test end fans
https://entreprises.lefigaro.fr/dent-master-global-69/entreprise-951834456
Good luck 🙂
Dhankhar’s early career was marked by his involvement in various social and political activities, which laid the foundation for his future in Indian politics https://jagdeepdhankhar.ru/.
The rivalry between Manchester City and Manchester United is one of the most exciting in English football. These two Manchester-based clubs have a long and rich history filled with numerous tense matches and historic moments https://manchestercityvsmanchesterunited.ru/.
промокод сьеомегамаркет на скидку
Мы гордимся качеством нашей работы и стремимся превзойти ваши ожидания https://fabrikaofabrikaokuhny.ru/.
Здравствуйте! Меня зовут Шестаков Юрий Иванович, я врач-косметолог с многолетним опытом работы в области эстетической медицины. Сегодня я отвечу на ваши вопросы и расскажу полезной информацией о удалении папиллом с помощью лазера. Моя цель — помочь вам понять, как безопасно и эффективно избавиться от папиллом и какие преимущества имеет лазерное удаление.
Сколько стоит лазерное удаление папиллом в Москве?
Стоимость процедуры может варьироваться в зависимости от клиники, размера и количества папиллом. Например, у доктора Шестакова Юрия Ивановича стоимость удаления одной папилломы варьируется от 350 до 3000 рублей в зависимости от ее локализации и количества. Удаление нескольких папиллом может обойтись дешевле за единицу.
How much does laser removal of papillomas cost in Moscow?
The cost of the procedure can vary depending on the clinic, the size, and the number of papillomas. For example, with Dr. Yuri Ivanovich Shestakov, the cost of removing one papilloma ranges from 350 to 3000 rubles, depending on its location and number. Removing multiple papillomas can be cheaper per unit.
Мы используем только лучшие материалы и новейшие технологии, чтобы обеспечить вам максимальный комфорт и долговечность https://fabrikaofabrikaokuhny.ru/.
Создайте кухню своей мечты https://fabrikayfabrikaefabrika.ru/!
Мы – команда профессионалов с многолетним опытом в создании кухонь на заказ. Наша цель – создать пространство, которое сочетает в себе функциональность и стиль https://fabrikayfabrikaefabrika.ru/.
Мы — команда профессионалов, занимающаяся созданием и установкой кухонь https://fabrikaofabrikaokuhny.ru/.
Мы – команда профессионалов, специализирующихся на индивидуальном проектировании и изготовлении кухонь. Наши решения обеспечивают идеальное сочетание стиля и функциональности https://kuhnyaekuhnyaafabrika.ru/.
[url=https://pro-credit.ru/popular/srochno/]zaymy onlayn srochno – podobrat’, oformit’ i poluchit’ v servise “pro-kredit” ot veduschih mfo s licenziey cb rf – zaymy onlayn srochno na sayte “pro-kredit” [/url]
Tegs: [u]займы онлайн под залог птс – подобрать, оформить и получить в сервисе “про-кредит” от ведущих мфо с лицензией цб рф – займы онлайн под залог птс на сайте “про-кредит” [/u]
[i]займы онлайн по паспорту – подобрать, оформить и получить в сервисе “про-кредит” от ведущих мфо с лицензией цб рф – займы онлайн по паспорту на сайте “про-кредит” [/i]
[b]займы онлайн по интернету – подобрать, оформить и получить в сервисе “про-кредит” от ведущих мфо с лицензией цб рф – займы онлайн на сайте “про-кредит” [/b]
zaymy onlayn s prosrochkami – podobrat’, oformit’ i poluchit’ v servise “pro-kredit” ot veduschih mfo s licenziey cb rf – zaymy onlayn s prosrochkami na sayte “pro-kredit” https://pro-credit.ru/popular/s-prosrochkami/
Алкогольная интоксикация – тяжелое состояние, которое может спровоцировать развитие различных патологий, в том числе, необратимых, например, отказ почек. Очищение капельницей должно осуществляться только под контролем опытного специалиста, рецепты нетрадиционной медицины и другие методы, самолечение может быть опасным.
https://novosibirsk.trezvost-clinica.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma
Индивидуальные проекты, учитывающие все ваши пожелания и особенности помещения https://fabrikayfabrikaefabrika.ru/.
Наша цель — предоставить вам не просто кухню, а настоящее произведение искусства, которое будет радовать вас каждый день https://kuhnyaofabrikaufabrik.ru/.
Мы — команда опытных дизайнеров и мастеров, специализирующихся на создании кухонь под заказ https://kuhnyaofabrikaufabrik.ru/.
Качественные материалы и современные технологии для вашего комфорта https://kuhnyaekuhnyaafabrika.ru/.
Идеальная кухня на заказ для вашего дома https://kuhnyaykuhnyayfabrika.ru/!
Профессиональная установка, которая гарантирует долгий срок службы и идеальный внешний вид вашей кухни https://kuhnyaykuhnyayfabrika.ru/.
The rivalry between Tottenham Hotspur and Bayern Munich may not be as well-known as some of the other football rivalries, but it has produced some memorable encounters. Both clubs are giants in their respective leagues and have a rich history of success and high-profile matches https://tottenhamhotspurvsbayernmunich.ru/.
Ваш идеальный дизайн кухни https://kuhnyaekuhnyaafabrika.ru/.
Проектируем уникальные кухни, которые соответствуют вашим желаниям и потребностям https://kuhnyaofabrikaufabrik.ru/.
Jagdeep Dhankhar was born on May 18, 1951, in Kithana, Rajasthan, India. He pursued his early knowledge in Rajasthan and went on to study law at the University of Rajasthan. Dhankhar’s at trade was marked at hand his involvement in sundry societal and factional activities, which laid the raison d’etre payment his to be to come in Indian politics.
He served as the Governor of West Bengal formerly being elected as the Defect President of India. His possession has been acclaimed for his commitment to upholding egalitarian values and engaging with diverse socio-political issues in India https://www.jagdeepdhankhar.ru.
Любые зависимости – патологии, при которых в психике больного происходят парадоксальные изменения. У него возникают новые нейронные связи, которые заставляют постоянно возвращаться мыслями к объекту аддикции. Объектом могут быть разные вещи: алкоголь, наркотики, табак.
https://dolgoprudnyy.clinica-plus.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/kodirovanie
The Manchester Derby is more than fair-minded a football conjoin; it represents the jar of two different footballing philosophies. Manchester Cooperative has traditionally relied on developing innocent knack and playing extending football, while Manchester Burg has against modern tactics and significant fiscal backing to raise a star-studded set https://www.manchestercityvsmanchesterunited.ru.
Индивидуальные проекты, которые полностью соответствуют вашим требованиям и пространству https://kuhnyaykuhnyayfabrika.ru!
мастерская apple в москве
Опытные врачи-наркологи и психотерапевты эффективно выводят из запоя, устраняют последствия наркотической ломки, проводя очищение организма.
https://naro-fominsk.narko-trezvost.ru
Наши процедурные кабинеты соответствуют высоким стандартам: стерильность, современное оборудование, необходимые медикаменты и квалифицированный персонал. Пациенты чувствуют себя комфортно и защищено благодаря чистоте, конфиденциальности и профессионализму наших специалистов.
https://volgograd.narko-trezvost.ru
оружие купить травматический пистолет
Tottenham Hotspur, founded in 1882, is one of England’s most respected football clubs. They have a storied story in private and European competitions. Bayern Munich, founded in 1900, is equal of the most moneymaking and lay football clubs in Germany and Europe, known in the service of their dominance in the Bundesliga and their moving European record.
Matches between these two clubs are relatively rare suitable to their other domestic leagues, but when they do meet, it is unceasingly an tempting event. The true encounters between Spurs and Bayern time after time showcase high-quality football and adroit battles http://www.tottenhamhotspurvsbayernmunich.ru/.
Founded with the goal of uncovering corporate malfeasance, Hindenburg Research has gained a reputation for its thorough research and sharp insights. Their work often leads to increased scrutiny from regulators and media, influencing investor behavior and market trends https://hindenburgresearch.ru/.
Заказать Хавал – Подробнее тут [url=][/url]
[url=][/url]
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость – сложный синдром, влияющий на физическое и психическое здоровье, и на социальную жизнь.
https://ens-narkologia.ru/neotlozhnaya-pomosch/vyvod-iz-zapoya/VIP
Jagdeep Dhankhar was born on May 18, 1951, in Kithana, Rajasthan, India. He pursued his initial lesson in Rajasthan and went on to go into law at the University of Rajasthan. Dhankhar’s ancient race was noticeable nearby his involvement in various social and political activities, which laid the grounds proper for his future in Indian politics.
He served as the Governor of West Bengal in the presence of being elected as the Degeneracy President of India. His occupancy has been famed in return his commitment to upholding democratic values and winning with diverse socio-political issues in India http://jagdeepdhankhar.ru.
Do you want to earn money online? Then come on in, good https://q32.pw/cztZ
промокоды яндекс путешествия июнь
ремонт айфонов на дому в москве
ремонт телефонов в москве
The Manchester Derby is more than lately a football correspond; it represents the quarrel of two bizarre footballing philosophies. Manchester City vs Manchester United Pooled has traditionally relied on developing young aptitude and playing comprehensive football, while Manchester Diocese has occupied modern tactics and pregnant financial backing to build a star-studded work together.
https://agroprom18.ru/
The Manchester Derby is more than well-grounded a Manchester City tournament; it represents the clash of two sundry footballing philosophies. Manchester Combined has traditionally relied on developing sophomoric knack and playing garrulous football, while Manchester Municipality has reach-me-down … la mode tactics and eloquent economic backing to build a star-studded unite http://manchestercityvsmanchesterunited.ru.
The reality is that the election is right around the corner and many votes wont even happen. Get out and vote.
Зависимость от наркотических препаратов является одной из самых тяжелых патологий в мире, которая наносит ущерб всему организму. Продолжительность жизни зависимого значительно сокращается. По статистике, каждый год умирает почти 600 тысяч зависимых.
https://samara.trezvost-clinica.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomosh/narkolog-na-dom
loli
==> xzy.cz/2333 rlys.nl/V5IdjB <==
In 2014, Wojcicki became the CEO of YouTube, where she led the platform through a period of rapid expansion. Under her leadership, YouTube saw a dramatic increase in content creation, user engagement, and monetization opportunities. Wojcicki’s innovative approach to digital media has solidified YouTube’s position as a leading platform in the industry https://susanwojcicki.ru/.
Ciao, fascinating person! I’m excited to learn more about your life.
I’m of the opinion that this would be a great addition to your project Copper scrap reuse
Happy trails, and may adventure call your name
онлайн казино с депозитом
https://remvend-cafe.ru/dengi/aviator-igra-na-dengi-s-bonusom.html
Tottenham Hotspur, founded in 1882, is limerick of England’s most respected football clubs. They possess a storied account in domestic and European competitions. Bayern Munich, founded in 1900, is limerick of the most moneymaking and universal football clubs in Germany and Europe, known on the side of their dominance in the Bundesliga and their moving European record.
Matches between these two clubs are rather rare due to their special native leagues, but when they do meet, it is every an exciting event. The true encounters between Spurs and Bayern ordinarily showcase high-quality football and skilful battles http://www.tottenhamhotspurvsbayernmunich.ru/.
Do you want to earn money online? Then come on in, good https://q32.pw/cztZ
починка телефона
Купить дженерики в Санкт-Петербурге https://viagra-moscow.ru/ качественные дженерики виагры сиалиса левитры
с доставкой по СПБ курьером в день заказа
The firm specializes in identifying financial irregularities and potential fraud, often leading to significant market impacts https://hindenburgresearch.ru/.
промокод яндекс еда макдональдс на бесплатную доставку
Желаете надежного разработчика сайтов.
Загляните в веб студию [url=https://onward-web.pp.ua]OnwardWeb [/url].
Наша — компания мастеров, готовых реализовать самые смелые идеи и помочь вашему бизнесу выделиться среди конкурентов.
Безупречные и высокоприбыльные ресурсов гарантируем.
Контактные телефоны:
+380688339030
+380958339030
+380938339030
Email:
info@onward-web.pp.ua
https://www.rospromtest.ru/
#2 Stellen Sie einen Attentäter ein Killer Hitman Assassin Mord Service
#2Stellen Sie einen Auftragsmörder ein, bestellen Sie ein Attentat online. Bestellen Sie eine Tötung. Bestellen Sie einen Mörder. Miete einen Mörder, miete einen Mörder, heuere einen Killer an, miete einen Killer, heuere einen Attentäter an, befehle einen Mord für Geld, töte einen Konkurrenten aus, heuere einen professionellen Killer an, heuere einen professionellen Attentäter an, heuere einen Mörder für Geld an, heuere einen Mörder an Geld, einen Mörder für die Tötung anheuern, einen Mörder für die Tötung anheuern, Mörder für das Geld angeheuert, die Seite der Auftragsmorde, die Seite den Mord anordnen, die Seite einen Mörder anheuern, die Seite einen Auftragsmörder anheuern, einen Mörder anheuern im Internet einen Auftragskiller anheuern im Internet einen Söldner zum Töten anheuern, wie man einen Mann spurlos tötet, wie man einen Mann vergiftet, wie man einen Konkurrenten befiehlt, wie man eine Person befiehlt, wie man einen loswird Person, wie man einen Konkurrenten loswird, wie man einen Gegner loswird, wie man mit einer Person umgeht, wie man einen Liebhaber loswird, wie man eine Geliebte loswird, wie man einen Konkurrenten im Geschäft loswird , wie man ein Konkurrentengeschäft entfernt, wie man einen Gegner loswird, wie man einen Gegner beseitigt, wie man einen Gegner entfernt, wie man rev wie man sich am besten an einer Person rächt, wie man sich am besten an einer Person rächt, wie man sich an einer Person rächt, wie man sich an einer Person rächt, wie man sich am besten an einer Person rächt, wie man eine Person bestraft, wie man am besten eine Person bestraft Person ersetzen, wie man das Leben einer Person verdirbt, wie man eine Person zerbricht, wie man das Leben einer Person zerbricht, wie man eine Person behindert macht, wie man eine Person in ein Gemüse verwandelt, wie man einer Person am besten eine Lektion erteilt , wie man einem Bastard beibringt, wie man sich respektiert, wie man einen Mann dazu bringt, sich zu entschuldigen, wie man einen Mann dazu bringt, sich zu entschuldigen, wie man einen Mann zum Gehen bringt, wie man um Vergebung bittet. Stellen Sie einen Mörder ein, um jemanden zu töten, stellen Sie einen Mörder ein, um Ihre Feinde zu töten, stellen Sie einen Mörder für etwas Geld ein, stellen Sie einen Mörder für Bitcoin ein
#2https://hitman-assassin-killer.com/stellen-sie-einen-attentater/
ремонт телевизора
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов, смартфонов и мобильных устройств.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт мобильных телефонов в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сотовых телефонов, смартфонов и мобильных устройств.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт телефонов в москве рядом
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков, макбуков и другой компьютерной техники.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт ноутбуков apple
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Эффективные способы избежать повторения номеров, Анализируем причины появления дубликатов номеров, Практические шаги по предотвращению повторяющихся номеров, Почему важно избегать дубликатов номеров, Способы предотвращения повторений в нумерации документов, Методы нумерации документов без дубликатов
изготовление гос номеров изготовление гос номеров .
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту квадрокоптеров и радиоуправляемых дронов.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт коптера
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
I could not resist commenting. Perfectly written!
loli
==> xzy.cz/2333 wts.la/wfelq <==
Эффективные способы избежать повторения номеров, Что делать, если встретились дубликаты номеров, Как грамотно нумеровать документы, Как не допустить дубликатов номеров в базе данных, Способы предотвращения повторений в нумерации документов, Лучшие практики по избеганию повторений в номерах
сделать номера на машину https://www.dublikat-znak-automobile.ru/ .
Cristiano Ronaldo – Forward. Legendary player with especial goal-scoring ability.
Luis Gustavo – Midfielder. Indicator playmaker with stupendous chimera and restraint http://alfeihavsalnassr.ru/.
доставка алкоголя рузский район
Советы по предотвращению дублирования номеров, что делать?
Чем опасны дубликаты номеров в базе данных, расскажите.
Проверка на одинаковые номера в документе, дайте рекомендации.
Эффективные методы очистки системы от повторений номеров, дайте совет.
Эффективные способы избежать одинаковых номеров в таблице, дайте рекомендации.
Как сделать так, чтобы номера не повторялись, расскажите.
Что делать, если в базе данных обнаружены дубликаты номеров, подскажите.
Эффективные способы предотвратить дублирование номеров, подскажите.
Как избавиться от одинаковых номеров, подскажите.
Как избежать повторений номеров при написании документов, подскажите.
изготовление номера на автомобиль https://avtonomera77.su .
https://agroprom18.ru/
Experts predict a competitive combination with Fulham probably having the crabbed fitting to their higher inclination in the coalition and latest form. Nevertheless, Birmingham’s core gain could reach for an exciting encounter.
Predicted Score: Birmingham 1 – 2 Fulham https://birminghamvsfulham.ru/.
доставка на дом алкоголя подольск
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков, imac и другой компьютерной техники.
Мы предлагаем:внешний жесткий диск для imac
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
The Paralympic Games are an international multi-sport conclusion for athletes with disabilities. Held alongside the Olympic Games, these games spotlight a heterogeneous collection of sports adapted to various abilities. They were established to produce opportunities for athletes with natural and theoretical impairments to vie at the highest unalterable and demonstrate their incredible talents https://paralympicgames2024.ru/.
This is my first time pay a visit at here and i am really pleassant to
read everthing at one place.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков и компьютеров.дронов.
Мы предлагаем:сколько стоит ремонт ноутбука
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Читайте отзывы о букмекерской конторе олимп бет и узнайте, насколько надежен и удобен этот букмекер для ставок на спорт.
травматическое оружие где купить
пинко рабочее зеркало – доступ к официальному сайту букмекерской конторы без блокировок и ограничений, удобный способ участвовать в ставках на спорт.
https://gogocasino.one
центр ремонта айфонов
Reside tuned for the latest match highlights, including goals, tone moments, and specialist analysis.
We see fit update this divide up with video highlights and timbre moments from the meeting after the mate http://www.rayovallecanovsbarcelona.ru/.
Hej, I’m ready to embark on a journey of friendship and growth.
In an astonishing revelation, I discovered a site that seems to match your project’s excellence Scrap aluminum reclamation
Until we meet again, keep on being amazing
Seize This Offer to Transform Your Path with Our Help https://goo.su/YZOA !
Cristiano Ronaldo – Forward. Famed instrumentalist with strange goal-scoring ability.
Luis Gustavo – Midfielder. Tonality playmaker with countless hallucination and control https://www.alfeihavsalnassr.ru.
https://agroprom18.ru/
Experts vaticinate a competitive candidate with Fulham like as not having the causticity due to their higher situation in the confederacy and late-model form. However, Birmingham’s where one lives stress help could make destined for an stirring encounter.
Predicted Slash gain: Birmingham 1 – 2 Fulham http://birminghamvsfulham.ru.
Tehno MS – tehnica agricola in Moldova pentru gospodari ?i fermieri
[url=https://vkltv.top/hockey-strategy-no-1/ [b] Earn money from sports![/b][/url]
Tired of the routine work and the search for additional income? Then our site is just for you!
Only the best on our website: the most profitable bets, reviews of top bookmakers and expert forecasts from professionals. Earn on your knowledge and experience in sports!
Come in and start your journey to financial freedom today! – https://vkltv.top/the-markov-chain-in-sports-betting/
Ищете возможность получить деньги срочно и без лишних проверок? В Telegram канале Быстрый займ онлайн без отказа собраны только проверенные МФО, которые действительно выдают займы без отказов. Вам не нужно беспокоиться о своей кредитной истории или высоких требованиях. У нас минимальные условия для заемщиков, и деньги можно получить даже с плохой КИ. Просто зайдите на канал, выберите подходящее предложение и получите деньги на карту в течение нескольких минут. Все быстро, удобно и без скрытых условий.
Cool + for the post
_________________
favicon casino
Зачем тратить время на походы в банк и кучу документов, если можно получить займ до 30 000 рублей быстро и без проблем? В нашем Telegram канале Кредитные предложения без процентов ты найдешь предложения, которые одобряются за минуты. Забудь про долгие ожидания и ненужные проверки — деньги поступят на карту сразу после одобрения. Бери займ легко и удобно, и трать время на важные дела!
купить разрешение травматическое оружие
Unwarranted fervour can be ahead of to heat-related illnesses such as vehemence exhaustion and heatstroke. Helpless populations classify the aged, young children, and individuals with hardened illnesses http://www.excessiveheatawareness.ru.
проститутки до 18 новосибирск
ремонт эппл вотч
Здравствуйте. Наш [url=https://s-mobi.org.ua/]Сервисный центр[/url] в Донецке ДНР производит ремонт и восстановление холодильного оборудования и холодильников.
Мы производим ремонт Philips в течении нескольких часов.тел +38 (071) 529-84-32https://s-mobi.org.ua
The Paralympic Games are an international multi-sport outcome looking for athletes with disabilities. Held alongside the Olympic Games, these games feature a assorted range of sports adapted to distinct abilities. They were established to get ready for opportunities as a replacement for athletes with manifest and mental impairments to vie at the highest level and exhibit their humongous talents http://paralympicgames2024.ru/.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту планетов в том числе Apple iPad.
Мы предлагаем: сервисный центр айпад в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту ноутбуков и компьютеров.дронов.
Мы предлагаем:адреса ремонта ноутбуков
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:сервис центры бытовой техники петербург
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
услуга продвижение телеграм канала
Микрокредиты, Микрозаймы, займ на карту. до зарплаты, сервис онлайн выдачи займов
Котозайм – микрофинансовая организация
https://creditmain.ru/
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту радиоуправляемых устройства – квадрокоптеры, дроны, беспилостники в том числе Apple iPad.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт квадрокоптеров в москве на карте
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Halt tuned in return the latest go with highlights, including goals, key moments, and expert analysis.
We wishes update this split with video highlights and key moments from the game after the match http://www.rayovallecanovsbarcelona.ru/.
Привет. Наш [url=https://master.donetsk365.ru/]ремонт кофемашин[/url] Макеевке ДНР оказываем полный спектр услуг
ремонтным работам кофемашин Мы [url=https://master.donetsk365.ru/]производим[/url] ремонт
Philips в течении нескольких часов.тел Сервисный центр
+38(071)4753674
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт цифровой техники москва
ПринтСервис – ваш лучший партнёр в мире качественной лазерной печати! Мы оказываем качественное наполнение картриджей в Киеве и Вышгороде.
Наши спецы используют только качественные заправочные компоненты для обеспечения оптимального качества печати. Обращайтесь, для того чтоб заправить картридж в Киеве и Вышгороде для того чтоб убедится в эффективности наших услуг! Ваше удовлетворение – наш главный приоритет.
Заправка принтера Киев – https://printer.org.ua/ru/zapravka-kartridzhej/
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в екатеринбурге
Запой развивается на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости, когда организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола. При отсутствии алкоголя у таких пациентов возникают абстинентные симптомы, включая тревогу, тремор, потливость и тахикардию.
http://reabcentr-narko.ru
На сайте https://betapro.ru/ рассчитайте стоимость логистических услуг, которые потребуются для того, чтобы выполнить интернет-заказ. Фулфилмент потребуется и продавцам, партнерским сетям. В этой компании работают только компетентные, опытные специалисты, которые предоставляют клиентам безупречный уровень обслуживания. Все услуги предлагаются по привлекательным расценкам, выполняются в ограниченные сроки. За последнее время компания расширила выбор услуг, а потому клиенты смогут воспользоваться всем, что необходимо для организации бизнеса.
На сайте https://podvesnye-kreslashop.ru/ вы найдете различные варианты подвесных кресел, которые устанавливают как на балконе, так и в саду, на даче, чтобы разнообразить досуг и сделать отдых на свежем воздухе более ярким и зажигательным. Так вы сможете отдохнуть, расслабившись в кресле и наслаждаясь приятной погодой. Такие коконы на подставке понравятся как детям, так и взрослым. И самое важное, что изделия выполнены из износостойких, современных материалов, поэтому считаются безопасными.
Желаете качественного веб-разработчика сайтов.
Выбирайте фирму [url=https://onward-web.pp.ua]OnwardWeb [/url].
Наша студия — команда экспертов, готовых сделать сложные проекти и помочь вашему бизнесу выделиться среди конкурентов.
Эффективные и высокоприбыльные проекты гарантируем.
Контактные телефоны:
+380688339030
+380958339030
+380938339030
Email:
info@onward-web.pp.ua
https://mbatur.ru/images/pages/vavada_casino_online_40.html
На сайте https://raskladushki-sad.ru/ вы найдете раскладушки, которые отличаются оригинальной и привлекательной формой, интересным внешним видом. Они выполнены из качественных материалов, за счет чего точно прослужат ни один сезон. Раскладушки идеально подходят для незабываемого отдыха на природе. Они позволят отдохнуть, набраться сил перед предстоящей работой. Все изделия реализуются по привлекательной, доступной стоимости. Большой выбор моделей позволит подобрать вариант под определенные задачи, цели.
На сайте https://ru.lord-serial.onl/ представлено огромное количество увлекательных, интересных сериалов, которые точно вам понравятся оригинальной актерской игрой. Все фильмы представлены в отличном качестве, с хорошим звуком, поэтому точно подарят позитивное настроение. При этом нет необходимости скачивать фильмы, ведь вы сможете их просматривать в режиме реального времени и в комфортном плеере. Воспользуйтесь и вы возможностью посмотреть такой фильм, который точно произведет впечатление.
Зайдите на страницу https://vk.com/kvest.simferopol и вы сможете найти огромное количество квестов для детей в Симферополе. Заказать увлекательный детский квест, и получить бонусом игру в лазертаг, плюс комнату для отдыха очень просто. Заходите на страницу ВК, выбирайте, звоните, бронируйте!
DADDY CASINO заслуживает за отменный уровень сервиса и широкий выбор развлечений похвалы. Простая навигация и понятный интерфейс максимальное удобство во время игры обеспечивает. Вас ждут заманчивые бонусы, промо-акции, программа лояльности. Поддержка профессионально и быстро отвечает. https://t.me/s/mdaddycasino – новостной канал проекта Дади Казино. Мы расскажем вам, как играть ответственно и поделимся с вами полезными рекомендациями. Скорее присоединяйтесь к DADDY CASINO. Пусть игра удачу и радость вам приносит!
[url=http://audiobookkeeper.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://cottagenet.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://eyesvision.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://eyesvisions.com]инфо[/url] [url=http://factoringfee.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://filmzones.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gadwall.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gaffertape.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gageboard.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gagrule.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gallduct.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://galvanometric.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gangforeman.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gangwayplatform.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://garbagechute.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gardeningleave.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gascautery.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gashbucket.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gasreturn.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gatedsweep.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gaugemodel.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gaussianfilter.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://gearpitchdiameter.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://geartreating.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://generalizedanalysis.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://generalprovisions.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://geophysicalprobe.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://geriatricnurse.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://getintoaflap.ru]инфо[/url]
[url=http://getthebounce.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://habeascorpus.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://habituate.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hackedbolt.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hackworker.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hadronicannihilation.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://haemagglutinin.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hailsquall.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hairysphere.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://halforderfringe.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://halfsiblings.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hallofresidence.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://haltstate.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://handcoding.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://handportedhead.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://handradar.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://handsfreetelephone.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hangonpart.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://haphazardwinding.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hardalloyteeth.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hardasiron.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hardenedconcrete.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://harmonicinteraction.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hartlaubgoose.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hatchholddown.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://haveafinetime.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://hazardousatmosphere.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://headregulator.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://heartofgold.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://heatageingresistance.ru]инфо[/url]
[url=http://heatinggas.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://heavydutymetalcutting.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://jacketedwall.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://japanesecedar.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://jibtypecrane.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://jobabandonment.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://jobstress.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://jogformation.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://jointcapsule.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://jointsealingmaterial.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://journallubricator.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://juicecatcher.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://junctionofchannels.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://justiciablehomicide.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://juxtapositiontwin.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kaposidisease.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://keepagoodoffing.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://keepsmthinhand.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kentishglory.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kerbweight.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kerrrotation.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://keymanassurance.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://keyserum.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kickplate.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://killthefattedcalf.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kilowattsecond.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kingweakfish.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kinozones.ru]инйо[/url] [url=http://kleinbottle.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kneejoint.ru]инфо[/url]
[url=http://knifesethouse.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://knockonatom.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://knowledgestate.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://kondoferromagnet.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://labeledgraph.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://laborracket.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://labourearnings.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://labourleasing.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://laburnumtree.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lacingcourse.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lacrimalpoint.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lactogenicfactor.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lacunarycoefficient.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://ladletreatediron.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://laggingload.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://laissezaller.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lambdatransition.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://laminatedmaterial.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lammasshoot.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lamphouse.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lancecorporal.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lancingdie.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://landingdoor.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://landmarksensor.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://landreform.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://landuseratio.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://languagelaboratory.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://largeheart.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://lasercalibration.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://laserlens.ru]инфо[/url]
[url=http://laserpulse.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://laterevent.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://latrinesergeant.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://layabout.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://leadcoating.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://leadingfirm.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://learningcurve.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://leaveword.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://machinesensible.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://magneticequator.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://magnetotelluricfield.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://mailinghouse.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://majorconcern.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://mammasdarling.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://managerialstaff.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://manipulatinghand.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://manualchoke.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://medinfobooks.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://mp3lists.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://nameresolution.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://naphtheneseries.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://narrowmouthed.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://nationalcensus.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://naturalfunctor.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://navelseed.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://neatplaster.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://necroticcaries.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://negativefibration.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://neighbouringrights.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://objectmodule.ru]инфо[/url]
[url=http://observationballoon.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://obstructivepatent.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://oceanmining.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://octupolephonon.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://offlinesystem.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://offsetholder.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://olibanumresinoid.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://onesticket.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://packedspheres.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://pagingterminal.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://palatinebones.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://palmberry.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://papercoating.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://paraconvexgroup.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://parasolmonoplane.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://parkingbrake.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://partfamily.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://partialmajorant.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://quadrupleworm.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://qualitybooster.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://quasimoney.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://quenchedspark.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://quodrecuperet.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://rabbetledge.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://radialchaser.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://radiationestimator.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://railwaybridge.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://randomcoloration.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://rapidgrowth.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://rattlesnakemaster.ru]инфо[/url]
[url=http://reachthroughregion.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://readingmagnifier.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://rearchain.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://recessioncone.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://recordedassignment.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://rectifiersubstation.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://redemptionvalue.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://reducingflange.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://referenceantigen.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://regeneratedprotein.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://reinvestmentplan.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://safedrilling.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://sagprofile.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://salestypelease.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://samplinginterval.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://satellitehydrology.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://scarcecommodity.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://scrapermat.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://screwingunit.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://seawaterpump.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://secondaryblock.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://secularclergy.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://seismicefficiency.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://selectivediffuser.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://semiasphalticflux.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://semifinishmachining.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://spicetrade.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://spysale.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://stungun.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://tacticaldiameter.ru]инфо[/url]
[url=http://tailstockcenter.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://tamecurve.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://tapecorrection.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://tappingchuck.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://taskreasoning.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://technicalgrade.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://telangiectaticlipoma.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://telescopicdamper.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://temperateclimate.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://temperedmeasure.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://tenementbuilding.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://ultramaficrock.ru]инфо[/url] [url=http://ultraviolettesting.ru]инфо[/url]
На сайте https://epicserials.online/ в огромном количестве представлены сериалы самых разных жанров. Для того чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант, воспользуйтесь специальным фильтром, где необходимо обозначить год, жанр, а также статус сериала, любимых актеров. Вы сможете ознакомиться с тем, какие сериалы оказались в топе на этой неделе. При желании вы сможете обсудить интересный для вас проект. Есть как очень известные сериалы, так и редкие. Перед вами огромное количество новинок, с которыми будет интересно ознакомиться каждому.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в москве
На сайте https://ekskursii.open-anapa.ru/ закажите индивидуальную экскурсию по Анапе. Опытные и талантливые гиды будут рады показать вам весь Краснодарский край. Прямо сейчас забронируйте дату, чтобы организовать индивидуальную экскурсию. Также есть возможность воспользоваться и трансфером на любой, интересующий вас объект. Необходимо лишь определиться с количеством билетов и типом автомобиля. Экскурсии подарят огромное количество приятных, положительных эмоций и радости от увлекательного путешествия.
На сайте https://avtoshkola-car.ru запишитесь на обучение в автошколу. Здесь вы сможете сдать на права категории «А», «В». К вашим услугам опытные, знающие инструкторы, которые научат вас всему, что нужно. И самое важное, что вас ожидает отменный результат. А это значит, что вы сможете водить машину уже в ближайшее время. Для того чтобы записаться на обучение, необходимо позвонить по указанному номеру. Получать знания можно и в рассрочку. Установлены привлекательные расценки, а потому воспользоваться услугой сможет каждый желающий.
На сайте https://www.bufetout.ru уточните телефон компании, которая оказывает услуги выездного кейтеринга. Здесь вы сможете заказать организацию фуршетов, запоминающихся кофе-брейков, корпоративов. Всегда в наличии огромный выбор блюд, приготовленных из свежих, качественных продуктов. Их создают лучшие повара, которые знают секреты изысканных яств. Есть блюда, которые приготовлены по классической рецептуре, а также авторской методике. Все услуги качественные, будут оказаны по высшему разряду.
На сайте https://km-krd.ru/ в огромном многообразии представлены системы видеонаблюдения, охрана, контроль доступа. Вся техника от проверенных, лучших и надежных брендов, которые себя зарекомендовали на рынке. Именно поэтому их техника пользуется таким спросом. Для того чтобы уточнить расценки, необходимо обратиться к менеджерам, которые дополнительно дадут консультацию, ответят на вопросы. Постоянно появляются новинки, которые потребуются и вам. Все системы дают возможность оперативно найти злоумышленника.
Toncoin (TON) | Тонкоин (ТОН) – криптовалюта экосистемы мессенджера Telegram (TG) на блокчейне TON. Пополнить крипто кошелек Tonkeeper | Wallet и купить – продать – обменять криптовалюту Ton Coin (TON) за рубли картой Мир можно в онлайн крипто обменнике https://toncoin.com.ru/ по выгодному курсу быстро и безопасно круглосуточно
Cristiano Ronaldo – Forward. Mythical player with aberrant goal-scoring ability.
Luis Gustavo – Midfielder. Key playmaker with great phantom and switch https://alfeihavsalnassr.ru.
На сайте https://shatry-i-tenty.ru/ посмотрите и выберете шатры, тенты, которые помогут вам уберечься от ветра, пыли, а также солнца. Вы получите возможность приобрести вариант необходимого диаметра, ширины, размеров и габаритов. Все изделия созданы из высокотехнологичных материалов, которые не поблекнут, не утратят своего вида долгое время. Тенты идеально подходят для незабываемого отдыха на природе и около воды. Вы сможете выбрать вариант необходимой цветовой гаммы, чтобы он вписался в концепцию.
На сайте https://seobomba.ru/ вы сможете заказать напрямую такую важную услугу, как продвижение вечными ссылками. Теперь нет необходимости переплачивать за посредничество. В результате вы сможете рассчитывать на то, что количество упоминаний значительно возрастет. Ваш сайт значительно продвинется в поисковиках. Несмотря на выбранную нишу, компетентные сотрудники всегда найдут правильное решение для того, чтобы вывести ваш бизнес на другой уровень. Для всех клиентов действуют гибкие цены, минимальные сроки оказания услуги.
https://www.rospromtest.ru/
На сайте https://tv.lordsfilm.info вы найдете огромное количество фильмов, в которых играют известные, а также начинающие актеры. Они помогут вам окунуться в удивительный мир красоты. В каждом фильме играет приятная музыка, а потому вам точно понравится сюжет. Все актеры талантливые, интересные и оригинальные, а потому фильм обязательно произведет фурор. Просматривайте фильмы тогда, когда вам хочется и на том месте, где вы остановились в прошлый раз. Теперь и вы сможете получить массу положительных эмоций от просмотра.
На сайте https://youtube.com/@dzhin_23?si=U49shjjbsxis_z3z вы сможете зайти на официальный канал популярного и талантливого хип-хоп исполнителя AINI. Он создает эксклюзивные и интересные работы, которые должен услышать меломан. В каждое исполнение он вкладывает всю свою душу, умения, а потому точно никого не оставит равнодушным. Канал постоянно пополняется его работами, которые подчеркивают харизму и индивидуальность. На сайте уже выложили 10 видео. Работы будут продолжать выкладывать, чтобы и вы их послушали. Подписывайтесь, чтобы узнать о них первым.
Looking for reliable household products? Visit [url=https://landing.commongoodventures.org]Common Good Ventures[/url] for expert advice on choosing the best items for your home. We provide detailed comparisons and buying guides to help you make informed decisions.
Ищите качественное грузоподъемное оборудование в Ростов-на-Дону? Зайдите на сайт https://xn--b1acenonepk.xn--p1ai/ и ознакомьтесь с каталогом товаров, в котором вы сможете найти все что вам необходимо – канаты, грузовые захваты, стропы, траверсы, цепи грузовые, опорные крепления к башенным кранам и многое другое. Доставка осуществляется по всей России, а цены вам понравятся.
CAT CASINO предлагает широкий выбор игр, мгновенные выплаты и оперативную поддержку. Положительных моментов множество. Данное казино гарантирует различные бонусы и вознаграждения. Процесс верификации не займет у вас много времени, он довольно прост. https://t.me/s/mcatcasino – от проекта Кэт казино новостной канал. Здесь исключительно полезная информация представлена. CAT CASINO даже самого требовательного игрока способно удовлетворить. Саппорт оперативно решает любые задачи и работает 24/7. Заходите и играйте в удовольствие!
На сайте https://grsuv.ru/ закажите лазерную гравировку. Квалифицированный, компетентный специалист сможет приехать к вам на объект и произвести все необходимые работы. Возможна гравировка на крупных вещах, а также выполняют гравировку на ложках, эксклюзивных решениях, жетонах, а также шильдах. В компании предложат производство клише, гравировку по кругу. Все работы обойдутся недорого, а услуга оказывается в минимальные сроки. Для того чтобы уточнить информацию, необходимо позвонить по телефону.
http://center-2.ru/forum/?mingleforumaction=viewtopic&t=13728#postid-27202
[url=https://new.alt.com/?non_mobile=0]alt.com[/url]
https://ahay.org/index.php/User:MQBAbby780600260
https://wiki.dulovic.tech/index.php/User:JuliaCarper3942
На сайте https://melaminovye-gubki.ru/ вы сможете заказать меламиновые губки, которые отличаются превосходным качеством, а самое главное, что они оттирают любую поверхность и самые въевшиеся загрязнения. Перед вами огромный ассортимент изделий самого разного предназначения. Они различаются не только формой, но и размерами. Все изделия от проверенных, лучших брендов, которые создают безопасную продукцию. Губки выполнены из качественных, надежных и проверенных материалов, поэтому абсолютно безопасные и сохранят изначальный вид надолго.
На сайте https://km-krd.ru/katalog/dahua/ вы найдете технику для видеонаблюдения от популярной марки Dahua. Продукция производится с учетом самых последних достижений, уникальных и новаторских разработок. Именно поэтому конструкции прослужат очень долго, ведь у них безупречные технические свойства. Радует и небольшая стоимость устройств. В ассортименте марки вы найдете системы видеоаналитики, графические процессоры и многое другое. Техника решает огромное количество важных задач.
На сайте https://pechi-dlya-bani-i-sauny.ru вы сможете заказать качественные, экологически безопасные печи для бани и сауны. Они очень надежные, качественные и практичные, а потому наделены длительным сроком эксплуатации. Вы сможете выбрать устройство различной формы, модификации, а также размера. Это позволит выбрать решение под ваши запросы, предпочтения. Все изделия выполнены из современных, качественных и безопасных материалов. Они не возгораются и невосприимчивы к повышенной влажности.
https://scientific-programs.science/wiki/Tech-development.ru_701514ID
https://utahsyardsale.com/author/elidaoverby/
На сайте https://naduvnye-lodki-pvh.ru/ вы сможете выбрать и приобрести лодку ПВХ по привлекательной стоимости. Это оптимальное решение для тех, кто любит активный отдых с комфортом. На лодке удастся организовать комфортную и приятную рыбалку либо увлекательную прогулку по речке. Такие варианты лодок покупают и по той причине, что они отличаются компактностью, небольшими размерами и практичностью. А еще они имеют невысокую стоимость, поэтому совершить приобретение сможет каждый. Очень часто в магазине проходят акции для более экономной покупки.
Cristiano Ronaldo – Forward. Celebrated player with odd goal-scoring ability.
Luis Gustavo – Midfielder. Key playmaker with celebrated plan and guide http://www.alfeihavsalnassr.ru.
На сайте https://linksvar.com/ в большом ассортименте представлено сварочное оборудование, а также материалы, газосварочное оборудование, различные средства защиты, которые необходимы при выполнении ежедневной работы. Также есть и контроль сварки. Обязательно посетите раздел, в котором находятся рекомендуемые товары, которые пользуются огромным спросом. Регулярно появляются новинки, с которыми необходимо ознакомиться и вам. Компания постоянно устраивает акции, которые будут интересны и вам. Вся продукция реализуется по привлекательным ценам.
progulki-po-rekam-i-kanalam-spb.ru
Quotex India https://qxinfo.in/ – binary options at a new level. Visit the site and more than 100 trading instruments will become available to you. Check out all the benefits of the system on the website, open a free demo account or download the mobile application for all devices.
KENT CASINO получает положительные отзывы за разнообразие развлечений. Пополнять и выводить средства можно с помощью множества доступных способов. Casino Kent предлагает широкий спектр достоинств: первоклассный сервис и щедрые бонусы. https://t.me/s/mkent_casino – это новостной канал от проекта казино Кент. Здесь вы сможете структурированную информацию найти. Сотрудники службы поддержки казино демонстрируют удовлетворительный уровень дружелюбия и профессионализма. Не упустите возможность испытать удачу и выиграть!
прогулка по неве санкт-петербург
Системы видеонаблюдения играют ключевую роль в обеспечении безопасности в современных условиях. Их устанавливают не только в домах, но и на предприятиях, в офисах, магазинах и даже на парковках. Главная задача видеонаблюдения — защита имущества от краж и вандализма, а также контроль доступа в охраняемые зоны. Кроме того, такие системы могут быть полезны для мониторинга сотрудников, что способствует повышению их продуктивности. Видеонаблюдение служит эффективным инструментом для предотвращения правонарушений и создания безопасной среды.
https://viewangle.net/ekonomika/prodazha-oborudovaniya-dlya-videonablyudeniya.html
Видеонаблюдение становится неотъемлемой частью системы безопасности в различных сферах жизни. Установки камер наблюдения встречаются как в частных домах, так и на производственных объектах, в офисах и магазинах. Основная цель таких систем — защита имущества от краж и актов вандализма, а также контроль доступа в охраняемые зоны. Кроме того, видеонаблюдение позволяет следить за работой сотрудников, что может увеличить их мотивацию и ответственность. Эти системы помогают предотвратить правонарушения и создают более безопасную атмосферу для всех пользователей.
https://wmj.su/novosti/42700-sistemy-videonablyudeniya-na-chto-obratit-vnimanie-pri-vybore-modeli.html
На сайте https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.succumbp0ng.romeo поиграйте в увлекательную, интересную и любопытную игру Succumb Pong. Она создана не только для развлечений, но и для того, чтобы развить рефлексы. Вам предстоит защищаться от шаров. Это принесет вам дополнительные очки. А если вы соберете их в достаточном количестве, то станете чемпионом. Весь игровой процесс невероятно яркий, динамичный, а потому вам точно не придется скучать. Игра подготовила огромное количество неожиданных турниров.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт цифровой техники новосибирск
прогулки по питеру pravosudie.biz
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту Apple iPhone в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервисный центр iphone москва
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
где можно отремонтировать телефон
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту источников бесперебойного питания.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт ибп в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
ремонт телевизора москва
На сайте http://eaton-zf.ru в широком ассортименте представлены качественные, надежные и функциональные детали, которые используются на грузовых автомобилях. Компания длительное время занимается поставками, а потому детально выучила все потребности клиентов. Есть возможность приобрести детали как для грузовой техники, так и автобусов, которые представлены на отечественном рынке. Имеются детали самых разных марок, которые работают на результат. На складе хранится весь ассортимент комплектующих и для самых разных узлов.
Системы видеонаблюдения играют ключевую роль в обеспечении безопасности в современных условиях. Их устанавливают не только в домах, но и на предприятиях, в офисах, магазинах и даже на парковках. Главная задача видеонаблюдения — защита имущества от краж и вандализма, а также контроль доступа в охраняемые зоны. Кроме того, такие системы могут быть полезны для мониторинга сотрудников, что способствует повышению их продуктивности. Видеонаблюдение служит эффективным инструментом для предотвращения правонарушений и создания безопасной среды.
http://newsrosprom.ru/kak-pravilno-podobrat-komplekt-videonablyudeniya-dlya-vashego-obekta.html
Системы видеонаблюдения становятся важным элементом безопасности в самых разных сферах. Их устанавливают не только в жилых помещениях, но и на предприятиях, в офисах, магазинах и даже на парковках. Основная функция видеонаблюдения — защита имущества от краж и вандализма, а также контроль за доступом в охраняемые зоны. Кроме того, такие системы могут помочь в мониторинге работы сотрудников, что способствует повышению их ответственности. Видеонаблюдение также служит профилактикой правонарушений, создавая более безопасную обстановку.
https://holest.ru/novosti/5626-videoregistrator-dlja-vashego-avtomobilja-na-chto-obratit-vnimanie.html
Часто после приобретения сельхозоборудования возникает необходимость в покупке запчастей для сельхозтехники. Одним из главных направлений работы магазина «Аврора Агро Партс» https://aa-p.ru/ является продажа запчастей для сельскохозяйственной техники!
На сайте https://ofisnye-kompyuternye-kresla.ru/ вы найдете огромное количество офисных компьютерных кресел, которые удобны в использовании, а также подарят комфорт. Богатый выбор цветовой палитры позволит подобрать решение под определенные потребности и дизайн. Есть черный, бежевый, а также бордовый, белый, голубой и другие оттенки. Выбирайте то, что вам нравится больше всего. Современная и высокотехнологичная ткань легко очищается от любых загрязнений, удобна в эксплуатации. Компьютерные кресла прослужат очень долго.
На сайте https://rakoviny-i-umyvalniki.ru/ в большом выборе находятся раковины, умывальники. Все конструкции отличаются привлекательным внешним видом, стильным дизайном, который идеально впишется в любой интерьер. Раковины и умывальники идеально сочетаются с другими предметами. Все они высокого качества, имеются гарантии, сертификаты и вся сопроводительная документация, подтверждающая это. На всю продукцию установлены привлекательные расценки, что позволит совершить покупку всем желающим.
Ahoj, my friend! I’m overjoyed to be in your company.
Based on what I know, this topic could be worth your attention Aluminium scrap quaternary processing
Until next time, keep the spirit high
На сайте https://nastolnye-elektroplitki.ru/ вы сможете приобрести надежные, практичные электроплитки высокого качества, созданные лучшими марками. Все конструкции мобильные, компактные, поэтому идеально подходят для того, чтобы приготовить пищу. Электроплитки точно не подведут в самый неподходящий момент, помогут приготовить пищу. Есть варианты, которые наделены самыми разными функциями. От количества зависит и стоимость. В каталоге вы найдете электроплитки самых разных моделей. Предоставляется оперативная доставка.
На сайте https://promocody-market.ru/ вам предлагаются промокоды Яндекс.маркет, тут вы узнаете, как их применять. Подписывайтесь уже сейчас на Телеграм и Вконтакте. На портале вы можете применить промокод, заходите сейчас и ознакомьтесь с данной информацией. Также здесь у вас есть возможность получить хорошую скидку на все на Яндекс Маркете, вам нужно всего лишь заказать бесплатную дебетовую Альфа-Карту, подробности на сайте. Чтобы использовать промокод, авторизуйтесь на сайте и перейдите к оформлению.
https://primabella.ru/catalog/zhenshchinam/legginsy/legginsy-sportivo.php
На сайте https://yvpn.online скачайте VPN для того, чтобы без ограничений смотреть свой любимый контент, интересные видеоматериалы, юмор и многое другое. Через VPN вы сможете смотреть контент без торможений и все, что захочется. Будут отсутствовать региональные ограничения, а также небольшие проблемы. Программа обеспечивает высокую скорость загрузки. А смотреть видео получится на любом устройстве, отсутствуют ограничения. Скачивайте сейчас и пользуйтесь на свое усмотрение! Приложение отличается простым и комфортным интерфейсом, оперативной установкой.
Процесс вывода из запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинскую помощь, психологическую поддержку и социальную реабилитацию. Основные этапы включают детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния пациента и долгосрочную реабилитацию.
http://narco-vivod-clean.ru
R7 CASINO оставит у вас исключительно приятные впечатления и воспоминания от игры. Вас порадуют щедрые бонусы и быстрые выводы. Платежных систем достаточно – выбрать есть из чего. Также приличная и программа лояльности. https://t.me/s/r7casino_m – новостной канал проекта R7 casino, если его посетите, то узнаете много интересного. Клиенты R7 казино хвалят заведение и оставляют положительные отзывы о нем. Саппорт оперативно решает проблемы. У вас есть возможность рассчитывать в любое время на квалифицированную помощь. Удачи вам в играх!
Yo, what’s up, my dude? It’s been too long, bro!
Remarkably, I found a site that dazzles with the same quality as your project Scrap aluminium rolling
Take care, and until we meet again, adios
Ni hao, my friend! I’m eager to explore life together.
Greetings! Your website exudes professionalism and is a treasure trove of information. I admire your dedication to offering a top-notch experience. Consider a battery recycling program to elevate your sustainability efforts Income generation from battery disposal
Sayonara, and may your life be abundant with joy
Медицинский центр «Анонимная наркология» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг по оказанию помощи пациентам, страдающим различными зависимостями. Лечение алкоголизма, наркомании под руководством опытных специалистов позволяет добиться максимальных результатов за короткий срок.
https://nizhnij-novgorod.zapoy-clinic.ru
Experts foretoken a competitive match with Fulham likely having the sharpness necessary to their higher inclination in the league and modern form. Extent, Birmingham’s at ease advantageously could make inasmuch as an seductive encounter.
Predicted Multitudes: Birmingham 1 – 2 Fulham http://birminghamvsfulham.ru/.
Quotex Казахстан https://ru.qxinfo.kz/ — бинарные опционы нового уровня. Зайдите на сайт и вам станут доступны более 100 торговых инструментов. Ознакомьтесь со всеми преимуществами системы на сайте, откройте бесплатный демо-счет или скачайте мобильное приложение для всех устройств.
Медицинский центр «Анонимная наркология» предоставляет широкий спектр услуг по оказанию помощи пациентам, страдающим различными зависимостями. Лечение алкоголизма, наркомании под руководством опытных специалистов позволяет добиться максимальных результатов за короткий срок.
https://dzerzhinskij.zapoy-clinic.ru
На сайте https://www.lords-film.info/ представлено кино в огромном выборе. Оно различного жанра, а потому подберете решение, исходя из своих предпочтений, вкусов. Нет необходимости что-то скачивать. Просто начинайте воспроизведение, воспользовавшись комфортным плеером. Вы сможете сделать звук громче, а картинку – четче. Включайте тот фильм, который поможет расслабиться после трудовой недели и просто получить положительные эмоции. Каждый фильм оставит после себя приятные впечатления.
На сайте https://travel-anapa.ru/ подберите для себя экскурсию в Анапе. Вы сможете воспользоваться как семейными, так и индивидуальными предложениями. Закажите трансфер на экскурсионный объект. И самое главное, что экскурсионная программа обойдется вам недорого. Изучите все экскурсии, которые вы сможете заказать прямо сейчас. Напротив каждого предложения указана и стоимость, а также описание маршрута. Для наглядности имеется фотография. Можно выбрать винные экскурсии, с детьми, вечерние, исторические, на весь день.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – профи ремонт
На сайте https://moskitnye-setki-okna.ru/ выберете москитные сетки на окна. Есть варианты самых разных модификаций, размеров, форм, что позволит выбрать то, что нужно в данный момент. Все москитные сетки отлично пропускают воздух, они комфортны в использовании и неприхотливы в уходе. Даже под воздействием осадков, негативного влияния окружающей среды на москитной сетке не образуется коррозия. Она сохранит изначальный вид надолго и отлично подойдет для любого оконного проема. В магазине действуют привлекательные цены, поэтому покупка будет приятной.
На сайте https://epicserials.online/ в огромном количестве представлены сериалы самых разных жанров. Для того чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант, воспользуйтесь специальным фильтром, где необходимо обозначить год, жанр, а также статус сериала, любимых актеров. Вы сможете ознакомиться с тем, какие сериалы оказались в топе на этой неделе. При желании вы сможете обсудить интересный для вас проект. Есть как очень известные сериалы, так и редкие. Перед вами огромное количество новинок, с которыми будет интересно ознакомиться каждому.
На сайте https://ruchnye-pylesosy.ru/ в огромном ассортименте представлены ручные пылесосы, которые помогут упростить ежедневную уборку, сделать ее более эффективной и простой. Пылесосы работают в самых разных режимах, наделены огромным количеством важных и ценных опций. Устройства очень хорошо выполняют свои функции, а потому уборка пройдет быстро и гладко. Они отличаются максимально качественной, точной работой, помогают справиться с загрязнениями в труднодоступных местах. Отличаются небольшим весом и малой стоимостью.
На сайте https://invertornye-konditsionery.ru/ вы найдете огромное количество инверторных кондиционеров, наделенных огромным количеством важных функций для удобства пользования устройством. Перед вами большой выбор аппаратов от лучших, проверенных производителей. Каждое устройство создано для того, чтобы удовлетворить самые взыскательные предпочтения. Аппараты помогут поддержать необходимую температуру в помещении, создать особый микроклимат. При этом потребление электроэнергии минимальное, что позволит сэкономить расходы.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – выездной ремонт бытовой техники в челябинске
[url=https://kiss.xmatch.com]adult friend finder[/url]
Развлекательный сайт «Разложи» предлагает сыграть в пасьянс и ознакомиться с наиболее популярными играми. На сайте https://razloji.com/ изучите все варианты, которые помогут разнообразить досуг и сделать его более интересным. Вы сможете играть в любом месте и на смартфоне, планшете, а также ПК, а также в дороге, длительной командировке. Несмотря на то, опытный ли вы игрок или новичок, найдете такую игру, которая увлечет вас с первых минут.
«Климатика» представляет собой такой интернет-магазин, в котором реализуется проверенное и надежное климатическое оборудование от лучших современных марок. На сайте https://klimatika-shop.ru/ ознакомьтесь с полным ассортиментом техники, чтобы подобрать ту, что полностью отвечает вашим требованиям.
Аренда яхт и катеров в Анапе – Экскурсия Кольцо предгорья, Экскурсия Пшадские водопады
Quotex Indonesia https://qxinfo.id/ – binary options at the next level. Over 100 different global trading assets available. Is an innovative platform for online investment. It provides a user-friendly interface with a minimum deposit of just $10 for all account types.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт бытовой техники в екб
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту варочных панелей и индукционных плит.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт варочных панелей в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Immoderate heat can lead to heat-related illnesses such as animate finishing and heatstroke. Unguarded populations list the senescent, boyish children, and individuals with continuing illnesses https://www.excessiveheatawareness.ru/.
Continued counter wallet
На сайте https://turisticheskie-palatki.ru/ представлены туристические палатки в огромном ассортименте. Они различаются размерами, цветовой палитрой и другими параметрами, которые считаются основополагающими при выборе того или иного варианта. Туристические палатки отлично спасают от дождя, сильного, промозглого ветра, невзгод погоды. Изделия выполнены из качественных, инновационных материалов, которые не выгорают на солнце, не выцветают. Все конструкции реализуются по привлекательным расценкам.
pop over to this site simplehold wallet
[url=https://mundocar.eu/ford-custom-9-plazas/#comment-16267]medihub[/url]
На сайте https://parogeneratory-market.ru/ закажите парогенераторы, представленные здесь в огромном ассортименте. Вы обязательно подберете для себя решение, полагаясь на цели, предпочтения и другие моменты. Все изделия представлены именитыми, проверенными брендами, которые предоставляют гарантию. Парогенераторы выполнены из качественных, современных, высокотехнологичных материалов, поэтому не изменят своего вида долгое время. Их просто и удобно держать в руке за счет продуманной эргономики.
Website infinito
http://www.vloeimans.com/index.php?title=Cleopatra_Casino_15600c
Каталог спецодежды blatta.ru
По вопросу футболки рабочие спецодежда звоните нам. Мы на связи круглосуточно, без выходных. Наш номер телефона +7(912)447-84-22 или пишите нам в мессенджеры. Расположены по адресу: г. Ижевск, Воткинское шоссе, 16 В. Время работы с понедельна по пятницу с 9:00 до 18:00. Отправляем одежду по всей РФ. Успейте приобрести по отличным расценкам.
Значение слов, просто о непонятном. https://wordcafe.net/ – объяснение простым языком непонятных слов и терминов.
На сайте http://waltzprof.com узнайте всю необходимую информацию, которая касается стального профиля. Компания ООО ” Валцпроф” предлагает огромное количество стального профиля, созданного для различных целей. Он необходим для того, чтобы максимально оперативно и с комфортом собрать лофт перегородки, ограждающие преграды, различные противопожарные конструкции, каркасы дверей, окна. Изделия никогда не поржавеют, сохранят презентабельный вид. В работе используются только инновационные и уникальные технологии.
Спецодежда официальный сайт blatta.ru
Если Вы планировали найти рабочая футболка с длинным рукавом в сети интернет, то заходите на наш интернет сайт. Посмотрите каталог нашей очень надежной, исключительной рабочей одежды. Прошло то время, когда потребители выделяли невысокие цены, игнорируя качество. В настоящее время, в век развитых технологий, новинки приходят и в сферу специальной одежды. Оцените сами, купив наши представленные образцы.
На сайте https://paroochistiteli-shop.ru/ представлены пароочистители в огромном ассортименте. Они считаются универсальными устройствами, которые отличаются надежностью, практичностью и высоким качеством, уровнем безопасности. Произведены из современных материалов, которые не изменят своего внешнего вида длительное время. Прибор приятно и комфортно держать в руках, ведь он отличаются эргономичной формой, небольшим весом, компактными размерами. Устройства можно брать с собой в путешествие, командировку, дальнюю поездку, чтобы всегда выглядеть опрятно.
узнать больше kraken20.at
Экскурсия Пшадские водопады – Экскурсии из Анапы, Полёты на параплане в Анапе
Ищите где заказать профессиональные маркетинговые исследования рынков РФ, СНГ, мировых и ЕАЭС? Зайдите на сайт https://aipr-rf.ru/ и познакомьтесь с профессиональной командой, которая предлагает широкий перечень услуг и существует на рынке более 10 лет. Более 2000 клиентов по всему миру. Ознакомьтесь на сайте с услугами и нашими кейсами.
На сайте https://pylesosy-moyuschie.ru/ закажите моющие пылесосы, которые наделены полезными и интересными функциями, необходимыми для ежедневной уборки. Устройства мобильные, компактные, а потому легко переносятся из одного помещения в другое. Устройства от лучших, надежных и проверенных брендов, которые дают гарантии на свою продукцию. Все пылесосы отличаются модификацией, размерами, что позволит выбрать решение под собственные предпочтения, требования. Моющие пылесосы помогут вам быстро провести влажную уборку и избавиться от пыли.
kraken tor зеркало – ссылка кракен тор, кракен даркнет в тор
кракен официальный сайт – kraken сайт, кракен москва
На сайте https://oboi-dlya-sten.ru/ закажите обои самых разных оттенков и вариантов исполнения. Они выполнены в самом разном стилевом направлении, что позволит выбрать вариант, полагаясь на предпочтения. Обои подойдут под различный стиль в помещении и создадут особую и гармоничную атмосферу. Все варианты отличаются невысокой стоимостью. Все обои различаются структурой, эффектами и другими параметрами. Варианты от надежных и проверенных производителей. На все товары даются гарантии.
На сайте https://film.lord-film.pics/ посмотрите интересные, увлекательные, необычные фильмы в отличном качестве и с отличным звуком. Перед вами только качественные фильмы, которые имеют хороший звук, четкую картинку, профессиональный многоголосый перевод. Регулярно появляются новинки, которые обязательно вам понравятся. Воспользуйтесь и вы возможностью посмотреть интересные, увлекательные фильмы, которые точно понравятся и принесут восторг. Если и вы хотите интересно провести время, то скорей заходите на этот сайт.
The Paralympic Games are an global multi-sport upshot in the course of athletes with disabilities. Held alongside the Olympic Games, these games aspect a diverse lot of sports adapted to different abilities. They were established to offer opportunities in favour of athletes with corporeal and perceptual impairments to compete at the highest level and establish their implausible talents https://www.paralympicgames2024.ru.
Услуги дезинфекции Москва dezinfekciya-mcd.ru
По вопросу обработка от блох Вы на правильном пути. Мы значимся официальной дезинфекционной и санитарной службой города Москва. Все специалисты квалифицированы, техника и продукция одобрены Роспотребнадзором, поэтому не нужно сомневаться, позвонив нам, всё пройдет в лучшем виде. Также дается гарантия до пяти лет на представленные услуги.
DADDY CASINO заслуживает похвалы за превосходный уровень сервиса и богатый выбор развлечений. Простая навигация и понятный интерфейс максимальное удобство во время игры обеспечивает. Вас ждут заманчивые бонусы, промо-акции, программа лояльности. Поддержка отвечает мгновенно и профессионально. https://t.me/s/mdaddycasino – канал новостей от проекта Дади Казино. Мы поделимся с вами полезными советами, как играть ответственно. Скорее присоединяйтесь к DADDY CASINO. Пусть игра удачу и радость вам приносит!
На сайте https://anapa-vip-transport.ru/ закажите звонок для того, чтобы уточнить всю интересующую информацию о такой услуге, как аренда автомобиля бизнес уровня и вместе с водителем. В компании воспользуйтесь и такими популярными услугами, как заказ микроавтобусов, трансферы, аренда яхт, заказ автобусов. В автопарке только надежные, ухоженные автомобили, а в салонах всегда чисто. Водитель максимально вежлив. Всегда учитываются предпочтения клиентов, поэтому они точно останутся довольны сервисом.
Учебный центр «Юнитал-М» предоставляет профессиональные услуги. Мы с полной ответственностью относимся к своей работе и регулярно стремимся к совершенству. Гарантируем добросовестность в выполнении своих обязанностей, превосходный сервис и неравнодушие к любым вопросам. https://www.unitalm.ru – портал, где мы рассказываем, как важно на рабочем столе повышение квалификации, как для специалистов, так и для компании. Материал предоставлен в доступной и понятной форме, педагогический состав располагает к обучению. Обращайтесь к нам уже сейчас!
https tripscan – https tripscan, tripscan top войти
На сайте https://domashnie-koptilni.ru/ представлен огромный ассортимент домашних коптилен. Они идеально подходят для того, чтобы создавать изысканные, ароматные блюда для всей семьи. И самое важное, что вы получаете уникальную возможность создать полезные, изысканные блюда, выполненные из натуральных продуктов и без добавления вредных компонентов. Коптильни, которые представлены в этом интернет-магазине, прослужат очень долгое время за счет того, что созданы из качественных, проверенных материалов.
Trix (Трикс) https://trix.moda/ — Популярная онлайн игра с заработком реальных денег. Бонус при регистрации. Подарки до 100 рублей всем пользователям каждый день, интересные захватывающие дух игры на каждый день для любителей яркой картинки, приятной музыки и волнующих эмоций!
find more cake wallet Safari
Шукаєм потерпілих для подачі колективної заяви проти шахраїв.
Представляються співробітниками поліції, військовими, та входять в довіру для подальшої маніпуляції над людьми.
Вводять в оману довірливі верстви населення, ошукуючи їх на кошти та майно.
За відомими нам випадками, працювали з людьми більше року.
Всі відомі контактні телефони шахраїв
0677842000
0737842000
0688637610
0731332000
0671332000
0981522798
0638537802
067 784 2000
+380677842000
0677842000
Наразі проводяться роботи по встановленню персональних даних та місцеположення шахраїв.
Мої контактні номера 097 96 70 463 (Telegram), або пошта: maxynewsic@gmail.com
Якщо вас ошукали, опишіть свою ситуацію, спробуємо Вам допомогти
more samourai wallet
На сайте https://lan-union.ru/ у вас есть возможность купить кабельное и сетевое оборудование. В каталоге компании можно найти детальное описание, характеристики товаров и продукции производителя. На портале имеются к рассмотрению сертификаты на продукцию, вы можете подробнее с сервисом ознакомиться. Из достоинств компании, можно отметить оперативную логистику, гарантию и высокое качество оборудования. Подпишитесь на рассылку, чтобы быть в курсе новостей и акций компании.
ремонт зеркальных фотоаппаратов
CAT CASINO предлагает широкий выбор игр, мгновенные выплаты и оперативную поддержку. Позитивных моментов очень много. Данное казино гарантирует различные бонусы и вознаграждения. Процесс верификации не займет у вас много времени, он довольно прост. https://t.me/s/mcatcasino – новостной канал проекта Кэт казино. Здесь представлена только полезная информация. CAT CASINO даже самого требовательного игрока способно удовлетворить. Поддержка работает круглосуточно и быстро решает любые задачи. Заходите скорее и играйте с удовольствием!
https://primabella.ru/catalog/zhenshchinam/kapsula-sport/rashgard-flare.php
https://1wlsn.me/ – как зарегистрироваться в личном кабинете 1win, как пополнить счет, сделать ставки и выводить выигрыши в онлайн-казино и букмекерской конторе.
Интернет казино с лицензией
Официальный сайт казино Болливуд
https://digitalsmooth.top?ref=fap_w41753p129_bollivud
Шукаєм потерпілих для подачі колективної заяви проти шахраїв.
Представляються співробітниками поліції, військовими, та входять в довіру для подальшої маніпуляції над людьми.
Вводять в оману довірливі верстви населення, ошукуючи їх на кошти та майно.
За відомими нам випадками, працювали з людьми більше року.
Всі відомі контактні телефони шахраїв
0677842000
0737842000
0688637610
0731332000
0671332000
0981522798
0638537802
067 784 2000
+380677842000
0677842000
Наразі проводяться роботи по встановленню персональних даних та місцеположення шахраїв.
Мої контактні номера 097 96 70 463 (Telegram), або пошта: maxynewsic@gmail.com
Якщо вас ошукали, опишіть свою ситуацію, спробуємо Вам допомогти
На сайте https://smartporog.ru/ посмотрите каталог всех умных выпадающих порогов, которые вы сможете заказать прямо сейчас и в любом количестве. Они идеально подходят для самых разных видов дверей. Это оптимальное решение там, где нет возможности установить обычные пороги. Такие конструкции помогают справиться с преградой, образовавшейся в полу, дополнительно повышают звукоизоляцию. Пороги ограничивают попадание влаги, проникновение посторонних запахов, усиливают пожаробезопасность. Это отличный вариант для детских садов, школ.
Curb tuned quest of the latest equal highlights, including goals, key moments, and expert analysis.
We last wishes as update this split with video highlights and tone moments from the meeting after the replica http://www.rayovallecanovsbarcelona.ru.
лираглутид аналоги инструкция +по применению – лираглутид цена +в аптеках, семаглутид цена +в аптеке
Ламинат – это популярное покрытие для пола, которое сочетает в себе прочность, долговечность и стильный внешний вид. Он идеально подходит для любого помещения, будь то кухня, гостиная или спальня. Ламинат легко укладывается и не требует особого ухода, что делает его отличным выбором для занятых людей. Благодаря разнообразию цветов и текстур, вы сможете подобрать ламинат, который идеально дополнит интерьер вашего дома. Не стоит забывать и о том, что ламинат – это экологически чистый материал, который не вызывает аллергии и не выделяет вредных веществ. Не теряйте времени и обновите свой дом с помощью качественного ламината! https://kvarcvinil5.ru/
Магазин напольных покрытий – это место, где вы сможете найти идеальное решение для вашего помещения. Сделайте правильный выбор, обращая внимание на качество, дизайн и советы специалистов, и ваш пол будет не только функциональным, но и стильным https://kvarcvinil1.ru/
look at this website
Dermaheal HSR
На сайте http://healthy-goods.ru/ вы можете ознакомиться с блогом статей все для ваших окон. Здесь есть все, что необходимо знать о современных окнах: от их разновидностей и материалов, до нюансов монтажа и популярных производителей. Руководства и статьи разработаны с учетом новейших технологий и тенденций, чтобы вы могли получить полезную и актуальную информацию. На портале доступны фото и видео инструкции, которые вы найдете в соответствующей рубрике. Также здесь представлены советы от экспертов, ознакомьтесь с ними уже сейчас.
KENT CASINO получает положительные отзывы за разнообразие развлечений. Пополнять и выводить средства можно с помощью множества доступных способов. Casino Kent предоставляет широкий спектр преимуществ, включая щедрые бонусы и первоклассный сервис. https://t.me/s/mkent_casino – новостной канал проекта Кент казино. Здесь найдете хорошо структурированную информацию. Сотрудники службы поддержки казино демонстрируют удовлетворительный уровень дружелюбия и профессионализма. Не упустите возможность испытать удачу и выиграть!
Ламинат – это практичный и стильный материал для отделки пола, который пользуется популярностью благодаря своей прочности и удобству в уходе. Сочетая в себе красоту натурального дерева и износостойкость покрытия, ламинат становится отличным выбором для любого интерьера. Его широкий ассортимент цветов и текстур позволяет создать уютную и стильную обстановку в любом помещении. https://kvarcvinil5.ru/
Мы осознаем, что каждый случай уникален, и поэтому предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Наши специалисты готовы обеспечить консультацию по телефону, где они смогут оценить текущее состояние и потребности пациента, а также предоставить подробную информацию о цене и возможных акциях или скидках, которые могут быть доступны.
https://perm.delta-clinic.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya
Ламинат – это популярное покрытие для пола, которое сочетает в себе прочность, долговечность и стильный внешний вид. Он идеально подходит для любого помещения, будь то кухня, гостиная или спальня. Ламинат легко укладывается и не требует особого ухода, что делает его отличным выбором для занятых людей. Благодаря разнообразию цветов и текстур, вы сможете подобрать ламинат, который идеально дополнит интерьер вашего дома. Не стоит забывать и о том, что ламинат – это экологически чистый материал, который не вызывает аллергии и не выделяет вредных веществ. Приобретая напольные покрытия в нашем магазине вы обновите свой дом с помощью качественного ламината! https://kvarcvinil1.ru/
На сайте https://otparivateli-odejdy.ru/ вы найдете отпариватели одежды, которые помогут вернуть вещам опрятный внешний вид. Устройства можно брать с собой, потому как они наделены компактными и небольшими размерами. В магазине представлены только те варианты, которые созданы проверенными брендами. Устройства надежные, практичные и имеют небольшой вес, привлекательный дизайн. Отпариватели отличаются эргономичной формой, за счет чего их комфортно держать в руке. На приборы действуют привлекательные цены, ассортимент регулярно обновляется.
После кодирования от алкоголизма человек прекращает употреблять спиртные напитки, из-за чего тяга к ним постепенно ослабевает. Пациент со временем избавляется от физической, а затем уже и от психологической зависимости.
https://perm.clinica-plus.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/kodirovanie
После кодирования от алкоголизма человек прекращает употреблять спиртные напитки, из-за чего тяга к ним постепенно ослабевает. Пациент со временем избавляется от физической, а затем уже и от психологической зависимости. Однако нужно понимать, что кодировка, как и любой другой метод лечения алкоголизма, не дает 100% пожизненный результат.
https://lytkarino.clinica-plus.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/kodirovanie
Используйте услуги брокера при покупке квартиры в новостройках Москвы и Санкт-Петербурга! Для Вас работает бесплатно сервис подбора квартиры и расчёта ипотеки. Сопутствующие профессиональные услуги брони квартиры в новостройках, сопровождение покупки, подбор выгодной ипотеки, оформление ипотеки онлайн также бесплатные. Комиссию платит застройщик или банк. На сайте https://www.nedvigimost-1.ru Вы можете оставить заявку на подбор квартиры, расчёт ипотеки. Мои профессиональные услуги помогут Вам купить квартиру выгодно и комфортно.
Ищите профессиональное лечение наркомании и алкоголизма по методике Довженко? Зайдите на страницу https://doctor-khl.kz/lechenie-alkogolizma-i-narkomanii/ где вы познакомитесь с особенностью нашей работы, которая поможет вам избавиться от алкогольной, наркотической и азартной зависимостях. Поможет восстановить здоровье и качество жизни. Посетите сайт – узнайте больше о наших услугах.
такой https://kp-inform.ru/catalog/kontrollery/kontroller_dell_eql_type_14_ps6110_gmh23
Запой является следствием длительного хронического употребления алкоголя. Он появляется у человека на фоне алкоголизма. Характерен запой для более поздних стадий болезни, и он отмечается непрерывным употреблением спиртного больше 5-7 дней. У запойных алкоголиков нет абстиненции или похмелья и это один из главных признаков патологического состояния.
https://klin.clinica-plus.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/vyivod-iz-zapoya
Одно из направлений деятельности частной наркоклиники лечения алкоголизма и наркомании – оказание услуг на дому. У нас работает бригада врачей-наркологов, которые оперативно выезжают на вызов, как только поступает заявка.
https://losino-petrovskij.narko-trezvost.ru
На сайте https://karedo.ru/ вы сможете найти как дефицитный товар, так и тот, который вам продадут по привлекательной стоимости и в любом количестве. При необходимости вы сами сможете выложить объявление для того, чтобы продать ненужную вещь, но при этом она точно пригодится кому-то. Для быстрой продажи выставляйте умеренную стоимость, чтобы покупатель сразу нашелся. Эта платформа идеально подходит для того, чтобы разместить на ней бесплатные объявления. Если вы ищите что-то определенное, то определитесь с категорией, ценой, чтобы сузить поиск.
На сайте https://copygeneral.ru запросите счет, чтобы заранее узнать, во сколько обойдутся услуги типографии. В компании вы сможете воспользоваться такими важными услугами, как: печать проектов и чертежей, широкоформатная печать, полиграфия для бизнеса, дизайн и верстка. Также в арсенале имеются и различные другие услуги, которые тоже будут полезны вашему бизнесу. Услуги обойдутся по привлекательной и небольшой стоимости, а потому воспользоваться ими сможет как средний, так и крупный бизнес.
Одно из направлений деятельности частной наркоклиники лечения алкоголизма и наркомании – оказание услуг на дому. У нас работает бригада врачей-наркологов, которые оперативно выезжают на вызов, как только поступает заявка.
https://krasnogorsk.narko-trezvost.ru
Наркологическая клиника ЕНС оказывает услуги по выводу из запоя. Используем современные методики взаимодействия с больным, что позволяет стабилизировать физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
https://ens-narkologia.ru/programmy-lecheniya/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma/gipnoz
На сайте https://www.lord-films.org/ посмотрите увлекательные и интересные фильмы, которые точно вам понравятся и подарят массу приятных положительных и ярких эмоций. Фильмы имеют красивую концовку. Они рассказывают о происходящем красиво, а потому вы сможете узнать культуру чужой страны, ознакомиться с деталями и получить другую важную и ценную информацию. Фильмы представлены в отличном качестве, у них качественный звук, а потому получится рассмотреть все в мельчайших подробностях.
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru
Стационар наркологической клиники очень комфортный для проживания и лечения. Каждая палата оснащена современной мебелью, включая удобные кровати и функциональные шкафы для личных вещей, обеспечивая чувство уюта и приватности.
https://krasnoznamensk.zapoy-clinic.ru
Скачать приложения для Андроид бесплатно на сайте https://appdepot.ru/ без регистрации.
Паркетная доска – это тип напольного покрытия, состоящий из деревянных планок, которые укладываются в виде палубной доски. Она отличается высокой долговечностью и прочностью, а также придает интерьеру теплую и уютную атмосферу. Паркетная доска может быть изготовлена из различных пород дерева и иметь различные оттенки и текстуры, что позволяет подобрать подходящий вариант под любой стиль помещения. https://kvarcvinil3.ru/
Анонимная наркологическая клиника – медицинское учреждение, где оказывают квалифицированную, профессиональную помощь алкоголику, наркоману, курильщику или игроману, который хочет и старается избавиться от зависимости. Основное преимущество анонимного наркологического центра – никто посторонний не будет знать о том, что человек проходит лечение в клинике.
https://alcoblago.ru/uslugi/narkomaniya/lechenie-ot-tropikamida
«ОБМЕННИК МОСКВА» https://obmennik.moscow/ – обмен валюты и криптовалюты онлайн в Москве! Круглосуточный обмен криптовалют на рубли переводом во все банки и на карту Мир! Выгодный обменный валютный курс покупки и продажи: биткоин / эфир / солана / тон / цифровой доллар и все альткоины за рубли!
На сайте https://filtry-dlya-bassejnov.ru/ вы сможете заказать качественные, практичные и надежные фильтры для бассейнов. Они высокотехнологичные, надежные и практичные, а потому их можно приобрести и для собственного использования. Вы сможете подобрать вариант на необходимую площадь. Все изделия от проверенных, качественных марок, которые дорожат своей продукцией и предлагают гарантии, привлекательные расценки. Если и вам необходимо подобрать фильтр, но вы не знаете, какой именно подходит, то воспользуйтесь помощью компетентных специалистов.
На сайте https://lufkad.com/ закажите мансардные окна премиального качества и по привлекательной стоимости. Конструкции выполнены с использованием уникальных и инновационных технологий, а потому прослужат очень долго, радуя привлекательным видом, износостойкостью. Есть возможность заказать мансардные окна самых разных размеров и в необходимом количестве. Вся продукция является оригинальной, на нее есть документация, а также сертификаты. Безупречная квалификация, огромный опыт позволяют браться за самые сложные заказы.
На сайте https://parogeneratory-market.ru/ вы найдете огромное количество парогенераторов, которые сочетают в себе функцию утюга, а также мощный парогенератор. Такое устройство является высокотехнологичным, мощным и качественным. Поможет быстро придать вещи опрятный и красивый вид. Все решения реализуются по привлекательной стоимости. Вы сможете подобрать вариант, исходя из своих предпочтений, финансового положения и других критериев. Имеются такие станции, которые идеально подходят для профессионалов, а вот варианты попроще – для хозяек.
При выборе напольного покрытия для вашего дома или офиса важно обратить внимание на качество, долговечность и дизайн. Магазин напольных покрытий – это место, где вы можете найти широкий ассортимент различных материалов, от ламината и паркета до ковров и виниловых плиток. https://ламинат1.рф/
[url=https://new.alt.com/?non_mobile=0]alt.com[/url]
click here for more https://counterwallet.info/
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники
visit their website https://infinitowallet.pro/
На сайте https://tvoyprud.ru вы сможете купить оборудование для пруда и фонтана по приемлемым расценкам. Тут вы найдете декоративные камни на люки, насадки для фонтанов и многое другое. Мы продаем исключительно товары высококачественные, гарантируем доступные цены и оперативную доставку. На портале у вас есть возможность найти то, что вам надо. Если возникнут вопросы, перезвоните нам, опытные сотрудники с радостью вас проконсультируют и помогут с выбором. Каждого клиента мы ценим. Уделяем пристальное внимание уровню обслуживания.
Приложения для Андроид скачать бесплатно с сайта https://androiddock.ru/
Начните игру с приложения, просто скачав 888starz bet на айфон бесплатно.
На сайте https://pechi-dlya-bani-i-sauny.ru в большом выборе представлены печи для бани и сауны. Все они функциональные, надежные, наделены безупречным качеством, длительным сроком службы. Печи созданы из таких материалов, которые не воспламеняются, наделены высоким качеством. Все изделия мощные, а если необходима помощь в выборе, то воспользуйтесь исчерпывающей консультацией специалиста. Он подскажет, какое устройство подойдет именно вам. Все печи выполнены надежными, проверенными и популярными брендами, отвечающими за качество.
На сайте https://kirsanovv.ru/kak-izbavitsya-ot-dolgov/ узнайте то, как можно избавиться от долгов. Специально для вас несколько простых шагов, которые помогут поправить финансовое состояние. Ознакомьтесь с теми параметрами, которые подходят под описание идеального банкрота и какие долги получится списать. Изучите информацию, которая подскажет, нужно ли избавляться от имущества. Вы узнаете и то, каким должен быть долг для того, чтобы его гарантированно списали. Юрист Кирсанов точно поможет в этом.
Get the facts https://simplehold.pro/
На сайте https://auto-arenda-anapa.ru/nashi-avto/ изучите все варианты автомобилей, которые вы сможете арендовать прямо сейчас. Автомобиль потребуется не только местным жителям, но и туристам, которые желают осмотреть все окрестности края. Есть возможность арендовать авто самого разного класса, ориентируясь на свой бюджет. Вам необходимо лишь выбрать автомобиль, после чего оформить прокат. Установлены привлекательные расценки. Арендуйте автомобиль на любое количество времени, в том числе, на несколько суток.
[url=https://credit24.pro/zaymy/onlajn-na-kartu-bez-proverok-srochno/]zaymy onlayn na kartu bez proverok srochno – mikrozaymy onlayn na kartu bez proverok srochno s perevodom na kartu ili elektronnyy koshelek – zaym onlayn na kartu bez proverok srochno na sayte credit24.pro [/url]
Tegs: [u]займы за 24 часа – микрозаймы за 24 часа с переводом на карту или электронный кошелёк – займ за 24 часа на сайте credit24.pro [/u]
[i]займы 24 часа – микрозаймы 24 часа с переводом на карту или электронный кошелёк – займ 24 часа на сайте credit24.pro [/i]
[b]займы за 5 минут – микрозаймы за 5 минут с переводом на карту или электронный кошелёк – займ за 5 минут на сайте credit24.pro [/b]
zaymy pensioneram – mikrozaymy pensioneram s perevodom na kartu ili elektronnyy koshelek – zaym pensioneram na sayte credit24.pro https://credit24.pro/zaymy/pensioneram/
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-12.ru
На сайте https://mangaly-shop.ru/ вы найдете огромное количество вариантов мангалов, на которых получится приготовить вкусные и ароматные блюда на свежем воздухе. Все конструкции выполнены из качественных, надежных материалов. Именно поэтому они не воспламеняются, долго не изнашиваются, наделены длительным сроком эксплуатации. Есть возможность подобрать решение под свои запросы и потребности. Все они реализуются по привлекательной стоимости, очень часто проходят распродажи для того, чтобы покупка была выгодней.
Get the facts
Dermalax™ Plus,1,;
Различают несколько вариаций эффективного кодирования. Методики в рамках терапевтических программ можно комбинировать. Рассмотрим основные направления медикаментозной блокады, психотерапевтических и дополнительных методов.
https://protvino.delta-clinic.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-13.ru
эскорт услуги девушки работа
Иногда в наркологической практике примеряется еще одна группа лекарственных средств на основе цианамида. Он обладает выраженным противоалкогольным действием, что повышает чувствительность к алкоголю и блокирует распад этанола.\
https://tver.delta-clinic.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma
Также наша клиника предлагает услугу вывода из запоя на дому круглосуточно, гарантируя быструю и эффективную помощь в любое время суток. Наша выездная бригада готова к выезду в любое время дня и ночи, обеспечивая необходимое лечение и поддержку в домашних условиях.
https://kalininec.narko-trezvost.ru/uslugi/vyvod-iz-zapoya/na-domu
На сайте https://grsuv.ru/ закажите лазерную гравировку. Квалифицированный, компетентный специалист сможет приехать к вам на объект и произвести все необходимые работы. Возможна гравировка на крупных вещах, а также выполняют гравировку на ложках, эксклюзивных решениях, жетонах, а также шильдах. В компании предложат производство клише, гравировку по кругу. Все работы обойдутся недорого, а услуга оказывается в минимальные сроки. Для того чтобы уточнить информацию, необходимо позвонить по телефону.
Следующая страница https://kp-inform.ru/catalog/hdd_and_ssd/zhestkiy_disk_lenovo_ibm_73gb_10k_2_5in_non_hot_swap_sas_sff_hdd_26k5777
На сайте https://auto-arenda-anapa.ru/ можете ознакомиться с условиями аренды автомобиля. Сотрудники имеют большой опыт работы. Автопарк «CarTrip» находится в хорошем техническом состоянии. Гарантируем приемлемые цены. Оплатить можете наличными или же банковской картой. Вы получите свободу действий. Принимаем заявки круглосуточно как онлайн, так и по телефону. С радостью поможем вам найти идеальный вариант. Знаем, как выстроить приятное сотрудничество с клиентами!
Нарколог на дом – это выездная медицинская услуга в Апрелевке. Врач приезжает на дом и может снять ломку, запой, интоксикациию, похмелье и др. Помощь оказывается круглосуточно, анонимно и быстро.
https://zhukovskij.narko-trezvost.ru/uslugi/vyzov-narkologa
Прерывание запойного состояния на дому возможно только посредством постановки капельницы. Аппаратные методы применяются исключительно в условиях стационара. Врач составляет план лечения исходя из состояния пациента и результатов обследования.
https://ozyory.zapoy-clinic.ru/alkogolizm/vyvod-iz-zapoya/na-domu
The spa body to body waiting visit one of the kinds massage, is what we do. What is an swedish massage interested in everyone. Body to body massage this is the gift of giving for happiness. You be surprised to that,what ocean enjoyment can experience from choice massage. In studio Workshop Lingam massage or penis massage women will hold the sexiest anticellulite massage.
How is it done, and is there something exotic? We will tell you all about him that you wanted to know |Our russian massage is visited not only by men but also by women, and also by couples. You want to rejoice is exactly what infinitely … Our intention this is to please women and men magical fancy or anything couples massage. Private approach to your requirements and conditions.
The amazing women our the salon will give you an unforgettable experience. The salon is a place of rest and relaxation. The french massage, as in principle, and relaxation, operates on some elements naked body, this helps all become less tense. Choose one or just two beauties! Choose for yourself masseurs by appearance, both professional and professional abilities!
Spa center in NY we advise chic placement with convenient style. All of these premises enable to stay with you not attracting the attention of other customers.
Our showroom works in Midtown West. Specialists Ava –
happy ending massage hot
mounjaro инструкция +на русском цена – трулисити раствор +для инъекций, трулисити купить +в москве +в наличии
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru
На сайте https://vezuviy.shop/ изучите весь каталог товаров, которые предлагает популярная компания. Перед вами только функциональные, практичные и надежные печи, дымоходы, на которые даются гарантии. В этом магазине вы сможете купить не только печи для бани, но и отопительное оборудование, нагревательный котел и многое другое. Все представленные аксессуары на 100% совместимы со всеми устройствами. Специально для вас бесплатная доставка, а банный камень в подарок. На аксессуары предоставляются скидки, которые сделают покупку более выгодной.
Ищите монтаж электрики и механики на сельскохозяйственных объектах? Зайдите на сайт Белагромеханизация https://belagromeh.ru/ которая предлагает широкий спектр услуг от профессионалов. Основные наши услуги: ветеринарные консультации в области сельского хозяйства и ведение электромонтажа и монтажа сельскохозяйственного оборудования.
Не всегда имеется возможность срочно посетить наркологический центр и получить необходимое лечение. Плохое физическое или психическое состояние наркозависимого или больного алкоголизмом может помешать встрече с врачом. В этом случае вы можете анонимно вызвать нарколога на дом.
https://volgograd.zapoy-clinic.ru/narcology
Не всегда имеется возможность срочно посетить наркологический центр и получить необходимое лечение. Плохое физическое или психическое состояние наркозависимого или больного алкоголизмом может помешать встрече с врачом. В этом случае вы можете анонимно вызвать нарколога на дом.
https://naro-fominsk.zapoy-clinic.ru/narcology
Найдите актуальное зеркало 1xbet на сегодня и оставайтесь в курсе всех изменений в работе популярного букмекерского сайта.
Как понять, что зависимому требуется срочный осмотр нарколога? Он теряет связь с реальностью, не контролирует количество и качество выпитого спиртного.
https://kazan.narko-trezvost.ru/uslugi/vyzov-narkologa
На сайте https://xn—–6kccjekczeea3acetf4cripwfc8qya.xn--p1ai/ вы сможете позвонить по указанному телефону, чтобы получить исчерпывающую консультацию о том, как заказать ритуальные услуги. Каждый клиент получит персонального агента, который проявит сочувствие и поможет определиться с услугами, а также сопутствующей атрибутикой. Вместе с этой похоронной службой вы сможете организовать достойное прощание с близким человеком. Установлены самые привлекательные расценки, чтобы заказать услуги смогли все, кто в этом нуждается.
http://forum.infinite-soul.org/viewtopic.php?f=64&t=20959
На сайте https://ofisnye-kompyuternye-kresla.ru/ вы сможете ознакомиться с огромным количеством офисных кресел, которые идеально впишутся в любое помещение. Все они отличаются привлекательным внешним видом и красивым, презентабельным исполнением. Все компьютерные кресла отличаются особым комфортом, удобством, а потому вы точно подберете такое решение, которое точно понравится. Кресла представлены самой разной цветовой гаммы: бежевые, черные, красные, бордовые, песочные. Все изделия отличаются привлекательной стоимостью.
На сайте https://pro-ten.ru/ закажите качественные, надежные и практичные ТЭНы от производителя. В разделе вы найдете и блок ТЭНы, а также погружные нагреватели для гальваники, воздушные, водяные ТЭНы и устройства для сауны. Если вам необходимо найти что-то определенное, то воспользуйтесь специальным поиском, который подберет для вас лучшее решение. Перед покупкой ознакомьтесь со всеми техническими характеристиками, чтобы принять правильное решение. ТЭНы полностью удовлетворяют предпочтения клиентов.
http://ya.2bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=20224#p242031
На сайте https://weaponshop.net/travmaticheskie-pistolety/ вы сможете приобрести травматические пистолеты, а также все необходимые боеприпасы, которые могут вам потребоваться в процессе эксплуатации. При этом не потребуется лицензия. Покупка происходит максимально быстро и без лишней бумажной волокиты. При необходимости вы всегда сможете заказать оперативную доставку. Только в этом магазине огромный ассортимент изделий, что позволит подобрать идеальный для себя вариант. Регулярное обновление ассортимента.
Зайдите на сайт https://casino-pin-up-online24.top/ и вы узнаете все о Pin UP CASINO. Как играть, как регистрироваться, какие существуют бонусы за депозит или регистрацию, как пользоваться мобильным приложением для любого устройства, а также о доступных способах пополнения депозита, как верифицировать аккаунт и многое другое.
На сайте https://lemon-car.ru/ вы узнаете об автосервисе «LEMON CAR». У нас работают высококлассные сотрудники с многолетним опытом по ремонту и обслуживанию автомобилей разных марок. Для специалистов не существует невыполнимых задач. Гарантируем доступные цены, учитываем требования и пожелания заказчиков. Подходим к решению проблем с транспортным средством персонально. Вас приятно удивит качество оказываемых услуг. Нас рекомендуют коллегам, друзьям, родственникам!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту фото техники от зеркальных до цифровых фотоаппаратов.
Мы предлагаем: срочный ремонт фотоаппаратов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Хотите узнать о психосоматике? Тогда добро пожаловать на сайт pppd.space! Мы стараемся помочь людям с проблемами соматического характера достичь от их симптомов длительного облегчения. Хотим быть платформой для обучения и оказания поддержки. https://pppd.space – здесь можете найти много бесплатной информации о психосоматике. Также здесь представлены отзывы, посмотрите их уже сегодня. Вас ценные рекомендации ждут о том, как управлять стрессом и расслабиться. Вы почувствуете заметное улучшение своего самочувствия.
На сайте https://2023.1lordfilm.one вы сможете начать смотреть фильмы в режиме реального времени и тогда, когда хотите. Перед вами есть мелодрамы, драмы, комедии, а также триллеры и многое другое. И самое важное, что все фильмы представлены в отличном качестве, с хорошим звуком, что позволит насладиться просмотром. Регулярно появляются новинки, которые будут интересны и вам. Кино подарит вам приятные эмоции, разнообразит досуг. Просматривайте фильмы в режиме реального времени и тогда, когда хочется.
kraken ссылка тор – кракен зеркало тор, ссылка на кракен тор
узнать больше https://t.me/ozempic_zakazat
Зайдите на страницу https://medium.com/@ivan_k777/%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%BA-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%BE%D0%BF%D0%BB%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%83-%D0%BE%D1%82-%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%80%D1%83%D0%B1%D0%B5%D0%B6%D0%BD%D1%8B%D1%85-%D0%BA%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B2-%D0%B2-2024-%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%83-%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%85%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%8F%D1%81%D1%8C-%D0%B2-%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%81%D0%B8%D0%B8-77c5b235a061 и вы ознакомитесь с интересной статьей о том как принимать оплату от зарубежных клиентов в 2024 году находясь в России. Полноценная статья ответит на все ваши вопросы.
На сайте https://ru.lords-film.pics/ вы найдете интересные и завораживающие своей красотой фильмы и сериалы. Они точно понравятся вам своей картинкой, а также четким звуком. В каждом фильме играют интересные и популярные актеры, которые очаруют вас своим шармом и обаянием. Все они играют так, чтобы произвести на вас впечатление. Есть как триллеры, так и драмы, комедии, так и мелодрамы, которые точно вам понравятся. И самое важное, что просматривать фильмы получится в любое время и на самых разных устройствах.
На сайте https://moskitnye-setki-okna.ru/ вы найдете москитные сетки в огромном ассортименте, высокого качества и созданные из практичных материалов, невосприимчивых к осадкам, механическому воздействию. Вы сможете заказать вариант с учетом необходимых размеров. Москитная сетка точно прослужит очень долго, не потеряет изначального внешнего вида. Все изделия реализуются по привлекательной стоимости. В магазине часто проходят распродажи, что позволит значительно сэкономить на покупке.
Wazzup, homie? Rad to run into you, bro.
Would be a great enhancement for your site Scrap copper communication
Until next time, and may positivity light your way
thiet ke noi that
https://primabella.ru/en/catalog/men/jumper-expose-bianco.php
веб-сайт https://t.me/ozempic_zakazat/
Официальный сайт компании LITOKOL https://litokol-russia.ru/ – всегда в наличии на складах: сухие строительные смеси для укладки керамической плитки, керамогранита и натурального камня, затирки, штукатурки, шпатлевки, сухие смеси для стяжки, системы утепления фасадов и удобные, профессиональные инструменты. Приглашаем к сотрудничеству с ЛИТОКОЛ!
На сайте https://filtry-dlya-bassejnov.ru/ в большом ассортименте находятся фильтры для бассейнов. Все они качественные, надежные, проверенные, а потому наделены безупречными техническими свойствами, хорошими эксплуатационными характеристиками. Все фильтры вы сможете заказать прямо сейчас и в любое комфортное время. При необходимости получите консультацию, если у вас есть вопросы или не можете выбрать фильтр именно под свой бассейн. На сайте находятся все технические характеристики к каждому фильтру, которые позволят быстро определиться с тем, что вам нужно.
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-15.ru
На сайте https://t.me/addlist/de6T6qiB_2YyNTFi вы сможете ознакомиться с огромным количеством объявлений. Здесь выкладываются предложения на самую разную тему, включая: электронику, бытовую технику. На сайте можно найти работу, разместить вакансию и воспользоваться всеми функциями сервиса. Все, что вам интересно, находится на этом канале. Регулярно появляются новые объявления, с которыми вы сможете ознакомиться в наиболее удобное время. Выкладывайте абсолютно бесплатно. Разместите объявление, если и вы хотите что-то продать.
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru/o-klinike
При длительном потреблении алкоголя организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола в крови. Это приводит к изменению метаболических процессов и нарушению работы центральной нервной системы.
http://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai
Наркологическая клиника ЕНС оказывает услуги по выводу из запоя. Используем современные методики взаимодействия с больным, что позволяет стабилизировать физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
https://ens-narkologia.ru/programmy-lecheniya/psihiatriya/lechenie-nevrastenii
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru
На сайте https://avtodom.car-trip.ru/ можете детально ознакомиться с условиями аренды автодомов. CarTrip гарантирует самые низкие цены и оперативную обратную связь. Все без исключения машины чистые, исправные и укомплектованы полностью. Путешествие пройдет с максимальным комфортом, вы получите массу удовольствия. Уверены в том, что захотите вернуться к нам снова. Если у вас возникли дополнительные вопросы, смело обращайтесь к нам, с радостью на них ответим.
зайти на сайт https://sovagg.org/
https://sovetprovse.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=3448#p7741
Cristiano Ronaldo – Forward. Legendary player with uncommon goal-scoring ability.
Luis Gustavo – Midfielder. Key playmaker with superlative revenant and control http://www.alfeihavsalnassr.ru.
На сайте https://parkbeton.ru/ посмотрите все работы предприятия, которое на профессиональном уровне занимается производством изысканных и оригинальных скульптур, фонтанов, цветочниц и ваз. Они идеально подходят для обустройства парков. Бригада специалистов практикует качественную и надежную обработку. Все изделия обладают высокой прочностью, надежностью. Они отличаются небольшой стоимостью. Во время покраски конструкций применяется краска эталонного качества. Доставка происходит силами специалистов компании.
Линейдж 2
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую медицинскую и социальную проблему, затрагивающую большое количество людей по всему миру. Одним из наиболее выраженных проявлений этой зависимости является запой, который характеризуется длительным и неконтролируемым потреблением алкоголя.
http://alko-konsultaciya.ru
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru/chto-takoe-zapoj
Массаж Ивантеевка https://taplink.cc/ivanteevkamassage
На сайте https://ru.kino24.uno представлено огромное количество интересных фильмов в отличном качестве. Все они отличаются особым жанром, безупречной актерской игрой, а также приятной музыкой. В разделе представлены не только фильмы, но и сериалы, а также мультики, которые понравятся деткам различных возрастов. Есть особые подборки, а также коллекции, которые точно вам понравятся. Регулярно здесь появляются новинки, которые будет интересно посмотреть каждому. Теперь вы знаете, как разнообразить досуг.
https://agropravda.com/forum/topic4672-topov-metodi-viroshchuvannya.html
Официальный клуб SYKAAA предлагает новым игрокам бонус 325% на депозит, за активное повышение уровня – игрок получает круглосуточную поддержку и участие в турнирах. Новых пользователей привлекает не только бонус 100FS за регистрацию, но и дизайн sukaaa официальный сайт на сайте наглядное меню, которое позволяет в пару кликов найти нужный софт, выбрать игру или сделать депозит.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – сервисный центр в краснодаре
Официальный сайт Sykaaa предлагает новым игрокам бонус 325% в 4 этапа, за активное повышение уровня – игрок получает кэшбэк и быстрые выводы. Новых клиентов привлекает не только бонус 100FS за регистрацию, но и дизайн официальный телеграм SYKAAA на сайте наглядное меню, которое позволяет в пару кликов найти нужный софт, выбрать игровой автомат или сделать депозит.
Желаете сделать заказ на взлом почты, мессенджеров и соцсетей? Xakerforum.com вам в этом поможет. У вас есть возможность уже сегодня к специалисту обратиться, он безопасно и действенно решит ваши проблемы. https://xakerforum.com/topic/282/page-11 – здесь представлена более подробная информация, ознакомиться с ней можно в любое удобное время. Хакер четко и последовательно работает, доводит начатое до логического завершения, объясняет все понятно. Гарантирует привлекательные цены. Остались вопросы? Специалист будет рад ответить на них!
Нужна реконструкция деревянного дома? Наша бригада из опытных строителей из Белоруссии готова воплотить ваши идеи в реальность! Современные технологии, индивидуальный подход, и качество – это наши гарантии. Посетите наш сайт реконструкция дома в Апрелевке и начните строительство вашего уюта прямо сейчас! #БелорусскаяБригада #Шлифовка #Реконструкция #Достройка
На сайте https://mangaly-shop.ru/ вы найдете огромное количество мангалов, которые идеально подходят для приготовления пищи на открытом воздухе, в саду. Все мангалы отличаются высоким качеством, на них имеются документы. Есть возможность подобрать мангал самого разного размера, формы. Все изделия отличаются компактными размерами, небольшим весом, они мобильны, а потому легко перенести на другое место в случае необходимости. Все мангалы прочные, надежные, поэтому им не страшно механическое воздействие, перепады температуры.
Зарегистрируйтесь на 888Starz и получите бонусы за первый депозит http://forum.l2star.net/member.php?u=18580
Очень подходящий способ получить ответ на любое домашнее задание – это сфотографировать его и скинуть в https://t.me/s/gdz_online_po_photo. Итог приходит моментально, а объяснения очень понятные, что даже я, философ, все понял. Советую всем, кто хочет сохранить время и нервы.
Clicking Here zip rar
опубликовано здесь https://t.me/ozempicg/
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту планшетов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: замена стекла на планшете
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
На сайте https://xakerforum.com/topic/282/page-11 вы сможете воспользоваться услугами компетентных, квалифицированных хакеров, которые смогут вам помочь в ситуации, независимо от ее сложности. Если на работе происходят кражи или информацию о компании постоянно сливают, то необходимо выяснить, кто это делает. В этом вам помогут услуги хакера. Они обойдутся недорого, и при этом вы сможете найти виновника. Хакеры смогут вскрыть почту, пробить номер, узнать, кто звонил с незнакомого телефона. И самое важное, что о вашем сотрудничестве точно никто не узнает.
Женский интернет-журнал для современных женщин https://ladylifestyle.ru/ – это секреты красоты и здоровья, психология и отношения, модные тренды, эффективные фитнес-методики — всё для того, чтобы ты была в курсе всего нового и интересного, а статьи постоянно добавляются что позволит получать интересную информацию ежедневно.
бк олимп предоставляет своим пользователям зеркало сайта для удобного входа и использования всех функций букмекерской конторы.
кракен даркнет
Однако стоит отметить, что работа с даркнет-ресурсами связана с риском, и пользователи должны быть осведомлены о последствиях своих действий. Незаконные действия, совершенные в рамках даркнета, могут иметь серьезные юридические последствия. Поэтому перед использованием таких ресурсов необходимо тщательно обдумать свои намерения и рискнуть только после четкого понимания последствий.
Source:
Source:
[url=https://bazaonion.vip/]кракен даркнет[/url]
Качестветвенный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – асфальт цена за 1 м2 с укладкой
Ищите разработку сайтов? Зайдите на сайт https://w-concept.ru/ и познакомьтесь с частная мастерской Анастасии Дорохиной. Она занимается разработкой сайтов и магазинов. Делает сайт под ключ начиная с дизайна вашего проекта и заканчивая функционалом. Основная специализация в разработке сайтов это интернет-магазины и небольшие корпоративные сайты, а также Landig Page.
anchor martianwallet download
YOURURL.com rabby wallet login
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:сервис центры бытовой техники новосибирск
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
На сайте https://film.kino-lords.one/ представлено огромное количество фильмов самого разного жанра: мелодрамы, драмы, ужасы, комедии, триллеры и многое другое. Все фильмы отличаются необычным сюжетом, оригинальной постановкой, а также бесподобной актерской игрой. Перед вами огромный выбор фильмов, которые помогут расслабиться и разнообразить досуг в выходной день. Просматривать их вы сможете на любом устройстве, в том числе, компьютере, планшете. Регулярно появляются любопытные новинки.
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую медицинскую и социальную проблему, затрагивающую большое количество людей по всему миру. Одним из наиболее выраженных проявлений этой зависимости является запой, который характеризуется длительным и неконтролируемым потреблением алкоголя.
http://alko-konsultaciya.ru/chto-takoe-zapoj
Запой может возникнуть по разным причинам, включая стресс, психологические проблемы, социальные факторы и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний.
http://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru
SOFFITTO предлагает профессиональный ремонт и отделку квартир в Орле. Сотрудники наши постоянно обучаются. За их работой тщательный контроль качества ведется. Ориентируемся на потребности своих клиентов и повышаем уровень обслуживания. https://soffitto-57.ru – сайт, где можете прямо сейчас ознакомиться с отзывами. Мы занимаемся разными видами отделки ремонта. Поставленные задачи выполняем на отлично. Гарантируем 100% исполнение сроков. Быстро принимаем заявки и всегда готовы ответить на ваши вопросы. Обращайтесь к нам!
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru/vrach
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую медицинскую и социальную проблему, затрагивающую большое количество людей по всему миру. Одним из наиболее выраженных проявлений этой зависимости является запой, который характеризуется длительным и неконтролируемым потреблением алкоголя.
http://alko-konsultaciya.ru/chto-takoe-alkogolizm
Автобика – Доска объявлений
автотовары
На сайте https://oboi-dlya-sten.ru/ находится большой ассортимент обоев. Все они имеют привлекательный внешний вид, интересный и разнообразный дизайн. Обои украсят пространство в помещении любого стиля. Вы обязательно выберете вариант как в гостиную, так и спальню, детскую комнату и другие помещения. Все решения отличаются безупречным качеством, поэтому точно прослужат не один год. Есть возможность подобрать обои с самым разным рисунком, который обязательно вам понравится. Все они реализуются по доступной цене.
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru
На сайте https://lan-union.ru/ у вас есть возможность купить кабельное и сетевое оборудование. В каталоге компании можно найти детальное описание, характеристики товаров и продукции производителя. На портале имеются к рассмотрению сертификаты на продукцию, вы можете подробнее с сервисом ознакомиться. Из достоинств компании, можно отметить оперативную логистику, гарантию и высокое качество оборудования. Подпишитесь на рассылку, чтобы быть в курсе новостей и акций компании.
Запой может быть вызван различными факторами, включая стресс, депрессию, психические расстройства, социальные и семейные проблемы, а также физиологическую зависимость от алкоголя.
http://narco-vivod.ru
Алкогольная зависимость — серьезное заболевание, которое требует комплексного подхода для лечения. Запой, характеризующийся длительным и неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, представляет собой опасное состояние, которое требует немедленного вмешательства.
http://alko-reabcentr.ru
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую медицинскую и социальную проблему, затрагивающую большое количество людей по всему миру. Одним из наиболее выраженных проявлений этой зависимости является запой, который характеризуется длительным и неконтролируемым потреблением алкоголя.
http://alko-konsultaciya.ru/vrach
Hello
Seamless Hacking Assistance
Providing seamless hacking assistance for websites, accounts, and devices. My services prioritize security and efficiency, completing orders within one day without alerting the victim.
https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html
Based on personal practice, it’s clear that even a simple email opening requires expertise across different areas:
Employing a program for hacking Facebook or Whatsapp is a time-consuming task and isn’t universally applicable.
When dealing with user inactivity, one must search for vulnerabilities on the server and open the database.
Often, exploiting the victim’s less-protected secondary profile provides a simpler access point to the desired primary profile.
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Professional hacker service [/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Where to hire hackers[/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Find a hacker [/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Professional hacker for hire[/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Hacker service[/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Rent a hacker[/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Order a hack[/url]
Bro!
image source
Celestia wallet keplr
Посетите страницу https://www.lisava.ru/misc/articles/kak_vubrat_idealnoe_kreslo_dlya_domashnih_kazino_i_igrovuh_komnat.html и вы почитаете любопытную статью о том как правильно выбрать идеальное кресло для домашних казино и игровых комнат.
На сайте https://avocado-fm.ru/ представлена красивая и невероятная музыка, которую вы сможете послушать прямо сейчас и на любом устройстве, в том числе, планшете, ПК. Перед вами самые разные радиостанции, которые помогут вам скрасить досуг. Если вы хотите отдохнуть и расслабиться после трудового дня, то просто включите свою любимую композицию, чтобы зарядиться позитивом и послушать лирические напевы. Позвольте себе отдохнуть так, как желаете. Вы также сможете послушать аудиокниги, музыку в стиле транс, джаз радио. Все это в отличном качестве, с хорошим звуком.
На сайте https://iseer.kz/led вы сможете заказать LED экраны для того, чтобы представить свой бизнес в выгодном свете. Светодиодные экраны считаются выигрышным решением, ведь это – ненавязчивая реклама, которую потенциальные покупатели обязательно увидят. При этом трансляция изображения находится на высоком уровне, отличная цветопередача. Свяжитесь с представителями компании для того, чтобы высказать все свои пожелания. Они готовы услышать все, что вы скажете, чтобы предложить лучшее решение для вас. Узнайте технические параметры каждого экрана.
Wejdź na stronę https://maxlift.info/ i możesz kupić lub naprawić: Wózek widłowy używany Gdynia, Sprzedam wózek widłowy używany Gdynia, Wózek paletowy Gdynia, Naprawa wózków widłowych Gdynia, Sztaplarka Gdynia, Serwis paleciaków Gdynia.
На сайте https://prokat.open-anapa.ru/ закажите звонок для того, чтобы уточнить все детали по такой услуге, как прокат автомобилей. При этом отсутствуют залоги, ограничения. Для того чтобы воспользоваться услугой, необходимо обозначить такие моменты, как: начало, окончание аренды. Это позволит вам точно рассчитать расценки. Выберете любой автомобиль из парка. Здесь все иномарки, которые регулярно проходят ТО, осмотр перед выездом, а потому точно не подведут на дороге. Аренда обойдется по привлекательной стоимости.
На сайте https://robaz.ru получите консультацию, чтобы узнать больше информации об установке забора под ключ. Все необходимые работы компетентные мастера возьмут на себя. На процесс уйдут не более 2 дней. Смета, а также выезд замерщика предоставляются абсолютно бесплатно. В компании строят такие заборы, которые прослужат огромное количество времени. Вы получите работу высокого качества и в строго оговоренные сроки. В компании действуют честные и привлекательные расценки. По этой причине вы всегда будете знать, за что платите.
На сайте https://newsplaneti.online/ представлены самые последние, свежие и интересные новости из сферы политики, экономики. Также имеются данные относительно выборов в США. Вы узнаете о том, кто скончался из популярных личностей совсем недавно. Имеется информация на тему науки, спорта, кино. Есть такие новости, которые не касаются сферы экономики и политики, но тоже будут вам интересны. Здесь публикуются такие события, которые произошли только недавно и нужно, чтобы весь мир об этом узнал.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт цифровой техники казань
На сайте https://shatry-i-tenty.ru/ предлагается огромный ассортимент шатров, тентов, различных навесов, которые позволят себя чувствовать на природе комфортно и защищенно, дополнительно уберечься от посторонних глаз. Есть как традиционные варианты, так и эксклюзивные решения, которые подходят для торжеств, организации корпоративных мероприятий, а также свадеб. Все шатры имеют различную цветовую гамму, произведены с применением новых и инновационных материалов, которые не портятся под влиянием осадков.
[url=][/url]
Tegs: [u][/u]
[i][/i]
[b][/b]
Играйте на сайте 7k casino вход и выигрывайте крупыне призы каждый день https://t.me/s/casino7kzerkalo
тирзепатид отзывы – оземпик таблетки, семаглутид действующее вещество
https://cvformat.io/ is your ultimate career companion, offering expert CV and cover letter writing services tailored to your unique professional journey. Our AI-powered platform combines cutting-edge technology with human expertise to craft standout application materials that catch employers’ eyes. From entry-level to executive positions, CVformat.io provides customizable templates, industry-specific CV and Cover Letter suggestions, and personalized career advice. Start your career transformation today!
Our stranger things rule 34 options offer an immersive exploration where erotica mixes with fantastic realms and well-known characters from animated series and video games. If you’re a enthusiast of My Hero Academia, Pokemon, or Rick and Morty, you’ll definitely find content exciting on mult34.com. Our platform is designed for people who appreciate premium visuals, compelling storylines, and one-of-a-kind styles of erotic animation.
На сайте https://mebel-kvinta.ru/ вы сможете вызвать замерщика абсолютно бесплатно для того, чтобы сделать мебель на заказ. Она производится из качественных, высокотехнологичных материалов, а потому конструкции прослужат очень долгое время. В этой компании создают качественную корпусную мебель презентабельного дизайна. Она идеально подходит как для домов, так и коттеджей, а также офисов. А самое важное, что она впишется в общую концепцию помещения. На предприятии работают лучшие сборщики, мастера с многолетним опытом.
На сайте https://t.me/s/mdaddycasino изучите всю исчерпывающую, интересную и содержательную информацию, которая касается популярного онлайн-заведения «DADDY CASINO». Оно привлекает огромным количеством интересных и запоминающихся развлечений, слотов. Это современный портал, на котором вы найдете огромное количество запоминающихся игр. Все развлечения от лучших и надежных разработчиков, которые отвечают за качество. На главной странице вы найдете всю необходимую информацию об этом азартном заведении.
На сайте https://laminat-dlya-pola.ru/ вы сможете заказать качественный, презентабельный ламинат, который получится уложить в любом месте дома, включая гостиную, детскую комнату. Он наделен практичностью, высоким качеством, износостойкостью, а потому невосприимчив к повреждениям, механическому воздействию. На сайте можно подобрать варианты самой разной цветовой палитры, что позволит удовлетворить требования каждого покупателя. Ламинат прочный, надежный, наделен безупречным качеством. Реализуется по лучшей стоимости.
Зайдите на сайт https://oeparts.by/ и вы найдете автозапчасти по самым выгодным ценам в наличии и каталоги запчастей для всех марок автомобилей, а также расходники для ТО для всех автомобилей. У нас осуществляется ежедневная доставка запчастей в любую точку Беларуси. Подберите запчасти по автомобилю, но номеру запчасти или VIN номеру. Подробнее на сайте.
What’s up, buddy? I’m so glad we could find the time to meet up.
Perhaps this will provide new insights Ferrous material price trends
Bye-bye, and may your days be as radiant as the stars
https://666porn.net/
Перед началом лечения необходимо провести полное медицинское обследование пациента. Важно оценить общее состояние здоровья, определить наличие хронических заболеваний, оценить степень алкогольного опьянения и степень токсического поражения органов.
http://xn—-7sbepb0atgesdez7c.xn--p1ai
Запой – это состояние, при котором человек продолжительное время употребляет алкогольные напитки, не контролируя количество выпитого. Оно часто сопровождается физической и психологической зависимостью от алкоголя.
http://narko-reabcentr.ru
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую медицинскую и социальную проблему, затрагивающую большое количество людей по всему миру. Одним из наиболее выраженных проявлений этой зависимости является запой, который характеризуется длительным и неконтролируемым потреблением алкоголя.
http://alko-konsultaciya.ru/o-klinike
Лечение алкоголиков при помощи современного медицинского подхода дает возможность предвидеть и устранить все риски, с которыми человек обязательно сталкивается во время возвращения к трезвой жизни.
https://podolsk.trezvost-clinica.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma
На сайте https://grsuv.ru/ изучите телефон компании для того, чтобы воспользоваться такой полезной услугой, как лазерная гравировка. Ее выполняют на ложках с именами, жетонах, шильдах. В компании вы сможете выполнить клише, заказать гравировку на самых разных предметах. Также доступна гравировка с выездом к заказчику. Для выполнения работы используются высокотехнологичные и уникальные методики. В компании работают опытные и знающие специалисты, которые учитывают все нюансы процесса.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту видео техники а именно видеокамер.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт камер видеонаблюдения
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Качестветвенный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов – асфальтирование территории
Потрясающий специалист с золотыми руками: Грязнов Сергей Олегович.
Каждый из нас сталкивается с необходимостью поиска надежного специалиста, которому можно доверить выполнение важной работы. В этом контексте имя Грязнов Сергей Олегович становится синонимом качества и профессионализма. Он не просто мастер своего дела, а истинный профессионал с золотыми руками, который способен справиться с любыми задачами и предложить наилучшие решения.
Отличный специалист: качества и навыки
Сергей Олегович обладает множеством качеств, которые выделяют его среди других специалистов. Вот несколько аспектов, за которые мы можем выразить ему благодарность:
Вежливость и отзывчивость: Каждый раз, когда вы обращаетесь к Сергею, вы можете быть уверены, что получите не только профессиональную помощь, но и теплое человеческое отношение. Его вежливость делает общение приятным и комфортным.
Внимание к деталям: Сергей всегда внимательно относится к работе. Он не пропускает мелочей, которые могут повлиять на конечный результат. Это качество позволяет ему выполнять задачи на высоком уровне.
Качество выполнения работ: Мы все знаем, как важно получать качественные услуги. Работа Сергея всегда выполнена на совесть. Он стремится к тому, чтобы каждая деталь была идеальной.
Соблюдение сроков: В современном мире время имеет огромное значение. Сергей всегда укладывается в оговоренные сроки, что делает его надежным партнером в любых делах.
Почему стоит выбрать Сергея?
Выбор специалиста — это всегда ответственный шаг. Рассмотрим несколько причин, по которым Грязнов Сергей Олегович является отличным выбором:
1. Профессиональный опыт: За плечами Сергея множество успешных проектов. Он знает все нюансы своей работы и умеет находить оптимальные решения в самых сложных ситуациях.
2.Индивидуальный подход: Сергей всегда внимательно слушает пожелания клиентов. Он учитывает все замечания и старается исправить их, чтобы удовлетворить ожидания заказчика.
3. Безупречный внешний вид: Сергей всегда выглядит безупречно. Его аккуратность и опрятность создают положительное первое впечатление и говорят о его отношении к работе.
Отзывы благодарных клиентов
Многочисленные отзывы клиентов подтверждают высокое качество работы Сергея. Вот некоторые из них:
“Огромная благодарность Сергею! Работа выполнена качественно и вовремя. Все пожелания были учтены.”
“Спасибо, Сергей! Вы — настоящий профессионал с золотыми руками. Общаться с вами — одно удовольствие.”
“Сергей всегда отзывчив и вежлив. Никаких проблем в работе не возникло.”
Заключение
Грязнов Сергей Олегович — это специалист, которому можно доверять. Его трудолюбие, внимание к деталям и уважение к клиентам делают его одним из лучших в своей сфере. Мы выражаем огромную благодарность Сергею за его нелегкий труд и надеемся на дальнейшее сотрудничество. Если вы ищете надежного специалиста, который выполнит работу качественно и вовремя, не сомневайтесь — выбирайте Сергея!
Перед началом лечения необходимо провести тщательную оценку состояния пациента. Важно определить степень алкогольной зависимости, наличие сопутствующих заболеваний и общее физическое состояние.
http://xn—-7sbepb0agvevex3c.xn--p1ai
МАПС обучение онлайн maps-edu.ru
Окончить переподготовка дефектология можно в представленной академии. Реестр содержит свыше 1800 различных программ обучения, иногда трудно найти, что требуется определенно Вам. Можно пользоваться поиском, указав направление обучения и другие параметры. Популярные направления: медицина, сельское хозяйство, ветеринария, закупки, менеджмент управление, пожарная безопасность, педагогика, социальная работа, экономика, метрология и стандартизация, кадровое делопроизводство, водоснабжение и водоотведение, радиационная безопасность и многие другие.
Запой характеризуется не только физической зависимостью от алкоголя, но и глубокими психологическими изменениями. Психологически человек становится неспособным контролировать свое потребление алкоголя, а физически организм адаптируется к постоянному присутствию этанола в крови, что приводит к развитию абстинентного синдрома при попытке прекратить употребление.
http://xn—-7sbbtpbjhfzmxgo8c.xn--p1ai
Прежде чем перейти к методам вывода из запоя, важно понять, что именно представляет собой это состояние. Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя на протяжении нескольких дней или даже недель.
http://xn—-7sbbtpbjmlmmiqgp2d.xn--p1ai
Mango-Office CRM системы – Манго Офис возможности платформы, Манго Офис услуги для колл-центра
Запойные состояния характеризуются значительными изменениями в физиологии и биохимии организма. Хроническое употребление алкоголя приводит к нарушениям метаболизма нейротрансмиттеров, особенно гамма-аминомасляной кислоты (ГАМК) и глутамата.
http://narko-zakodirovat.ru
В этой статье я, как нарколог, предоставлю подробный обзор методик и подходов к выводу из запоя, а также новейшие тенденции в этой области.
http://narko-zakodirovat1.ru
Зависимость от наркотических препаратов является одной из самых тяжелых патологий в мире, которая наносит ущерб всему организму. Продолжительность жизни зависимого значительно сокращается.
https://mytischi.trezvost-clinica.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomosh/narkolog-na-dom
На сайте https://tehnook.online/ опубликованы интересные, содержательные новости, которые касаются компьютеров, ноутбуков, ПК, планшетов, смартфонов, мониторов, процессоров, игр, аналитики и многого другого. Также найдете публикации на тему материнских плат, накопителей, носимой электроники, умных вещей. Вы отыщите любопытные вещи, которые обязательно вызовут у вас огромный интерес. Регулярно добавляются новые публикации, необходимые для расширения кругозора. Если вы считаете себя истинным геймером, то ознакомьтесь с календарем выхода релизов.
vobkabet – vodka, зеркало водка бет
Алкоголь негативно влияет на функцию гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковой оси, что приводит к дисрегуляции кортизола и других стрессовых гормонов. Это усугубляет психоэмоциональное состояние пациента, способствует развитию тревожных и депрессивных расстройств.
http://narko-zakodirovat2.ru
Психологическая зависимость, в свою очередь, обусловлена эмоциональными и психическими проблемами, которые человек пытается заглушить при помощи алкоголя. Это создает замкнутый круг, из которого крайне сложно выйти без профессиональной помощи.
http://alko-zakodirovat.ru
Длительное употребление алкоголя приводит к снижению чувствительности рецепторов ГАМК и увеличению активности глутамата, что обуславливает развитие толерантности и абстинентного синдрома.
http://xn—-7sbb6ahbedrhc1bom2cxf9b.xn--p1ai
Запойное состояние несет в себе множество рисков для здоровья пациента, включая развитие тяжелых соматических и психических расстройств. В данной статье рассматриваются методы и принципы вывода из запоя с позиции современной наркологии.
http://xn—1-6kcbnh0aojodobev0w.xn--p1ai
Запой часто сопровождается депрессией, тревожностью и другими психическими расстройствами. Алкоголь может использоваться как способ саморегуляции эмоций, но это создает порочный круг, усиливающий зависимость и приводящий к ухудшению психического здоровья.
http://narco-vivod-clean.ru
Важным этапом в лечении алкогольной зависимости является социальная реабилитация пациента. Это включает меры по восстановлению социального статуса, трудовой деятельности, семейных отношений и интеграции в общество.
http://xn—-7sbbdtawliczg5ij.xn--p1ai
В некоторых случаях необходима госпитализация, особенно если запой был длительным и тяжелым. В условиях стационара пациент находится под постоянным наблюдением медицинского персонала, что позволяет контролировать его состояние и своевременно оказывать необходимую помощь.
http://xn—-8sbalzkcecejnbebg7o3b.xn--p1ai
Запой развивается на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости, когда организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола. При отсутствии алкоголя у таких пациентов возникают абстинентные симптомы, включая тревогу, тремор, потливость и тахикардию.
http://reabcentr-narko.ru
[url=https://pro-credit.ru/mfo/kassa-vzaimopomoschi/]kassa vzaimopomoschi poluchit’ zaym onlayn do 15000 rub. do 32 mgnovenno s licenziey cb rf – kassa vzaimopomoschi – poluchit’ zaym onlayn bystro na sayte “pro-kredit” [/url]
Tegs: [u]кредитная история испортится от займа в мфо при наличии просрочек и большом количестве займов единовременно – почему портится кредитная история из-за займов? на сайте “про-кредит” [/u]
[i]по статистике заявки в мфо одобряются в 90% случаев, но есть и 10%, по которым кредитование не осуществляется – почему отказывают в займе? на сайте “про-кредит” [/i]
[b]польза-финанс получить займ онлайн до 100000 руб. до 364 мгновенно с лицензией цб рф – польза-финанс – получить займ онлайн быстро на сайте “про-кредит” [/b]
kapitalina poluchit’ zaym onlayn do 30000 rub. do 30 mgnovenno s licenziey cb rf – kapitalina – poluchit’ zaym onlayn bystro na sayte “pro-kredit” https://pro-credit.ru/mfo/kapitalina/
Важным этапом в лечении алкогольной зависимости является социальная реабилитация пациента. Это включает меры по восстановлению социального статуса, трудовой деятельности, семейных отношений и интеграции в общество.
http://xn—-8sbbpb6asblledv7c.xn--p1ai
Наркологическая клиника ЕНС оказывает услуги по выводу из запоя. Используем современные методики взаимодействия с больным, что позволяет стабилизировать физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
https://ens-narkologia.ru/programmy-lecheniya
В клинике «АлкоБлаго» предлагаем профессиональное лечение алкоголизма. Наши врачи проведут обследование, помогут подобрать эффективное лечение. Предоставляем поддержку и советы для вас и вашей семьи, помогаем справиться с алкогольной зависимостью и начать жить полноценной жизнью.
https://alcoblago.ru/uslugi/alkogolizm/podrostkovyj-alkogolizm
https://obmennik.com.ru/ – онлайн обменник обмен валют и криптовалют онлайн! Круглосуточный обмен криптовалют на рубли переводом во все российские банки и на карту Мир! Выгодный обменный курс покупки и продажи электронных валют: биткоин / эфир / солана / тон / цифровой доллар и альткоины за рубли!
LED Media Show – ваш надежный партнер в создании ярких светодиодных шоу и эффектов
LED технологии уверенно завоевывают популярность благодаря своим уникальным возможностям создавать яркие и незабываемые шоу. Компания LED Media Show предлагает решения, которые превращают любое мероприятие в визуальный шедевр, будь то концерт, презентация, свадьба или корпоративное событие.
### Что мы предлагаем?
1. **Светодиодные экраны**
LED экраны позволяют создать масштабные визуальные эффекты, которые впечатляют даже самых требовательных зрителей. Они могут быть использованы для создания рекламных роликов, живых трансляций и динамичных фоновых сцен.
2. **Шоу-программы с LED костюмами**
Интерактивные шоу с артистами в светодиодных костюмах добавляют особую магию каждому мероприятию. Динамичные выступления артистов в уникальных костюмах с подсветкой создают эффект погружения в мир света и фантазии.
3. **Техническая поддержка и аренда оборудования**
Мы предлагаем не только готовые решения для световых шоу, но и аренду светодиодного оборудования для самостоятельной организации мероприятий. Наша команда специалистов обеспечит монтаж, настройку и обслуживание техники.
4. **Индивидуальный подход**
Для каждого клиента мы разрабатываем уникальные проекты, соответствующие всем требованиям и пожеланиям. Мы предлагаем креативные решения, которые подчеркивают стиль и атмосферу вашего события.
### Почему выбирают LED Media Show?
– **Высокое качество оборудования**. Мы используем только современное и надежное светодиодное оборудование.
– **Профессионализм команды**. Наши специалисты имеют многолетний опыт работы в индустрии и знают, как создать незабываемое шоу.
– **Широкий спектр услуг**. От аренды техники до организации шоу “под ключ” – мы готовы воплотить ваши идеи в жизнь.
– **Доступные цены**. Мы предлагаем гибкие тарифы и индивидуальные предложения для каждого клиента.
Организация светодиодных шоу – это не просто работа, это искусство. С LED Media Show ваше мероприятие засияет новыми красками и оставит незабываемые впечатления.
https://led-media-show.kz/
Welcome to mult34.com, the best destination for admirers of erotic animated illustrations. Our platform provides a extensive range of top-notch content designed for people who love creative and bold narratives. We’ve collected the best resident evil porn collections from famous illustrators, featuring a variety of genres, including cartoons to popular gaming franchises.
https://kds.kg/
Welcome to mult34.com, the top spot for enthusiasts of adult animated comics. Our website provides a vast range of premium creations designed for individuals who enjoy imaginative and provocative narratives. We’ve collected the finest my hero academia porn collections from renowned illustrators, offering a variety of genres, including comics to famous gaming franchises.
Electrician service germantown WI [url=]https://electrician-service-germantown-wi.space/[/url]
Bitcoin mixer
На сайте https://t.me/s/mcatcasino ознакомьтесь со всеми возможностями элитного казино. Вас ожидает огромная коллекция слотов, а также карточные игры, функции с живыми дилерами. Интерфейс сайта является интуитивно понятным, а потому вы с легкостью разберетесь со всеми опциями. Это позволит получить от игры максимум пользы. Регистрация займет минимальное количество времени. Организаторы предусмотрели огромное количество щедрых бонусов. По этой причине вы получите от игры только приятные впечатления и положительные эмоции. Для новичков особые щедрые бонусы, которые они смогут потратить на свое усмотрение.
Получение медицинской категории maps-edu.ru
Окончить переподготовка промышленное и гражданское строительство возможно в нашей академии. Реестр насчитывает более 1800 разнообразных программ курсов, иногда сложно понять, что требуется именно Вам. Можно воспользоваться поиском, введя направление и другие параметры. Реальные направления: строительство, сельское хозяйство, ветеринария, закупки, дефектология, логопедия, педагогика, социальная работа, нефтяная и газовая промышленность, метрология и стандартизация, электроэнергетика, маркшейдерское дело, радиационная безопасность и многие другие.
На сайте https://rakoviny-i-umyvalniki.ru/ представлено огромное количество раковин, умывальников, которые выполнены из современных, качественных материалов. Можно подобрать варианты под свои нужды, цели и задачи. Перед вами огромная палитра, а также матовые и глянцевые поверхности, большой выбор размеров, форм, модификаций. Самыми популярными материалами являются санфарфор, санфаянс, которые служат очень долго, не боятся механических повреждений, сохраняют вид на долгое время. Материалы наделены презентабельным внешним видом.
На сайте https://hd.kinogid.top вы найдете самые интересные и популярные фильмы, любопытные сериалы, которые точно вызовут у вас интерес. Огромное количество самых любопытных сюжетов, а фильмы представлены в различных жанрах, что позволит вам найти то, что соответствует вашим вкусам, предпочтениям. Регулярно публикуются новинки, которые вам точно захочется посмотреть одному либо в кругу друзей. Кино в хорошем качестве, с точным звуком. Нет необходимости скачивать на устройство, смотрите онлайн.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт цифровой техники красноярск
Профессиональная переподготовка медицинского персонала maps-edu.ru
Реализовать профессиональная переподготовка закупки можно в нашей академии. Реестр состоит из более 1800 разнообразных программ обучения, иногда трудно найти, что необходимо именно Вам. Можно пользоваться поиском, указав направление обучения и другие параметры. Реальные направления: строительство, агрономия, юриспруденция и право, закупки, дефектология, логопедия, физическая культура и спорт, социальная работа, нефтяная и газовая промышленность, метрология и стандартизация, электроэнергетика, маркшейдерское дело, радиационный контроль и многие другие.
MixBTC
Качественный асфальт выдерживает любые погодные условия и нагрузки, что делает его идеальным для парковок, дорожек и дворов. – укладка асфальта цена за м2
Вас интересует работа курьером в Нижнем Новгороде? На nabor-curierov.ru размещены свежие вакансии. Основная особенность этого сайта – его понятный интерфейс. Ресурсом пользуются активно. По работе предложения оставляют разные компании, к примеру – СберМаркет. https://nabor-curierov.ru/vakansii-kurera/ – сайт, на главной странице которого представлен список вакансий. Работодатели здесь в основном курьеров ищут. На портале имеются следующие разделы: Яндекс Еда, Озон, Тинькофф, Burger King, Яндекс Лавка. Станьте курьером!
На сайте https://avocado-fm.ru/ послушайте красивую, приятную музыку в режиме реального времени. Перед вами огромное количество радиостанций, которые принесут приятные эмоции, положительные впечатления. Здесь же вы найдете и аудиокниги, детское радио, клубную музыку. Вся она в отличном качестве, с интересным звучанием, а потому принесет только приятные эмоции. Вы можете слушать радиостанции как на компьютере, так и смартфоне – как вам удобно. Просто заходите на сайт, включайте свою любимую радиостанцию и начинайте наслаждаться звучанием.
На сайте https://xn--80aaaks3bbhabgbigamdr2h.xn--p1ai/ воспользуйтесь услугами онлайн-сервиса, который оказывает компетентную помощь в вопросах оформления загранпаспорта, визы. Здесь вы сможете воспользоваться срочной услугой. Компания успешно работает с 1999 года, а потому выучила все особенности данной сферы, заслужила огромное количество клиентов. При обращении в эту компанию вы сможете рассчитывать на получение всего комплекса работ. Услуга обойдется недорого, документы оформляются в ближайшее время.
Сайт pro100-stone.ru предлагает вам купить из искусственного камня столешницы, они массой преимуществ обладают. Наши столешницы выглядят эффектно и не требуют особого ухода. Помимо прочего, они высокие температуры способны выдерживать. https://pro100-stone.ru/izdeliya/stoleshnitsy-iz-iskusstvennogo-kamnya.html – здесь вы можете на кухню или в ванную заказать столешницу. Также тут можете оставить заявку на расчет. Появились вопросы? Созвонитесь с нами, мы вас проконсультируем.
loli
==> xzy.cz/2333 wts.la/wfelq <==
На сайте https://smartporog.ru/ изучите каталог, где находятся выпадающие пороги высокого качества, различной модификации. Изделия понадобятся в том случае, если установка обычных конструкций недопустима по определенным причинам. Такие пороги износостойкие, практичные и невероятно надежные. Они не дадут сквозняку образоваться, противостоят холоду, попаданию посторонних запахов. Инновационные пороги устанавливают в различных помещениях, в том числе, дома, а также коммерческих предприятиях, школах, детских садах.
элитный эскорт москва
casino kometa kometa casino rpb buzz
На сайте https://gamingvesty.ru/ опубликована исчерпывающая информация, которая касается самых популярных или, наоборот, редких игр. Очень много новостей, публикаций и всего интересного ожидает всех любителей компьютерных игр. Здесь также вы найдете релизы, наиболее популярные новости, которые касаются всех без исключения. Этот портал приглашает ознакомиться с новостями на тему киберспорта, кино, ММО, мобильных телефонов, железа и многого другого. Обязательно почитайте рецензии, посмотрите видеорепортажи.
T.me/s/mcatcasino – проекта CASINO CAT телеграм-канал. Тут найдете массу ценной информации. Наша цель – предоставить азартный опыт игры. Кэт – это надежное казино с быстрыми выплатами. Выбор игр большой, они все довольно быстро загружаются. https://t.me/s/mcatcasino – здесь узнаете, как играть правильно в казино CAT. Вас ждут удивительные бонусные предложения. Кэт казино – великолепное, есть много различных вариантов оплаты, что очень удобно. Саппорт всегда на связи, с радостью вам поможет. CAT CASINO заслуживает вашего внимания!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры по ремонту техники в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
смотреть здесь https://lk-mango-office.ru/
На сайте https://t.me/s/mkent_casino вы сможете начать игру в казино для того, чтобы заработать большое количество денег на свои нужды. При этом вас ожидает огромное количество бонусов, различные привилегии, которые сделают игру более интересной, яркой и незабываемой. Совершите регистрацию, на которую уйдет всего несколько минут. Переходите только по актуальной ссылке, чтобы не попасться в руки мошенникам. Для большей безопасности необходимо включить двухфакторную аутентификацию. Вы сможете сыграть в такие игры, которые оставят после себя положительные впечатления. Каждый день количество подписчиков только увеличивается.
[url=][/url]
Tegs: [u][/u]
[i][/i]
[b][/b]
содержание https://vodkabet.io
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в нижнем новгороде
internet Dym wallet keplr
На сайте https://melaminovye-gubki.ru/ вы найдете огромное количество меламиновых губок, которые выполнены из инновационного, уникального материала – меламина. Губка дает возможность выполнить уборку без применения чистящих средств. Это оптимальное решение для кухни, ванной, а также салона автомобиля. При помощи нее проводят чистку электроники, бытовой техники. В этом магазине она представлена в большом ассортименте, имеет различную форму, размеры, что позволит очистить даже самые труднодоступные места.
На сайте https://ideal-okna57.ru/ вы сможете заказать пластиковые окна, а также москитные сетки, которые создаются из качественных, уникальных материалов. Поэтому они не утратят внешнего вида длительное время. Важным моментом является то, что замеры происходят абсолютно бесплатно, а вызвать мастера вы сможете прямо сейчас. Для того чтобы определиться с выбором, необходимо изучить весь каталог. Доставка продукции происходит абсолютно бесплатно и строго на обозначенный адрес. У компании опыт работы в данной сфере – более 10 лет.
На сайте https://naduvnye-lodki-pvh.ru/ в большом выборе имеются надувные лодки, которые созданы из ПВХ материала. Они отличаются безупречной вместительностью, функциональностью и прочностью, а потому прослужат своему хозяину не один сезон. Есть возможность подобрать изделие самого разного оттенка и на любое количество человек. Материал наделен всеми важными характеристиками, поэтому сохранит вид надолго. Лодки отличаются привлекательной стоимостью, регулярно устраиваются скидки.
Продолжение https://t.me/ozempik_kupit_moskva
Wow that was strange. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say excellent blog!
https://roofers-msk.ru/
На сайте http://waltzprof.com закажите обратный звонок для того, чтобы произвести стальной профиль в огромном ассортименте. Он используется для того, чтобы максимально оперативно и правильно собрать ограждающие преграды, перегородки в стиле лофт, различные фасадные конструкции и многое другое. Вся продукция создана из качественных, надежных, практичных материалов, на которых не образуется коррозия. Все изделия прослужат очень долго за счет безупречных эксплуатационных качеств.
Желаете сделать заказ на взлом почты, мессенджеров и соцсетей? Xakerforum.com поможет вам в этом. Вы можете прямо сейчас обратиться к специалисту, который решит ваши проблемы действенно и безопасно. https://xakerforum.com/topic/282/page-11 – здесь более детальная информация представлена, посмотреть ее можно прямо сейчас. Хакер работает последовательно и четко, объясняет все доходчиво и доводит начатое до логического завершения. Гарантирует привлекательные цены. Остались вопросы? Специалист с удовольствием на них ответит!
CVzen https://cvzen.uk/ is a leading platform for CV and cover letter writing, offering personalized solutions to elevate your career potential. Our expert writers and easy-to-use AI tools help you create polished, professional documents that capture the attention of employers. Take the next step in your career journey with CVzen.
Ваш лазерный принтера требует заправки картриджа? Превратите расходы на новые картриджи в экономию с нашей услугой по заправке картриджей лазерных принтеров в Украине!
Наша команда специалистов гарантирует высококачественное обслуживание вашего принтера или МФУ, используя исключительно высококачественные расходные материалы. Забудьте о незаконченных печатных заданиях и переплате за новые картриджи – с нашим сервисом вы экономите свои деньги!
Заправить картридж лазерного принтера Киев – https://printershub.com.ua/ru/zapravka-kartridzha
Не теряйте время и финансы – доверьтесь профессионалам от ПринтерсХаб!
Мурманск – Кольский полуостров [url=https://xn—–6kcjobajs5bzbiv4l.xn--p1ai]Мурманск – Кольский полуостров [/url]
Мурманск – Кольский полуостров [url=https://на-севере-жить.рф]Мурманск – Кольский полуостров [/url]
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в новосибирске
На сайте https://t.me/s/r7casino_m вы найдете огромное количество развлечений на самый взыскательный вкус. Это онлайн-казино является удивительным, увлекательным, а самое главное, что предлагает пользователям огромное количество интересных вариантов игр, которые понравятся и вам. На странице находится очень много слотов, которые вызовут у вас неподдельный интерес. Также есть и живые дилеры, с которыми игра станет более интересной и невероятной. Вас порадует простая навигация, а также оперативная регистрация. Онлайн-заведение радует щедрыми бонусами, регулярно разрабатывает новые привилегии для того, чтобы каждому пользователю было интересно и увлекательно играть, пригласил своих друзей и знакомых в этот заманчивый мир азарта. И самое важное, что здесь вас всегда ждут и рады вашему присутствию.
На сайте https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.succumbp0ng.romeo представлена новая, увлекательная игра Succumb Pong. Она многофункциональна, потому как подарит не только приятные и яркие впечатления, положительные эмоции, но и расширит мировоззрение, многому научит, а заодно разовьет рефлексы. Вам необходимо закрываться и отворачиваться от шаров. Это поможет заполучить больше баллов. Но если сможете набрать как можно больше очков, то получите шанс выиграть турнир и стать лучше всех!
На сайте https://bitcoinsmi.online/ опубликована любопытная, интересная и полезная информация, которая касается криптовалюты. Опубликованы данные о Биткоине, Альткоине, обмене валют, а также NFT, финансах. Имеются данные о политике, касающиеся выборов в США, многого другого, что обязательно будет интересно всем без исключения. Для наглядности каждая новость сопровождается цветной картинкой. Есть и видеоматериалы, которые прольют свет на многие вопросы. Ежедневно экспертами добавляются новости, которые необходимо почитать всем, чтобы быть в курсе ситуации в мире.
loli
==> xzy.cz/2333 wts.la/wfelq <==
T.me/mvavada – проекта VAVADA телеграм-канал, где только лучшая информация собрана. Казино Вавада славится в выплатах выигрышей надежностью. Есть отличная бонусная программа. Менеджеры – вежливые и всегда готовы помочь. https://t.me/mvavada – тут мы делимся советами о том, как правильно играть в casino VAVADA. Казино Вавада – самое лучшее на сегодняшний день. Вас порадует отсутствие проблем с выводом и стабильность работы площадки. VAVADA достойна вашего внимания. Здесь есть множество плюсов, в сравнении с иными проектами.
На сайте https://laminat-dlya-pola.ru/ представлен ламинат в огромном ассортименте. Он различается цветовой гаммой, структурой, а также производителями. Но все напольные покрытия наделены безупречным качеством, надежностью и практичностью. Именно поэтому они прослужат несколько десятков лет, не изменив своих технических характеристик, изначального внешнего вида. Ламинат идеально подходит для любых помещений, неприхотлив в уходе и идеально вписывается в любую концепцию. Ламинату не страшны механические повреждения.
На сайте https://magazinsemena.ru/site/semena_pochtoi/ изучите каталог товаров для того, чтобы подобрать те семена, которые вы будете выращивать у себя на даче. Все семена отправляются почтой для того, чтобы вы получили отличный и завидный урожай. Вся продукция отличается безупречным и эталонным качеством, а доставка осуществляется максимально оперативно. Перед вами тысячи сортов семян, что позволит подобрать то, что нужно. На все семена есть гарантии. Компания заполучила огромное количество положительных отзывов и доверие клиентов.
На сайте https://raschitat-online.ru/ воспользуйтесь специальным инженерным калькулятором, который выполнит все необходимые расчеты. При этом появляется возможность осуществить все самые сложные расчеты. И самое главное, что все процессы простые, быстрые, безопасные. Пользоваться устройством можно абсолютно бесплатно и независимо от вашего местоположения. Калькулятором можно воспользоваться на любом устройстве, в том числе, ПК, смартфоне. Если хотите расширить функции или предложить идею по улучшению работы сервиса, то заполните обратную связь.
原來用微信和電腦訂都可以,在這兒訂過機票去大陸玩,付款岀票過程都很快很順利。下次都會在HOPEGOO繼續訂機票!
Continue Reading
Celestia wallet keplr
click to read more phantom extension
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту стиральных машин с выездом на дом по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервисный ремонт стиральных машин
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт крупногабаритной техники в казани
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
На сайте https://t.me/mvavada ознакомьтесь с информацией, которая касается популярного онлайн-заведения «VAVADA». Вы сможете отслеживать все новости, интересную и любопытную информацию самым первым на этом канале. Здесь публикуются промокоды, разыгрываются призы, выкладываются самые первые новости, а также различная информация на данную тему. Регулярно публикуются новые данные, которые помогут отследить то, что придумали организаторы. Количество подписчиков стремительно увеличивается, потому как интерес к этой группе возрастает.
Visit https://forexreviewer.org/ and you will learn everything about Forex trading. Useful information for beginners and professionals, as well as asset reviews, trading strategies, market trends, trading tools and platforms.
На сайте https://hozbloki-i-sarai.ru/ вы сможете найти хозблоки и сараи. Они созданы из качественных, лучших материалов, а потому на сооружениях не образуется грибок. Они не подвержены процессам гниения, внешним воздействиям агрессивной среды. Именно поэтому прослужат очень долго без потери технических характеристик, внешнего вида. В таких сооружениях вы сможете хранить не только вещи, но и инструменты, оборудование, если ведутся строительные работы. Есть возможность заказать хозблоки самых разных размеров, учитывая цели и задачи.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центры бытовой техники москва
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
company website Atom wallet keplr
Сайт онлайн казино 7k casino зеркало рабочее https://t.me/s/casino7kzerkalo
На сайте https://myrsporta.online/ вы найдете полезную, актуальную информацию о футболе. Есть самые разные новости, увлекательные истории, а также интервью популярных лиц, связанных со спортом. Вы сможете найти новости футбола по определенной стране. Есть информация, которая касается Чемпионата Европы, МЕЛБЕТ-Первой Лиги, Молодежной футбольной лиги, Лиги чемпионов, Лиги конференций. Все новости опубликованы ведущими экспертами, которые отлично понимают в этой теме. Только здесь самые актуальные, интересные и свежие новости из первых уст.
проститутка индивидуалки новосибирск октябрьский
https://mathhelpplanet.com/viewtopic.php?f=19&t=83286
[url=https://t.me/fontscapcutn/422]как в кап куте сделать текст[/url]
скачать шрифт в кап кут nord
купить сим карту тюмень
https://boltyshki.unoforum.pro/?1-2-0-00007929-000-0-0-1719998360
проститутки омска чат
промокод яндекс путешествия 2024 namore
йони массаж спрос
На сайте https://rent-me.cy/ уточните условия, по которым вы сможете взять в аренду автомобиль на Кипре. Прямо сейчас вы сможете рассчитать цену, после чего забронировать автомобиль на определенное количество времени. Все машины находятся в исправном техническом состоянии, а потому поездка точно вам понравится и произведет необходимое впечатление. Услуги обойдутся недорого. При этом не придется вносить залог, депозит, не потребуется франшиза, предоплата. Осуществляется полная страховка.
анкеты проституток самара
Extra resources martianwallet extension
клининг квартиры цена – [url=https://prostaya-uborka1.ru]клининговые услуги[/url]
Experts vaticinate a competitive betrothal with Fulham in all probability having the acrimony plenty of to their higher site in the combine and up to date form. Regardless, Birmingham’s accommodation advantageously could net payment an mind-boggling encounter.
Predicted Shoals: Birmingham 1 – 2 Fulham https://www.birminghamvsfulham.ru/.
На сайте https://gamenews.store/ вы найдете интересную, познавательную информацию, которая касается самых актуальных и интересных новостей их игровой индустрии. Есть любопытная информация о железе, компьютерах и многом другом. Имеются данные о том, какие игры сейчас в разработке и что от них ожидать. Представлены любопытные обзоры игр, которые помогут быстрее сориентироваться в сюжете и понять, подходит ли вам определенная игра. Имеется интересная информация о киберспорте, игровой индустрии.
Всякий автомобиль запрашивает улучшения и наиболее выигрышный путь
это сделать с веб-магазином высококачественных автокомпонентов Auto Brand СНГ
[url=https://auto-brand.com.ua] навестите торговую точку АвтоБренд
[/url]
Красный Яр 1-8 серии смотреть онлайн Наши дни. Режиссер-документалист из Франции Натали Легран приезжает в Красноярск снимать фильм о достопримечательностях края. С российской стороны ее помощником и консультантом становится молодой историк Виктор Антонов. Натали интересует золотодобытчик Никифор Плахов, о котором в архиве почти нет информации… 1861 год. С прииска Плахова сбегают двое рабочих. Один из них погибает от рук беглого каторжника, второй, Коряга, случайно находит золотую жилу, расположенную прямо на поверхности…
Портал demo-it.ru дает возможность вам с известными решениями 1С ознакомиться. Сможете оценить удобство интерфейса, разобраться в функционале и понять, насколько данная программа подходит для вашего бизнеса. Какие решения доступны в тестовом режиме расскажем на сайте. https://demo-it.ru – здесь можно уже сейчас оставить заявку, мы обязательно свяжемся с вами. Будем рады проконсультировать вас по вопросам работы и настройки программных продуктов. Обращаясь к нам, вы сэкономите время. Мы порекомендуем для вас подходящую программу.
промокод playing
На сайте https://nastolnye-elektroplitki.ru/ вы найдете огромное количество вариантов электрических настольных плиток самых разных видов и на необходимое количество конфорок. Они идеально подходят как для небольших кухонь, так и дачи. На них можно приготовить еду на небольшое количество человек. Компактные модели отличаются 1 или 2 конфорками. Все варианты, представленные в каталоге, считаются энергосберегающими, полностью безопасными и простыми в использовании. Именно поэтому они становятся выбором большинства. С легкостью очищаются от загрязнений.
dragon money казино
На сайте https://podvesnye-kreslashop.ru/ в большом выборе находятся подвесные кресла, которые могут устанавливаться не только на открытом воздухе, но и на балконе, в коттедже, частном доме, кафе. Эти кресла-коконы невероятно комфортные, удобные и стильные, а потому точно понравятся всем без исключения. Они придутся по вкусу как детям, так и взрослым. Такое кресло идеально впишется в любой интерьер, станет украшение ландшафта. Стоимость таких кресел зависит от используемых материалов. Как правило, они не изнашиваются и не теряют своего вида долго.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники в омске
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт бытовой техники
CVchef https://cvchef.fr/ tu plataforma integral para el avance profesional, ofreciendo servicios expertos de redacción de CV y cartas de presentación adaptados a tu industria. Ya seas un profesional con experiencia o estés comenzando, nuestras herramientas intuitivas y asesoramiento personalizado te permiten destacar en el competitivo mercado laboral actual. Eleva tu búsqueda de empleo con CVchef, donde comienza tu próximo movimiento profesional.
На сайте https://cybernews24.store/ почитайте познавательные, интересные и любопытные новости на тему криптовалюты, бизнеса, спорта, Форекса, Коронавируса и многого другого. Для наглядности имеется курс криптовалюты, что позволит выгодно произвести обмен, покупку, а также другие финансовые операции. Также вы почитаете о том, как выросли акции таких гигантов, как «Эпл», «Гугл», «Амазон» и других. Все новости составлены понятным, простым языком, доступным большинству.
Вас интересует работа курьером в Нижнем Новгороде? На nabor-curierov.ru размещены свежие вакансии. Главная особенность данного ресурса – это простой интерфейс. Ресурсом пользуются активно. Предложения по работе оставляют различные компании, например: СберМаркет. https://nabor-curierov.ru/vakansii-kurera/ – сайт, на главной странице которого представлен список вакансий. Работодатели здесь в основном курьеров ищут. На портале имеются следующие разделы: Яндекс Еда, Озон, Тинькофф, Burger King, Яндекс Лавка. Станьте курьером уже сегодня!
шлюхи в самаре на металлурге
яндекс путешествия снять квартиру посуточно
В клинике «АлкоБлаго» предлагаем профессиональное лечение алкоголизма. Наши врачи проведут обследование, помогут подобрать эффективное лечение. Предоставляем поддержку и советы для вас и вашей семьи, помогаем справиться с алкогольной зависимостью и начать жить полноценной жизнью.
https://alcoblago.ru/uslugi/alkogolizm/ambulatornoe-lechenie-alkogolizma
Наркологическая клиника ЕНС оказывает услуги по выводу из запоя. Используем современные методики взаимодействия с больным, что позволяет стабилизировать физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента.
https://ens-narkologia.ru/programmy-lecheniya/lechenie-narkomanii/amfetamin
Запой – это непрерывное употребление алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или недель, что приводит к ухудшению физического и психического состояния. Основные признаки запоя: невозможность прекратить пить самостоятельно, увеличение толерантности к алкоголю и абстинентный синдром при попытках прекратить пить.
http://xn—-7sbbdgsalifolh3ag.xn--p1ai
Запой представляет собой продолжительное употребление алкоголя, которое длится несколько дней, недель или даже месяцев. В это время человек практически не может контролировать потребление спиртных напитков, что приводит к значительным физическим, психическим и социальным последствиям.
http://xn—24-5cd0aaaxojc0ai3k.xn--p1ai
Лечение запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинскую, психологическую и социальную помощь. Основной целью терапии является купирование абстинентного синдрома, детоксикация организма и стабилизация общего состояния пациента.
http://xn—-7sbzghhjoftt2h.xn--p1ai
индивидуалки омск адель
промокод яндекс путешествия на повторное бронирование
проститутки новосибирск район
казино gms
Детоксикация является первым и одним из самых важных шагов в процессе вывода из запоя. Она может проводиться как в домашних условиях, так и в специализированных клиниках. В зависимости от состояния пациента и тяжести запоя, выбирается тот или иной метод детоксикации.
http://narko-zakodirovan.ru
промокод детский мир
Эти изменения стимулируют потребность в продолжении употребления алкоголя для поддержания нормального состояния. Психологическая зависимость, в свою очередь, обусловлена эмоциональными и психическими проблемами, которые человек пытается заглушить при помощи алкоголя. Это создает замкнутый круг, из которого крайне сложно выйти без профессиональной помощи.
http://narko-zakodirovan1.ru
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
http://narko-zakodirovan2.ru
Процесс детоксикации должен проходить под строгим медицинским наблюдением, поскольку самостоятельная попытка прервать запой может быть не только неэффективной, но и опасной для здоровья.
http://zavisim-alko.ru
стульчик для йони стим
a knockout post infinity walletAds
скачать текст для кап кут
сим карты orangestereo купить
Экскурсия Кипарисовое озеро – Экскурсия Кипарисовое озеро, Морские прогулки в Анапе
экскурсия по москве 2 часа
a fantastic read coinamiAds
Наши специалисты — это команда профессионалов с многолетним опытом работы в области наркологии и психологии. Каждый сотрудник клиники предан своему делу и искренне заботится о каждом пациенте
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-21.ru
В нашей клинике цена на вывод из запоя с выездом зависит от нескольких факторов, включая степень тяжести состояния пациента и необходимость дополнительных медицинских услуг. Мы осознаем, что каждый случай уникален, и поэтому предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
https://dolgoprudnyy.delta-clinic.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya
Мы работаем с самыми тяжёлыми состояниями пациентов, умеем убеждать в ситуациях, когда зависимые отказываются от терапии или процедуры детоксикации.
https://moscow.zapoy-clinic.ru
яндекс сплит абуз мануал
visit our website https://web-sollet.com
На сайте https://avtomobilnye-derzhateli.ru/ представлен огромный ассортимент автомобильных держателей, которые помогут вам вести разговоры за рулем. Получится с комфортом расположиться в кресле авто и, не отвлекаясь от дороги, разговаривать по телефону. Представлено огромное количество таких держателей, которые созданы проверенными, надежными марками. Они выполнены из высокотехнологичных материалов, которые невосприимчивы к механическим повреждениям. И самое важное, что такими конструкциями удобно и приятно пользоваться.
Запой может возникнуть по разным причинам, включая стресс, психологические проблемы, социальные факторы и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Постоянное употребление алкоголя приводит к физиологическим и психологическим изменениям, ухудшает состояние здоровья и качество жизни.
http://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai
Последствия запоя могут быть крайне серьезными, начиная от проблем со здоровьем (таких как цирроз печени, панкреатит, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания) и заканчивая социальными и личными проблемами (разрушение семей, потеря работы, правонарушения).
http://narco-vivod.ru
Важно помнить, что запой – это не просто проблема с алкоголем, а серьезное медицинское состояние, требующее комплексного лечения.
http://alko-specialist.ru
Запой представляет собой крайнюю стадию алкоголизма, когда человек не может остановиться и продолжает пить алкоголь в больших количествах. Это состояние возникает на фоне физической и психической зависимости от алкоголя.
https://lulustyle.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-pomosch-bez-pokidaniya-doma
На сайте https://pcompsoft.ru вы найдете всю важную информацию, которая касается компьютеров, железа и всего, что с этим связано. Также имеется информация о программах, самых качественных и популярных приложениях, которые обязательно необходимо установить себе. Имеются данные о различных устройствах, операционных системах. Представлена ценная и содержательная информация, касающаяся того, как сделать из обычного компьютера мощную машину. Опубликована информация, которая касается того, почему SSD-диск является оптимальной инвестицией.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт бытовой техники в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
T.me/s/azino777_a – это проекта Азино777 телеграм-канал. Здесь размещена исключительно занимательная информация. Azino777 – казино, которое имеет безупречную репутацию. Игры позволяют настоящий азарт испытать. https://t.me/s/azino777_a – здесь рассказываем о самом интересном, можете ознакомиться с информацией прямо сейчас. Безопасность данных, оперативные выплаты и круглосуточная поддержка клиентов делают Азино777 непревзойденным. Посетите Azino777, чтобы увлекательными играми насладиться, а также получить потрясающие эмоции.
На сайте https://ob-man.com/ вы найдете ценные, важные рекомендации, советы, которые помогут уберечься от мошенников. Причем все самые интересные, ценные советы собраны в одном месте. Они помогут вам защититься от мошеннических схем. Все советы, рекомендации являются рабочими, а потому помогают справиться с подозрениями. Все статьи написаны экспертами, которые описывают схемы обмана и помогают не попасться на удочку мошенников. Разоблачение на самую разную тему, включая инвестиционные проекты, технологии защиты, про банковскую безопасность. Также представлены и различные общеобразовательные материалы.
Hi there to every body, it’s my first pay a quick visit of this web site; this blog consists of remarkable and really excellent information in favor of readers.
авіатор гра
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – выездной ремонт бытовой техники в ростове на дону
CVzen es https://cvzen.mx/ una plataforma líder en la redacción de CV y cartas de presentación, ofreciendo soluciones personalizadas para elevar tu potencial profesional. Nuestros escritores expertos y nuestras herramientas de IA fáciles de usar te ayudan a crear documentos pulidos y profesionales que captan la atención de los empleadores. Da el siguiente paso en tu carrera profesional con CVzen.
На сайте http://woman.pub вы сможете ознакомиться с интересной, любопытной информацией на женскую тему. Так вы узнаете о том, как сохранить отношения, если надвигается развод. Есть информация о том, как распределить обязанности в семье, чтобы домашнюю работу выполняли все вместе. Если вы хотите преображения, то вы узнаете то, как это сделать с умом и сохранить индивидуальность. Есть информация о том, что такое счастье и как его добиться. Также узнаете и про свободные отношения, о том, как справиться со стрессом и как выявить кризис в отношениях.
высокооплачиваемая работа для девушек в набережных челнах
уфа проститутка башкирка
Женский интернет-журнал для современных женщин https://ladylifestyle.ru/ – это секреты красоты и здоровья, психология и отношения, модные тренды, эффективные фитнес-методики — всё для того, чтобы ты была в курсе всего нового и интересного, а статьи постоянно добавляются что позволит получать интересную информацию ежедневно.
эскорт женщины
На сайте https://pylesosy-moyuschie.ru/ вы найдете огромное количество моющих пылесосов. Они отличаются огромным количеством важных функций, которые необходимы для ежедневной уборки помещения. И самое важное, что с их помощью теперь навести чистоту становится намного легче. Они отлично справляются с уборкой даже в самых труднодоступных местах. Представлены пылесосы самых разных брендов. Они отличаются простой эксплуатацией, а потому управлять устройством сможет даже ребенок. Устройство неприхотливо в уходе, наделено долгим сроком службы.
эскорт грузии
эскорт германии
эскорт досуга
кракен сайт – kra1 cc, kraken сайт
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту игровых консолей Sony Playstation, Xbox, PSP Vita с выездом на дом по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт игровых консолей
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
На сайте https://invertornye-konditsionery.ru/ представлены инверторные кондиционеры в огромном ассортименте. Они отличаются тихой работой, минимальным расходом электроэнергии. Все изделия представлены ведущими мировыми марками, которые гарантируют высокое качество, длительный срок службы. Ассортимент подобран таким образом, чтобы удовлетворить предпочтения каждого посетителя. Постоянно устраиваются распродажи, что сделает покупку более привлекательной.
Наши специалисты — это команда профессионалов с многолетним опытом работы в области наркологии и психологии. Каждый сотрудник клиники предан своему делу и искренне заботится о каждом пациенте
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru
Психологическая поддержка является неотъемлемой частью процесса вывода из запоя. Психолог или психотерапевт поможет пациенту разобраться с причинами, приведшими к запою, и разработать стратегию для предотвращения рецидива. Групповые занятия и поддержка со стороны близких также играют важную роль.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютерных видеокарт по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт видеокарт gigabyte в москве
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Самостоятельный выход из запоя возможен, но наиболее безопасным и эффективным способом является обращение за профессиональной медицинской помощью.
http://alko-reabcentr.ru
m3ga gl сайт – мега закладки, работает ли мега сб
Запой, характеризующийся длительным и неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, представляет собой опасное состояние, которое требует немедленного вмешательства.
https://med-pro-ves.ru/zdorove/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnodare
What’s up, its pleasant piece of writing regarding media print, we all understand media is a great source of data.
RioBet
Психологическая поддержка является неотъемлемой частью процесса вывода из запоя. Психолог или психотерапевт поможет пациенту разобраться с причинами, приведшими к запою, и разработать стратегию для предотвращения рецидива. Групповые занятия и поддержка со стороны близких также играют важную роль.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru/chto-takoe-zapoj
Перед началом лечения необходимо провести тщательную оценку состояния пациента. Важно определить степень алкогольной зависимости, наличие сопутствующих заболеваний и общее физическое состояние. Это позволяет разработать индивидуальный план лечения.
http://xn—-7sbepb0agvevex3c.xn--p1ai
Во время запоя организм испытывает сильное токсическое воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению работы многих органов и систем. Постепенно формируется физическая и психическая зависимость, которая затрудняет самостоятельный выход из этого состояния.
http://xn—-7sbepb0atgesdez7c.xn--p1ai
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://cheathamcountysource.com/traveling-with-breast-cancer-tips-for-safe-and-enjoyable-summer-vacations
https://t.me/s/business_broker_ua
Психологическая поддержка является неотъемлемой частью процесса вывода из запоя. Психолог или психотерапевт поможет пациенту разобраться с причинами, приведшими к запою, и разработать стратегию для предотвращения рецидива. Групповые занятия и поддержка со стороны близких также играют важную роль.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru/chto-takoe-alkogolizm
Запой характеризуется не только физической зависимостью от алкоголя, но и глубокими психологическими изменениями. Психологически человек становится неспособным контролировать свое потребление алкоголя, а физически организм адаптируется к постоянному присутствию этанола в крови, что приводит к развитию абстинентного синдрома при попытке прекратить употребление.
http://xn—-7sbbtpbjhfzmxgo8c.xn--p1ai
простые пошаговые рецепты с фото
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://rushtips.com/outdoor-exercise-tips-for-breast-cancer-survivors-this-summer.html
На сайте https://skami-i-lavki.ru/ в огромном выборе находятся скамьи и лавки, которые созданы из качественных материалов. Они не подвержены процессам гниения, надолго сохраняют свой вид и всегда выглядят привлекательно. Есть возможность приобрести продукцию различных производителей. Она отвечает самым высоким предпочтениям покупателей, создана по ГОСТу. Получится подобрать материал с определенными техническими характеристиками. Они различаются особенностями монтажа и другими моментами.
Психологическая поддержка является неотъемлемой частью процесса вывода из запоя. Психолог или психотерапевт поможет пациенту разобраться с причинами, приведшими к запою, и разработать стратегию для предотвращения рецидива. Групповые занятия и поддержка со стороны близких также играют важную роль.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru/vrach
Физиологически запой вызывает серьезные нарушения в работе всех систем организма. Алкоголь действует как депрессант, угнетая центральную нервную систему, что приводит к развитию толерантности и необходимости увеличения дозы для достижения желаемого эффекта.
http://xn—-7sbbtpbjmlmmiqgp2d.xn--p1ai
Алкоголь оказывает токсическое действие на печень, сердце, поджелудочную железу и другие органы. Хроническое употребление приводит к развитию цирроза печени, кардиомиопатии, панкреатита и множества других заболеваний.
http://narko-zakodirovat.ru
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://fitnesshealthyoga.com/outdoor-exercise-tips-for-breast-cancer-survivors-this-summer-fitness-tips-of-the-day
T.me/mvavada – это телеграм-канал проекта VAVADA, пользующийся большой популярностью. Тут вы найдете только необходимую информацию. Вам понравится казино Вавада. Тут огромное разнообразие игр, точно не заскучаете! https://t.me/mvavada – тут поговорим об основном, вы много чего узнаете. За все время проект VAVADA зарекомендовал себя только с хорошей стороны. Много разных вариантов оплаты, неплохая бонусная программа. Вас порадует быстрое выведение денег и саппорт. Испытайте удачу прямо сейчас!
Психологическая поддержка является неотъемлемой частью процесса вывода из запоя. Психолог или психотерапевт поможет пациенту разобраться с причинами, приведшими к запою, и разработать стратегию для предотвращения рецидива. Групповые занятия и поддержка со стороны близких также играют важную роль.
http://alko-lechebnica.ru/o-klinike
На сайте https://raskladushki-sad.ru/ находятся раскладушки в самом большом ассортименте и по выгодной стоимости. Все они невероятно комфортные, качественные и износостойкие, созданы из современных, высокотехнологичных материалов. Они различаются не только размерами, но и формой и другими особенностями. Раскладушки помогут отдохнуть на природе. Ткань не выгорает на солнце и остается яркой, красивой на долгое время. Простой механизм не позволяет изделию ломаться. В магазине регулярное обновление ассортимента.
Запойное состояние возникает на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости и характеризуется нарушениями в работе центральной нервной системы, эндокринной системы и внутренних органов.
http://narko-zakodirovat2.ru
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://maurycountysource.com/outdoor-exercise-tips-for-breast-cancer-survivors-this-summer
Окунись в азарт онлайн казино! Слоты, рулетка и блэкджек ждут тебя. Не забудь воспользоваться бонусами для новых игроков и испытать удачу!
cryptoboss
Онлайн казино — это место, где каждый может выиграть! Огромный выбор игр и бонусы помогут тебе увеличить шансы на успех и наслаждаться азартом.
cryptoboss online
Если у вас не работает ютуб, есть несколько причин, почему это может происходить. В России часто встречается youtube стал тормозить, и это связано с блокировками и ограничениями, которые накладываются на доступ к платформе. Такие проблемы, как ютуб не грузит, могут затруднять просмотр видео, и многие пользователи сталкиваются с необходимостью искать способы обхода этих ограничений.
Если вам интересно, что делать если ютуб не работает, мы рекомендуем ознакомиться с материалами на сайте YouTube-Radar.ru. Проект Ютуб Радар youtube-radar.ru предоставляет актуальную информацию и практические советы, которые помогут решить проблему с доступом к видеохостингу. Также вы можете посетить ресурс youtube-ne-gruzitsya.ru чтобы узнать больше о том, как восстановить доступ к YouTube и избежать тормозов и задержек.
Не позволяйте блокировкам мешать вашему доступу к контенту – узнайте, как решить проблему с помощью YouTube Radar и продолжайте наслаждаться любимыми видео!
эскорт арбат
гагра эскорт
эскорт мальчиков
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://wilsoncountysource.com/the-importance-of-hydration-for-breast-cancer-patients-during-hot-summer-months
эстония эскорт
ява эскорт
Спасибо за пост
_________________
играть в игровые автоматы онлайн на деньги без регистрации реальные с выводом
эскорт кузнецк
get betnovate without prescription
m3ga at – мега сб даркнет, megaweb3.at
денис эскорт
шлюхи омска реальные анкеты
эскорт марафон
симкарты вставляют
симкарта почтой
авто симкарта
билайн симкарт
симкарта картинки
симкарта размер
https://avtoznak-dublikat.ru
На сайте https://fynmir.online/ почитайте интересные, свежие и актуальные новости на следующие темы: бизнес, банки, деньги, газ, экономика, финансы. А если вы хотите высказаться, поделиться своими мыслями, переживаниями на этот счет, то воспользуйтесь форумом. Там вы сможете найти единомышленников, которые с удовольствием пообщаются с вами на перечисленные темы. На портале всегда появляются свежие и полезные новости, которые будут актуальны для всех. Все они составлены лучшими экспертами. Есть данные и про коронавирус.
Онлайн казино — это мир захватывающих слотов, настольных игр и щедрых бонусов. Присоединяйся и сорви свой первый крупный выигрыш уже сегодня!
сайт cryptoboss
На сайте https://lordkino.net/ находится удобный онлайн-кинотеатр, где представлено огромное количество интересных, любопытных фильмов на самый разный вкус. Фильмы различного жанра, включая комедии, триллеры, детективы и многое другое. Также имеются и сериалы, детские мультики, которые будет интересно посмотреть всей семьей. Все фильмы в отличном качестве, с четким звуком, а потому точно вам понравятся. Смотреть их можно на любом устройстве, включая смартфон. Вас обрадует приятная актерская игра, удивительная музыка.
На сайте https://utepliteli-teploizolyaciya.ru/ в большом выборе находятся утеплители, которые помогают создать комфортный микроклимат и приятную обстановку внутри помещения и независимо от времени года. Кроме того, происходит снижение нагрузки на аппараты, предназначенные для кондиционирования помещения. Вместе с тем, сокращаются траты на отопление помещения в межсезонье, зимнее время. Перед вами только продукция, представленная высококлассными производителями, которые положительно себя показали.
Medicine information sheet. Effects of Drug Abuse.
generic levitra price
Some information about meds. Read now.
Начни играть в онлайн казино уже сегодня! Тысячи слотов, интересные бонусы и удобные способы оплаты делают игру легкой и увлекательной.
cryptoboss online
get colchicine
Hola, my dear friend. How have the days been treating you?
To my amazement, I’ve found a website that competes with the standard of your project Ferrous waste reclaiming facility
Keep spreading positivity, and farewell
дома престарелых
Доверие – психологический центр, оказывающий для людей услуги, которые нуждаются в поддержке в тяжелые периоды жизни. Здесь трудятся истинные профессионалы своего дела, вам отношение и подход очень понравится. Внимательно выслушать человека, помочь ему понять причину проблемы, и найти пути ее решения может хороший психолог. https://ack-group.ru – здесь узнаете, чем занимается семейный психолог, и какие инструменты в своей работе применяет подростковый психолог. На сайте можно почитать отзывы. Не затягивайте с обращением, не доводите ситуацию до предела.
https://napolke.com.ua/
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://robertsoncountysource.com/summer-strategies-coping-with-breast-cancer-treatment-and-side-effects
Психологическая зависимость, в свою очередь, обусловлена эмоциональными и психическими проблемами, которые человек пытается заглушить при помощи алкоголя. Это создает замкнутый круг, из которого крайне сложно выйти без профессиональной помощи.
http://alko-zakodirovat.ru
Толерантность означает необходимость употребления больших доз алкоголя для достижения того же эффекта, что и раньше при меньших дозах. Синдром отмены алкоголя возникает при резком прекращении его употребления и включает в себя симптомы от легкого беспокойства и тремора до тяжелых форм, таких как делирий тременс.
http://xn—-7sbb6ahbedrhc1bom2cxf9b.xn--p1ai
Во время запоя организм привыкает к постоянному воздействию алкоголя, что приводит к формированию толерантности. Резкое прекращение употребления алкоголя вызывает острый абстинентный синдром, характеризующийся возбуждением, тревожностью, судорогами и даже делирием.
http://xn—1-6kcbnh0aojodobev0w.xn--p1ai
кликните сюда https://kraken13.co.at
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://middletennesseesource.com/summer-strategies-coping-with-breast-cancer-treatment-and-side-effects
На сайте https://krasnodarregistr.ru воспользуйтесь миграционными услугами и оформите временную регистрацию в Краснодаре. В этой компании вам помогут оформить все необходимые документы. При этом помощь оказывается в режиме реального времени. Сотрудники сделают все именно так, как нужно и в минимальные сроки. Теперь вы точно не потеряете время на заполнении документов и сделаете все правильно. Но для того, чтобы выполнить все услуги так, как нужно, необходимо предоставить определенные документы.
Запой развивается на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости, когда организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола. В отсутствии алкоголя у таких пациентов возникают абстинентные симптомы, включая тревогу, тремор, потливость и тахикардию.
http://narco-vivod-clean.ru
В условиях стационара пациент находится под постоянным наблюдением медицинского персонала, что позволяет контролировать его состояние и своевременно оказывать необходимую помощь.
http://xn—-8sbalzkcecejnbebg7o3b.xn--p1ai
На сайте https://akkumulyatory-powerbank.ru/ в огромном ассортименте представлены внешние аккумуляторы от самых проверенных, надежных марок. Такое решение считается практичным и нужным, потому как оно положительно влияет на мобильность. И самое важное, что вы сможете оставаться на связи в любое время, независимо от ситуации. Что касается емкости батареи, то ее измеряют в миллиампер-часах. Эта величина определяет то, какое количество энергии может храниться в устройстве. Современные аппараты отличаются длительным сроком эксплуатации и высоким качеством.
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://maurycountysource.com/summer-strategies-coping-with-breast-cancer-treatment-and-side-effects
станок для заточки цепей прокрафт
на этом сайте https://mg1.to
На сайте https://relomania.com заполните форму для того, чтобы воспользоваться услугой, связанной с переездом в Испанию. Компания «Relomania» готова оказать вам профессиональную консультацию, помощь наиболее удобным способом. Определитесь с тем, какой вид ВНЖ вам подходит больше всего. Компания практикует индивидуальные и персонализированные решения, а потому они точно вам подойдут. Все расценки являются прозрачными, честными, нет скрытых комиссий, а потому вы будете знать, за что платите. Все сотрудники отличаются огромным опытом.
thanks, interesting read
_________________
casino daddy играть
Наши специалисты — это команда профессионалов с многолетним опытом работы в области наркологии и психологии. Каждый сотрудник клиники предан своему делу и искренне заботится о каждом пациенте
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru
В некоторых случаях необходима госпитализация, особенно если запой был длительным и тяжелым. В условиях стационара пациент находится под постоянным наблюдением медицинского персонала, что позволяет контролировать его состояние и своевременно оказывать необходимую помощь. В госпитале проводятся процедуры детоксикации, направленные на выведение токсинов из организма и стабилизацию состояния пациента.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-12.ru
Запой развивается на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости, когда организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола. В отсутствии алкоголя у таких пациентов возникают абстинентные симптомы, включая тревогу, тремор, потливость и тахикардию. Для предотвращения этих неприятных симптомов человек продолжает употреблять алкоголь, что приводит к затяжному запою.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-13.ru
Процесс вывода из запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинскую помощь, психологическую поддержку и социальную реабилитацию. Основные этапы включают детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния пациента и долгосрочную реабилитацию.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-14.ru
выберите ресурсы https://mega555-moriarti.com
Medicine information leaflet. Effects of Drug Abuse.
how to buy esomeprazole without a prescription
Some trends of medicines. Get information now.
сайт автосервис
автосервис рядом на карте
ремонт сто
Познакомьтесь из нашим проф коллективом, яже создаёт чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
ремонт сто
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, яже учреждает уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
дом престарелых московская область
На сайте https://rabota-webcams.ru/ опубликованы объявления, предложения о работе вебкам-моделью. Разные компании приглашают стройных, красивых, подтянутых и интересных девушек, которые смогут эффектно себя показать перед камерой. При этом вы получите за это хорошие деньги. В большинстве агентств деньги выплачиваются сразу и наличными. Перед вами список всех студий, в которые вы сможете обратиться за работой. В них работают настоящие профессионалы, которые при необходимости подскажут и научат всему.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту фототехники в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт вспышек
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Подробнее на сайте сервисного центра remont-vspyshek-realm.ru
Hi there to all, how is the whole thing, I think every one is getting more from this web page, and your views are nice in favor of new visitors.
зеркало РиоБет казино
На сайте https://turisticheskie-palatki.ru/ представлены качественные, функциональные и надежные туристические палатки, созданные из инновационных и современных материалов. Они защитят от сильного, промозглого ветра, невзгод погоды, а также солнца, дождя. Плотный материал не просвечивает, а простой механизм не позволит конструкции сломаться. Туристические палатки компактные, они мобильные, легко помещаются в багажник. Не утратят своего вида долгое время. Напротив каждого изделия содержится краткое описание, которое позволит быстрее определиться с выбором.
Нужна реконструкция деревянного дома? Наша бригада из опытных строителей из Белоруссии готова воплотить ваши идеи в реальность! Современные технологии, индивидуальный подход, и качество – это наши гарантии. Посетите наш сайт реконструкция дома и начните строительство вашего уюта прямо сейчас! #БелорусскаяБригада #Шлифовка #Реконструкция #Достройка
https://rosemetalpress.com/?s=Promo%20Code%20for%20MelBet%20Bangladesh%202024:%20MEGA555%20Free%20Bet%20Bonus
https://nlga.us/?s=Promo%20Code%20for%20MelBet%20Turkey%202024:%20MEGA555%20Welcome%20Bonus%20€100
https://learnomnifocus.com/search/MelBet%20Promo%20Code%20Today%20Bangladesh%202024:%20MEGA555%20Bonus%20100%%20up%20to%20$130
https://www.vedainformatics.com/?s=MelBet%20Promo%20Code%20Today%20Philippines%202024:%20MEGA555%20Welcome%20Bonus%20€100
дома престарелых с психическими отклонениями
Today, I went to the beach front with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to tell someone!
официальный chatgpt
дом престарелых в подмосковье
Выше- магазин НашаМебель предлагает широченный набор кухонь, которые помогут создать уют равным образом благоустроенность в вашем семье http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель предлагает широкий ассортимент кухонь, которые помогут создать устроенность также удобство в течение вашем жилище https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
https://xn--174-eddyne0ahc4c.xn--p1ai/
автосервис на карте
ремонт автосервис
автосервис ремонт
карта автосервис
На сайте http://polifarm-print.ru посмотрите телефон типографии, которая создаст качественную продукцию. Каждый клиент сможет воспользоваться огромным количеством услуг, чтобы получить необходимый результат. Здесь же получится заказать и много коробок самых разных форм, видов, размеров, модификаций. Есть возможность приобрести тару под пончики, пиццу, для косметики, коробки для медицины и многое другое. Типография располагает большим количеством вырубных штампов, что позволит вам выделиться на фоне других.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютероной техники в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: лучшие сервисные центры по ремонту компьютеров
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Drug information. Long-Term Effects.
can i buy cheap macrobid pill
Some trends of medication. Read information now.
Роза Ветров – цветочная мастерская, которая предлагает для вас шикарные цветы. Ассортимент разнообразен, вы обязательно найдете то, что так необходимо. Мы гарантируем, что букеты будут собраны качественно. На обращения реагируем быстро. Готовы помочь вам с выбором и ответить на все вопросы. Ищете купить цветы на дом? Flowersspb.com – здесь есть возможность посмотреть условия оплаты. Вы можете прямо сейчас заказать свежие цветы с быстрой доставкой. Уверены в том, что у вас останутся самые лучшие впечатления от нашего сервиса.
эскорт в туле работа
На сайте https://osushiteli-vozduharf.ru/ представлены осушители воздуха в большом выборе. Все они от лучших, надежных и проверенных марок, которые создают продукцию высокого качества и разработанную в соответствии с ГОСТом, нормативами. И самое важное, что техника отличается долгим сроком службы. Осушители помогут поддерживать правильный уровень влажности, что особенно важно, если в помещении она избыточная. Иначе на стенах появится плесень. Все агрегаты ремонтопригодные. Устройства реализуются по лучшей стоимости.
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели для кухни» занимается образованием и еще продажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки делаем отличное предложение широкий номенклатура продукции, который откликается наиболее теперешним эталонам равным образом направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели для кухни» загорается твореньем и перепродажей качественной кухонной мебели. Наша сестра делаем отличное предложение широкий прибор продукта, который парирует наиболее современным шаблонам а также направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели для кухни» захватывается организацией и перепродажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Я делаем отличное предложение широченный ассортимент продукта, который говорит наиболее современным штампам и направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
ремонт автосервиса
автосервисы на карте
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – это чемодан надежный партнер в течение учреждении кухонных интерьеров. Пишущий эти строки работаем на исследованию, фабрике и аппарате первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, какие соединяют в течение себя язык, работоспособность равно долговечность. Наша послание – предоставить клиентам субъективные ответы, основанные один-два учётом ихний пожеланий и еще надобностей, чтоб каждая кухня влетела приятным и удобным районом для жизни равно творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://mtg-biz.ru/ вы сможете ознакомиться с информацией, которая посвящена электронным очередям и тому, как это удобно в настоящих реалиях. Деятельность компании во многом зависит от квалификации работников и того, как устроено обслуживание, каков сервис. Клиенты не хотят ждать, а стремятся получить результат в минимальное количество времени. Если провести анализ, то он поможет выявить ошибки в обслуживании и сделать его максимально оперативным. При этом необходим регулярный и комплексный мониторинг работников.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в Санкт-петербурге – это ваш фундаментальный партнер в образовании кухонных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся на разработке, изготовлении равным образом установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, какие сочетают в течение себе язык, функциональность и долговечность. Наша миссия – обеспечить клиентам личные ответа, сделанные с учётом ихний пожеланий и потребностей, чтобы всякая кухня таким образом уютным и спокойным местом чтобы существования и еще творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – этто ваш надежный участник в течение сотворении кухонных интерьеров. Автор этих строк работаем сверху разработке, производстве и аппарате высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, которые соединяют в течение себя стиль, работоспособность равным образом долговечность. Наша миссия – предоставить клиентам субъективные решения, основанные немного учётом их пожеланий а также необходимостей, чтобы каждая кухня замерзла приятным а также удобным постом для животе и еще творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
buying generic cipro
my link trustee plus
В нашем интернет-магазине представлены только высококачественные модели, которые прослужат долгие годы.
Женские сумки из натуральной купить недорого
look at this web-site bread wallet app
эскорт самара работа
Кожаная сумка — это классический выбор, который всегда в моде и никогда не теряет своей актуальности.
Интернет магазин женских сумок купить недорого
Выше- интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий сортамент мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость улучите все нужное чтобы формирования приятного (а) также высокофункционального экстерьера https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
https://infosport.ru/partners1/rentgenografia-v-guta-klinik
Свой интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” зовет широкий ассортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы вырвете шиздец нужное для образования уютного также многофункционального внутреннего убранства https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
На нашем сайте Super Sumki 20Vek вы найдете большой выбор качественных рюкзаков и сумок по доступным ценам.
Кросс сумка женская купить недорого 2024
На сайте https://avtomobilnye-derzhateli.ru/ вы найдете качественные, функциональные автомобильные держатели, при помощи которых вы сможете свободно разговаривать по телефону и не нарушать правил ПДД. Они удобные, а потому устройство не выпадет на ходу, сохранит свой вид на долгое время. Конструкции выполнены из современных, прочных и практичных материалов. Все изделия отличаются компактными размерами, скромным весом, поэтому отлично зафиксируют телефон. Устройства представлены различными марками.
содержание https://chl-heli.ru/catalog/vilochnye-pogruzchiki/elektropogruzchiki/
https://logoped18.ru/mir-one/rentgenografiya.php
Процесс вывода из запоя требует комплексного подхода, включающего медицинскую помощь, психологическую поддержку и социальную реабилитацию. Основные этапы включают детоксикацию, стабилизацию состояния пациента и долгосрочную реабилитацию.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru
В некоторых случаях необходима госпитализация, особенно если запой был длительным и тяжелым. В условиях стационара пациент находится под постоянным наблюдением медицинского персонала, что позволяет контролировать его состояние и своевременно оказывать необходимую помощь. В госпитале проводятся процедуры детоксикации, направленные на выведение токсинов из организма и стабилизацию состояния пациента.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-15.ru
Запой развивается на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости, когда организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола. В отсутствии алкоголя у таких пациентов возникают абстинентные симптомы, включая тревогу, тремор, потливость и тахикардию. Для предотвращения этих неприятных симптомов человек продолжает употреблять алкоголь, что приводит к затяжному запою.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru
Наркологический центр — это ваш надежный партнер в борьбе с зависимостью. Мы понимаем, что каждый случай уникален, и делаем все возможное, чтобы вернуть наших пациентов к полноценной и трезвой жизни.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru
Наши специалисты — это команда профессионалов с многолетним опытом работы в области наркологии и психологии. Каждый сотрудник клиники предан своему делу и искренне заботится о каждом пациенте
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru
how to buy cheap starlix no prescription
На сайте https://kondicioneri-hisense.ru/ в огромном ассортименте представлены высокотехнологичные, надежные и совершенные кондиционеры популярной марки Hisense. Они наделены безупречным качеством, имеются гарантии, что подтверждает безупречную работу. Стильный и привлекательный дизайн позволит вписаться устройству в любой интерьер. Все аппараты наделены огромным количеством опций, которые упрощают эксплуатацию устройства, повышают комфорт, создают свой микроклимат. Функции кондиционеров самые разные. Они могут даже обогревать помещение при необходимости.
Познакомьтесь капля нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже учреждает чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Познакомьтесь маленький нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже строит чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы в течение реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
cost generic motrin without a prescription
Познакомьтесь не без; нашим проф коллективом, яже создаёт чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
работа в эскорт услугах водителем в
нажмите, чтобы подробнее комета казино
Chat GPT revolutioniert, wie Unternehmen ihre Kunden betreuen
https://telegra.ph/chat-gpt-an-hochschulen-09-19
Выше магазин НашаМебель предлагает широкий выбор кухонь, что помогут создать уют также комфорт в вашем таунхаусе https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Ich habe durch die Keto-Diat gelernt, viele neue Lebensmittel zu schatzen.
https://telegra.ph/keto-diat-kaufen-09-19-2
Отечественный этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широченный сортамент кухонь, коие помогут сделать уют и удобство в течение вашем обиталище http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
m salah soccer player [url=http://www.mohamed-salah-az.com/]www.mohamed-salah-az.com[/url] fc barcelona messi mohamed salah az com .
Ювелирные изделия высокого класса в Москве на сайте https://agafonovs.ru/ – это большой ассортимент готовых изделий от Мастерской Агафоновых, а в случае, если в наличии не окажется того, что могло бы порадовать ваш вкус, всегда есть возможность разработки украшений, ювелирных подарков и объектов по индивидуальному дизайну на заказ.
Chat GPT ermoglicht es, gro?e Mengen an Daten schnell zu analysieren
https://telegra.ph/seo-schmiede-chat-gpt-09-19
Выше- этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широченный ассортимент кухонь, что помогут сделать уют да комфорт на вашем здании http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Ich hatte nie gedacht, dass ich mich so wohlfuhlen wurde, wenn ich weniger Kohlenhydrate esse.
https://telegra.ph/als-veganer-keto-diat-wie-eiwei?-denken-09-19-2
Keto hat mir geholfen, bewusster auf meine Ernahrung zu achten.
https://telegra.ph/was-darf-ich-bei-keto-diat-essen-09-19
Наша компания «Сайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» обучается учреждением равно реализацией лучшей кухонной мебели. Мы делаем отличное предложение широченный ассортимент продукции, который парирует наиболее прогрессивным трафаретам и еще направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
самара проститутки заказать
Наша юкос «Сайт по мебели чтобы кухни» увлекается образованием а также продажей лучшей кухонной мебели. Мы делаем отличное предложение широкий гарнитур(а) продукции, который соответствует наиболее современным штампам и еще направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
чеки с ндс купить
Am Anfang schmerzen die Finger, aber das geht mit der Zeit vorbei
https://telegra.ph/gitarre-spiele-lernen-09-19
can i purchase zocor without prescription
Наша юкос «Сайт по мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется сотворением а также перепродажей качественной кухонной мебели. Мы предлагаем широченный запас продукции, яже откликается самым современным эталонам (а) также направленностям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Sollet wallet login – Vi sollet, Sollet.io
На сайте https://iz-nerzhaveyki.ru/ вы получите всю необходимую информацию, которая касается гибкой подводки, комплектующих, выполненных из нержавейки, фитингов, шаровых кранов, фланцевых кранов, фильтров, обратных клапанов, арматуры и многого другого. На сайте представлены детали самого разного диаметра, что позволит выбрать решение под определенные запросы и цели. Здесь также указана дополнительная информация о комплектующих, характеристики и что в каких случаях используется.
проекты коттеджей
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – это ваш фундаментальный участник в течение формировании кухонных интерьеров. Наш брат специализируемся сверху разработке, изготовлении равно установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, коим соединяют в течение себе язык, функциональность да долговечность. Наша цель – уделить покупателям личные ответа, образованные раз-два учётом их пожеланий да надобностей, чтобы всякая кухня стала уютным и еще спокойным площадью для бытья а также творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – этто ваш надежный участник на создании кухонных интерьеров. Да мы с тобой специализируемся на разработке, фабрике равно установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, какие сочетают в себе язык, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша назначение – уделить посетителям субъективные ответа, построенные один-другой учётом ихний пожеланий и еще надобностей, чтоб любая кухня стала уютным и удобным местом для бытья равным образом творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
like it coinomi walletAds
Denk je aan de goede oude tijd toen er home buttons en bubble icons waren? Er is een manier om het allemaal terug te brengen en die gevoelens terug te brengen. Een app genaamd OldOS (via the Verge) herstelt iOS 4 naar de nieuwe iPhone. Bijzonderheden https://mashable.com/article/iphone-3g-oldos
Der Einstieg ins Gitarrespielen war einfacher als ich dachte
https://telegra.ph/gitarre-spielen-lernen-puhdys-09-19
Испытай удачу в онлайн-казино! Слоты, фриспины и бонусы ждут всех игроков, готовых к большим выигрышам.
криптобосс официальный сайт вход
helpful hints coinomiAds
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютерных блоков питания в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт блоков питания corsair
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Die Umstellung auf Fett als Hauptenergiequelle ist am Anfang etwas hart, aber es lohnt sich!
https://telegra.ph/keto-diat-oder-low-carb-09-19-2
see page infinitywalletAds
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – это ваш фундаментальный партнер в создании кухонных интерьеров. Наша сестра работаем сверху разработке, фабрике равным образом установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, которые соединяют на себе стиль, работоспособность (а) также долговечность. Наша предназначение – дать посетителям персональные вывода, сделанные с учётом их пожеланий и необходимостей, чтоб любил шакша стало быть приятным также спокойным местом чтобы жизни а также творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
проекты двухэтажных домов и коттеджей
хомут диафрагма – ультрафиолетовый фонарь купить, контрастный грунт
Азарт и победа ждут тебя в онлайн-казино! Получи бонусы и испытай удачу в любимых слотах и играх.
криптобосс промокод при регистрации
магнитная флуоресцентная суспензия – магнитный неразрушающий контроль, проявитель для капиллярного контроля
Друзья, если планируете обновить ванную комнату, советую обратить внимание на один интернет-магазин раковин и ванн. У них действительно большой ассортимент товаров от ведущих производителей. Можно найти всё: от простых моделей до эксклюзивных дизайнерских решений.
Я искал раковина, и они предложили несколько вариантов по хорошей цене. Качество продукции на высоком уровне, всё сертифицировано. Порадовало и то, что они предлагают профессиональные консультации и услуги по установке. Доставка была быстрой, всё пришло в целости и сохранности. Отличный магазин с хорошим сервисом!
пневмоостров – автоматический воздушный клапан, пневмодроссель куплю
хомут диафрагма – гель для ультразвукового контроля, капиллярный метод неразрушающего контроля
תשכח את כל מה שאתה מרגיש כעת, בין אם זו תחושת בדידות, בחיים אשר יכולים לתת לנו סיבה לחיות. אז כאשר החיים לוקחים אתכם למטה, בצפון כאשר תושבי הקריות, או לפחות הגברים שביניהם, רוצים כמה רגעים של שקט ועונג מטורף, הם קופצים על הדיסקרטיות ומעניקות שירות נערות ליווי במרכז
магнитно порошковый метод неразрушающего контроля – дефектоскопист по ультразвуковому контролю, пояс мерительный
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий подбор мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость выкопаете все нужное чтобы сотворения уютного и высокофункционального экстерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Готов к большим выигрышам? В онлайн-казино тебя ждут огромные бонусы и возможность сорвать джекпот.
криптобосс промокод на дополнительные акции hds5
Denk je aan de goede oude tijd toen er home buttons en bubble icons waren? Er is een manier om het allemaal terug te brengen en die gevoelens terug te brengen. Een app genaamd OldOS (via the Verge) herstelt iOS 4 naar de nieuwe iPhone. Ontdek meer – https://mashable.com/article/iphone-3g-oldos
эротическое шоу – ижевск стриптиз клуб, стриптиз в кружевах
дом с мансардой из газобетона – готовые проекты жилых домов, проекты одноэтажных домов
אבל האמת שסקס מזדמן טוב לבריאות שלכם, הנפשית וגם אחת אחרת, על מנת לגוון ולנסות דברים חדשים. ואם כבר מדברים על דברים חדשים, אחר. זוהי הזדמנות להגשים חלומות, לשחרר גברים מקומיים, אנשי עסקים ותיירים המבקרים בתל אביב. זוהי סביבת בילוי נעימה ובטוחה browse around this site
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный комплект мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость найдете все необходимое чтобы создания уютного и высокофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Хочу поделиться своим опытом ремонта телефона в этом сервисном центре. Остался очень доволен качеством работы и скоростью обслуживания. Если ищете надёжное место для ремонта, обратитесь сюда: номер ремонта телефонов.
строительство каркасных домов проекты – построить каркасный дом, лучший кирпич для строительства дома
резка оргстекла в москве – изготовление полимерной продукции, производство изделий из полипропилена
Азарт и удача ждут тебя в онлайн-казино! Слоты, рулетка и блэкджек в любое время дня.
криптобосс автоматы
производство кранового оборудования – краны однобалочные опорные электрические, мостовый кран
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий ассортимент мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость разыщете все необходимое для создания уютного и еще многофункционального интерьера https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://serialexpress.ru вы сможете приобрести интересные, увлекательные телесериалы в огромном количестве и те, что давно полюбились публике. Есть и редкие варианты, которые тоже найдут своего зрителя. В разделе вы найдете и увлекательные мультики, которые понравятся деткам самого разного возраста. Женщины придут в восторг от теленовелл. В большом выборе представлены и документальные фильмы, которые раскроют вам правду, вы узнаете много нового, интересного и содержательного. Регулярное обновление ассортимента.
На сайте https://ok-mebel.com/ вы сможете заказать кухни, гостиные самой разной модификации, конфигурации и цветовой палитры. Также представлены и спальни, а также детские, которые идеально впишутся в любое помещение и интерьер. Воспользуйтесь и вы возможностью приобрести качественную, солидную мебель, выполненную из современных, износостойких материалов. Она функциональная и удобная, а потому подарит только пользу. Также имеется и мебель для офиса, а также шкафы, прихожие и многое другое.
Начни своё приключение в онлайн-казино! Прими участие в игре, получай бонусы и увеличивай свои шансы на выигрыш.
cryptoboss casino бездепозитный бонус hds5
Познакомьтесь раз-два нашим проф коллективом, который созидает чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://kaiser-russia.su вы сможете приобрести качественную, надежную сантехнику Kaiser, которая отличается длительным сроком эксплуатации. Кроме того, она отличается привлекательным дизайном, стильным внешним видом, а потому впишется в любое помещение. В каталоге вы найдете: смесители для ванной, кухни, душевые и многое другое, что обязательно пригодится. Для того чтобы вам было удобно совершать покупки, все товары поделены на категории. Ознакомьтесь с техническими характеристиками, фото.
Познакомьтесь со нашим проф коллективом, который создаёт чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в течение реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Scale up your account and manage MORE!
Regardless of your budget, we suffer with an extraordinary volunteer for you!
Lay down any amount up to $400 and rig out a LARGESSE of 100-120% of your lees amount!
Neck if you don’t have a mammoth amount, you can still spread your deposit and relish in more mirth while playing!
Take a shot it absolute any longer and start playing with leftover funds in your account!
Your winnings are waiting for you!
https://shorturl.at/V1G8d
аккредитация медицинских психологов под ключ
Запой развивается на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости, когда организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола. В отсутствии алкоголя у таких пациентов возникают абстинентные симптомы, включая тревогу, тремор, потливость и тахикардию. Для предотвращения этих неприятных симптомов человек продолжает употреблять алкоголь, что приводит к затяжному запою.
http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-21.ru
Интересные и увлекательные статьи у нас.
https://robertsoncountysource.com/traveling-with-breast-cancer-tips-for-safe-and-enjoyable-summer-vacations
Познакомьтесь маленький нашим проф коллективом, который созидает уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в течение реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Анонимная наркологическая клиника – медицинское учреждение, где оказывают квалифицированную, профессиональную помощь алкоголику, наркоману, курильщику или игроману, который хочет и старается избавиться от зависимости. Основное преимущество анонимного наркологического центра – никто посторонний не будет знать о том, что человек проходит лечение в клинике.
https://medcentr-kristall.ru/kodirovanie/kodirovanie-esperal
Клинические проявления запоя разнообразны и зависят от стадии и тяжести состояния. На начальных этапах наблюдаются симптомы, такие как головные боли, тремор, повышенное потоотделение и тахикардия.
http://xn—-7sbbdtawliczg5ij.xn--p1ai
Интернет-магазин «ЛинкСвар» невероятно популярен. Предоставляем большой выбор аксессуаров, сварочных материалов и принадлежностей. Обеспечиваем самые выгодные цены. Вас ожидают хорошие скидки. С удовольствием поможем вам в выборе необходимого оборудования. Уважаем своих клиентов и к их пожеланиям всегда прислушиваемся. Ищете сварочный полуавтомат helvi unitech 328? Linksvar.com – сайт, где представлены полезные статьи, здесь можно изучить каталог и ознакомиться с условиями оплаты. Все товары прошли сертификацию. Обращайтесь, мы быструю и удобную доставку гарантируем.
Sollet io – Best Solana wallet, Sollet wallet
Hola, my friend! I’m overjoyed that our schedules aligned today.
It appears that engaging with this subject could be insightful Expert doctor electronic health consultations
Auf Wiedersehen, and may your life be a tapestry of happiness
Выше магазин НашаМебель предлагает широкий сортимент кухонь, коим помогут создать уют а также благоустроенность в вашем доме https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
How would you reate my tits?
Sexy gifs/images/videos
<a href=”https://remont-kondicionerov-wik.ru”>сервис кондиционеров</a>
Выше этношоп НашаМебель призывает широченный ассортимент кухонь, кои помогут сделать уют также уют на вашем логове http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель призывает широченный ассортимент кухонь, которые помогут создать уют да удобство в вашем доме https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели для кухни» воспламеняется созданием и реализацией лучшей кашеварной мебели. Наш брат делаем отличное предложение широченный набор продукта, который говорит самым сегодняшним трафаретам и еще тенденциям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
https://mathhelpplanet.com/viewtopic.php?f=19&t=83300
Подробнее [url=https://r7casino.io/]р7 casino[/url]
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели для кухни» занимается организацией также продажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Автор делаем отличное предложение широченный ассортимент продукции, который расплачивается наиболее нынешним шаблонам а также направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Видеонаблюдение может оказаться необходимым в самых разных условиях. Такие системы устанавливаются как в частных домах, так и на производственных площадках, в офисах, гаражах и магазинах. Они обеспечивают безопасность, защищая имущество от краж и вандализма, а также контролируют доступ в охраняемые зоны. Также видеонаблюдение позволяет следить за работой сотрудников, что может повысить их эффективность. Установка камер способствует предотвращению правонарушений и созданию безопасной обстановки.
https://infouborka.ru/stati/montazh-sistem-videonablyudeniya-professionalnaya-ustanovka-i-nastrojka-oborudovaniya-pod-klyuch-v-kaliningrade.html
Наша юкос «Фотосайт числом мебели для кухни» занимается созданием и продажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки предлагаем широкий номенклатура продукции, который отвечает самым сегодняшним стандартам и еще тенденциям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://otparivateli-odejdy.ru/ вы найдете отпариватели одежды, которые помогут вернуть вещам опрятный внешний вид. Устройства можно брать с собой, потому как они наделены компактными и небольшими размерами. В магазине представлены только те варианты, которые созданы проверенными брендами. Устройства надежные, практичные и имеют небольшой вес, привлекательный дизайн. Отпариватели отличаются эргономичной формой, за счет чего их комфортно держать в руке. На приборы действуют привлекательные цены, ассортимент регулярно обновляется.
проститутки самары вип
Хотите узнать, где вызвать девушку легкого поведения в городе Самара? Мы предоставляем топовые шлюхи Самары для наслаждения! У нас всегда надёжные шлюхи с шикарной внешностью и лучшим сервисом. Планируете пригласить девушку на свидание? Обращайтесь к нам, и ваши мечты осуществятся!
Не пропустите возможность встретиться с самыми сексуальными девушками Самары. ??
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный партнер в существе кашеварных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся на разработке, изготовлении а также аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, каковые соединяют в себе стиль, функциональность и долговечность. Наша делегация – вручить посетителям личные резолюции, созданные не без; учётом их пожеланий также потребностей, чтобы каждая шакша замерзла уютным а также спокойным постом для жизни и еще творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Видеонаблюдение необходимо в самых разнообразных условиях. Эти системы можно встретить не только в частных домах, но и на производственных площадках, в офисах, гаражах и магазинах. Они обеспечивают безопасность, защищая имущество от краж и вандализма, а также контролируя доступ в охраняемые зоны. Кроме того, видеонаблюдение позволяет наблюдать за работой сотрудников, что может повысить их продуктивность. Установка камер помогает предотвратить правонарушения и создать безопасную обстановку.
установка видеонаблюдения в Калининграде
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный партнер в существе кашеварных интерьеров. Я специализируемся сверху исследованию, производстве и установке высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, что сочетают в себе стиль, функциональность и долговечность. Наша поручение – предоставить клиентам индивидуальные ответы, учрежденные капля учётом ихний пожеланий а также необходимостей, чтоб любил кухня принялась приятным (а) также спокойным местностью чтобы бытию равным образом творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://all-pump.ru/ ознакомьтесь с каталогом насосного оборудования, промышленных насосов. Всю продукцию вы сможете приобрести прямо сейчас и по лучшим расценкам. А если вы точно знаете, что нужно, то воспользуйтесь каталогом. В строку рекомендуется вбить название того, что ищите, после чего система выдаст вам подходящие под запросы варианты. Вся продукция отличается безупречным качеством, имеются гарантии на нее. Все поставки организуются максимально оперативно. К каждому клиенту индивидуальный подход.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан надежный участник в течение существе кухонных интерьеров. Мы работаем на исследованию, изготовлении равно аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые сочетают в течение себя стиль, функциональность также долговечность. Наша поручение – даровать посетителям личные ответы, основанные из учётом ихний пожеланий да необходимостей, чтобы всякая кухня остановилась уютным и спокойным наделом для века да творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный ассортимент мебели для кухонь. У нас вы вырвете шиздец нужное для формирования уютного также многофункционального интерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Испытай свою удачу на слотах, рулетке и покере! Онлайн-казино дарит бонусы новым игрокам.
cryptoboss casino официальный зеркало
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный ассортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы выкопаете шиздец необходимое для создания уютного и многофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Бонусы, акции и шанс сорвать джекпот — все это ждет тебя в онлайн-казино! Присоединяйся прямо сейчас.
cryptoboss официальное зеркало
ссылка toe omg omg – новые омг, omgomg ссылка
mega darknet onion – мега шоп мориарти, мега даркнет маркет
омг сайт – omgomg зеркало, ссылка на омг
Захватывающие игры, щедрые бонусы и быстрые выводы — всё это в онлайн-казино для тебя!
cryptoboss casino официальный
Начни свой игровой путь в онлайн-казино с бонусами и шансами на большие джекпоты!
игорный клуб криптобосс официальный
mega зеркало тор – мориарти мег, mega магазин мориарти
кракен дарк – kraken даркнет маркетплейс, kraken зеркало
сайт kraken darknet – кракен сайт, https captcha kraken20 at
Стань победителем в онлайн-казино: быстрые выплаты, щедрые бонусы и тысячи игр на выбор.
cryptoboss casino бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию
Отечественный интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный запас мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость найдете все необходимое чтобы создания уютного да функционального интерьера https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Стартуй в онлайн-казино прямо сейчас! Бонусы за регистрацию и возможность выиграть крупный джекпот.
криптобосс бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию
Ощути азарт и адреналин онлайн! Казино с лучшими играми и мгновенным выводом средств.
криптобосс промокод при регистрации
Играй в лучшие игры казино онлайн. Бонусы и высокие шансы на выигрыш каждый день!
криптобосс регистрация cryptoboss casino3 one
Познакомьтесь один-два нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже организовывает уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты на явь https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Познакомьтесь со нашим проф коллективом, яже создаёт чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
ультрафиолетовый фонарь купить – держатель для рентгенпленки, проявитель для капиллярного контроля
Открой для себя лучшие слоты и настольные игры в онлайн-казино. Щедрые бонусы и удобные способы вывода.
cryptoboss casino промокод бездепозитный cryptoboss ru casino
Казино онлайн — это бесконечный мир азарта. Играй в любимые игры и выигрывай на каждом шагу!
cryptoboss casino промокод
Вращай слоты и играй в покер онлайн! Онлайн-казино предлагает мгновенные выводы и бонусы каждому.
cryptoboss casino промокод hds5
Захватывающие игры, щедрые бонусы и быстрые выводы — всё это в онлайн-казино для тебя!
криптобосс промокод при регистрации hds5
несущие масла – муфта коллиматор, магнитный контроль
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютероной техники в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: сервисный ремонт компьютеров
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
магнитный контроль – флуоресцентная суспензия, набор для капиллярного контроля
Свой этношоп НашаМебель призывает широкий сортамент кухонь, тот или другой посодействуют сделать уют также комфорт на вашем здании http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Хочешь почувствовать азарт без выхода из дома? Онлайн-казино с огромным выбором игр — это твой шанс на успех!
криптобосс автоматы
Захватывающие игры и огромные джекпоты в онлайн-казино! Начни выигрывать прямо сейчас.
cryptoboss casino игровые автоматы
большое спасибо
_________________
букмекерская контора что такое вилки в ставках
Ощути вкус азарта с тысячами игр в онлайн-казино! Присоединяйся и выигрывай!
криптобосс игровые автоматы на деньги
Наш магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный сортимент кухонь, какие посодействуют создать устроенность равным образом удобство в течение вашем жилище https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Скучно? Попробуй онлайн-казино! Бесплатные бонусы и шансы на реальные выигрыши каждый день.
игровые автоматы криптобосс
Окунись в мир игровых автоматов и рулетки! Онлайн-казино с реальными выигрышами для каждого.
cryptoboss бонус
Онлайн-казино открывает двери в мир азарта. Играй и побеждай с первого депозита!
cryptoboss casino бонус
A new dating site with wealthy ladies.https://qrcd.org/6jg2
Онлайн-казино — это твой шанс на крупные выигрыши! Играй и получай бонусы за каждый депозит.
cryptoboss промокод на бездепозитный бонус
Онлайн-казино: твой шанс на крупные выигрыши и ежедневные бонусы. Начни прямо сейчас!
cryptoboss бездепозитный бонус
Выше этношоп НашаМебель предлагает широкий подбор кухонь, что посодействуют сделать уют равно удобства в течение вашем доме http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели для кухни» занимается формированием да перепродажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Наша сестра предлагаем широченный гарнитур(а) продукции, яже говорит самым современным шаблонам и направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте http://www.inner-moscow.ru вы сможете приобрести все, что необходимо, включая: валы, зубчатые рейки, корпусы подшипников, подшипниковые узлы, ступицы, смазки. Всем желающим доступны такие услуги, как: изготовление по чертежам, производство под заказ, экспресс-доставка из Китая. Вся продукция отличается долгим сроком службы, безупречным качеством. На нее имеются гарантии, обойдется по привлекательной стоимости. Если ищите что-то определенное, то воспользуйтесь поиском. Он автоматически подберет нужное.
Наша юкос «Сайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» увлекается тварью и продажей лучшей кухонной мебели. Автор предлагаем широченный комплект продукции, яже говорит наиболее сегодняшним стандартам также направленностям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте https://sak-travel.kz/ вы сможете сыграть в Олимп Казино, сделать ставки. На портале организован максимально простой и полностью безопасный игровой процесс. Принимайте участие в ставках, чтобы выиграть как можно больше денег на свои нужды. Здесь всегда все по-честному, а потому вы получите ровно столько, сколько и выиграли, без задержек. Важным моментом является то, что вы сможете воспользоваться и демо-версией, если просто хотите научиться играть. Любой новый клиент сможет воспользоваться приветственным бонусом.
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается основанием да реализацией лучшей кашеварной мебели. Наша сестра делаем отличное предложение широченный выбор продукции, который расплачивается самым сегодняшним эталонам и направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный партнер на создании кашеварных интерьеров. Я специализируемся на исследованию, изготовлении и установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, каковые соединяют на себе стиль, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша послание – предоставить клиентам субъективные заключения, созданные с учётом их пожеланий равно надобностей, чтоб каждая шакша влетела уютным также спокойным площадью чтобы жизни равно творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – это ваш фундаментальный участник в течение создании кухонных интерьеров. Ты да я специализируемся на исследованию, изготовлении а также установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, коие сочетают на себе язык, работоспособность а также долговечность. Наша поручение – предоставить клиентам индивидуальные заключения, организованные из учётом их пожеланий а также надобностей, чтобы любая шакша остановилась приятным а также удобным наделом чтобы бытию равным образом творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://mvpol.ru/ оформите заказ для того, чтобы заказать производство промышленных полов. Компания создает наливные полы для склада, бетонные полы, прочные, надежные полы для парковок, автосервисов. Со всем ассортиментом ознакомьтесь на официальном портале. Здесь у вас получится воспользоваться полным комплексом услуг высокого качества. Все полы выполнены из качественных, надежных материалов, наделенных безупречными эксплуатационными сроками. Основной приоритет компании – бережное отношение к своим клиентам.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту фото техники от зеркальных до цифровых фотоаппаратов.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт проекторов москва
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
ссылка на сайт https://pinup-play-game.space/ru/stormy-witch-witch-themed-crash-game-with-a-potential-x10000-win-multiplier/
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту камер видео наблюдения по Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт систем видеонаблюдения
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
перенаправляется сюда https://1win-play-game.space/1win-october-pub/
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный участник на создании кухонных интерьеров. Да мы с тобой специализируемся на исследованию, производстве равно установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, коим соединяют в течение себя стиль, работоспособность равным образом долговечность. Наша делегация – предоставить посетителям индивидуальные ответа, построенные не без; учётом ихний пожеланий равно надобностей, чтоб любая шакша застопорилась уютным и удобным постом чтобы существования (а) также творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
продолжить https://onlinecrashgame.space/golfing-glory/
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” зовет широченный гарнитур(а) мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы нападете все нужное чтобы создания приятного и еще высокофункционального экстерьера https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Hello
Advanced Cyber Intrusion
Specializing in advanced cyber intrusion services for websites, accounts, and devices. I operate with efficiency and secrecy, ensuring completion within a day.
https://www.techspot.com/news/59433-hire-digital-mercenary-minutes-hacker-list.html
From personal experience, it’s evident that even a basic email opening necessitates proficiency in diverse areas:
The use of a program to hack Facebook or Whatsapp is a time-intensive process and isn’t universally effective.
When encountering user inactivity, exploring server vulnerabilities and accessing the database becomes crucial.
Frequently, exploiting the lesser-protected secondary profile of the victim provides a smoother route to the desired primary profile.
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Hacker to hire[/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Rent a hacker[/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Professional hacker service [/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Hire a professional hacker[/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Hacker service[/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Find a hacker [/url]
[url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/13/business/dealbook/owner-of-anonymous-hackers-for-hire-site-steps-forward.html?searchResultPosition=1]Hacker for hire[/url]
Bro!
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широкий набор мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость откопаете все необходимое чтобы тварей уютного а также многофункционального интерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
What it pays for
Determining the Cause of Engine Failure
How to protect your home from tree damage
can you file an insurance claim for a blown engine
We reduce industry jargon so you get the clearest form of information possible.
Is it cheaper to rebuild or replace an engine?
There are more than 16,000 new car dealerships scattered across the country at this time. And almost all of them are willing to do just about anything to attract people to their lots.
Depending on when and how the damage occurred, a hydrolocked engine may or may not be covered by your comprehensive insurance policy.
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, яже создаёт уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты на явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Познакомьтесь маленький нашим проф коллективом, который формирует чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания в течение явь https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Хотите букеты невесты приобрести в Москве с оперативной доставкой? Интернет-магазин «Флорион» предоставляет такую возможность. Предлагаем широкий ассортимент стильных композиций. Можно просмотреть ассортимент, внимательно изучить каждый букет, сравнить стоимость и выбрать подходящий вариант, не покидая своего дома. Ищете букеты невесты купить? Florion.ru/catalog/svadebnye-bukety – портал, где можно для свадьбы заказать лучшие украшения. Букеты профессиональными флористами создаются. Гарантируется свежесть и качество цветов. Обращайтесь к нам!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры по ремонту техники в нижнем новгороде
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Наш магазин НашаМебель зовет широкий ассортимент кухонь, которые помогут создать уют (а) также удобство в течение вашем доме http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Выше- этношоп НашаМебель призывает широченный комплект кухонь, какие посодействуют сделать уют и благоустроенность в течение вашем доме https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте https://elektrogrili-dlya-doma.ru/ вы найдете электрогриль в огромном ассортименте и по доступным ценам. Все устройства функциональные, качественные, отлично работают, а потому приготовят вкусную, ароматную и полезную пищу. Это оптимальное решение для того, кто обожают жареное и сочное мясо, но не хочет ехать на природу или не имеет на это возможности. Такое устройство поместится на каждой кухне, даже небольшой. Электрогрили выполнены из качественных материалов, которые не воспламеняются, являются износоустойчивыми.
click this site https://onlinecrashgame.space/en/deep-rush/
see post https://pinup-play-game.space/football-manager-crash-game-football-manager-with-a-potential-win-multiplier-of-x1000/
Наша юкос «Сайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» занимается произведением да реализацией качественной кашеварной мебели. Автор делаем отличное предложение широкий асортимент продукции, который отвечает наиболее современным шаблонам а также направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Наша компания «Сайт числом мебели для кухни» занимается образованием да реализацией качественной кашеварной мебели. Мы делаем отличное предложение широченный гарнитура продукта, который отвечает самым сегодняшним образцам да направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
https://guruhitech.com/bypassing-censorship-how-proxy-vpns-empower-free-speech-online/
Петровский Тракторный Завод https://tractors-ptz.ru/ это модернизированные Трактора Кировец и Т-150К после капитального ремонта разных модификаций, двигателя ЯМЗ и ТМЗ, навесное оборудование собственного производства, комплекты переоборудования, а так же мы предоставляем услуги по капитальному ремонту тракторов и двигателей ЯМЗ и ТМЗ.
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – этто чемодан фундаментальный участник на творении кашеварных интерьеров. Да мы с тобой специализируемся сверху исследованию, фабрике равно аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые соединяют на себе стиль, функциональность и долговечность. Наша посланничество – обеспечить покупателям индивидуальные заключения, созданные с учётом их пожеланий и надобностей, чтобы каждая кухня застопорилась уютным (а) также удобным местом чтобы существования равно творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш надежный партнер в течение основании кухонных интерьеров. Я работаем сверху исследованию, изготовлении также аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, коим соединяют в себя язык, функциональность да долговечность. Наша поручение – обеспечить клиентам индивидуальные ответы, учрежденные капля учётом ихний пожеланий да потребностей, чтобы всякая шакша остановилась уютным и удобным районом чтобы бытию также творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается твореньем равным образом перепродажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки предлагаем широченный прибор продукции, который соответствует самым прогрессивным стандартам также тенденциям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
anonymous https://1win-play-game.space/en/1win-football-freestyler/
Нужна реконструкция деревянного дома? Наша бригада из опытных строителей из Белоруссии готова воплотить ваши идеи в реальность! Современные технологии, индивидуальный подход, и качество – это наши гарантии. Посетите наш сайт реконструкция дома и начните строительство вашего уюта прямо сейчас! #БелорусскаяБригада #Шлифовка #Реконструкция #Достройка
Dating site find your love https://qrcd.org/6jg2
толстые проститутки самара
Хотите узнать, где вызвать девушку легкого поведения в Самаре? У нас есть профессиональные индивидуалки Самары для вашего удовольствия и релакса! У нас всегда надёжные девушки с безупречным внешним видом и безупречным сервисом. Хотите вызвать девушку на вечер? Звоните нам, и ваши мечты осуществятся!
Не теряйте возможность провести время с самыми горячими индивидуалками города Самара.
На сайте https://ruchnye-pylesosy.ru/ находится огромное количество ручных пылесосов, которые вы сможете заказать прямо сейчас и по лучшей стоимости. Все аппараты наделены огромным количеством функций, а потому с их помощью получится произвести тщательную уборку. Пылесосы понравятся всем без исключения, ведь они отлично справляются со своими функциями. Ручные аппараты мобильны, их легко держать в руке и брать с собой, если нужно прибрать на даче, в коттедже либо другой комнате. Устройства представлены популярными марками.
https://telegra.ph/wie-lerne-ich-gitarre-spielen-selber-09-19
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры в перми
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Ламинирование ресниц Мурманск[url=https://vk.com/laminirovanie_resnic_murmansk]Ламинирование ресниц Мурманск [/url]
Отечественный интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный выбор мебели для кухонь. У нас вы посчитаете все необходимое для сотворения уютного (а) также функционального экстерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Выше инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широченный сортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость выкопаете шиздец нужное для тварей приятного и высокофункционального интерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Ищите надежного поставщика комплектующих для производителей пластиковых окон в Казахстане? Посетите https://arsi.kz/ и вы найдете качественную фурнитуру для пластиковых и алюминиевых окон, оконный профиль и подоконники в компании Arsi. 10 лет на рынке, более 600 постоянных клиентов на территории Казахстана. Получите подробную информацию о нас на сайте и объекты с использованием фурнитуры от нашей компании.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан фундаментальный участник в течение образовании кухонных интерьеров. Да мы с тобой работаем сверху исследованию, производстве а также аппарате высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, коим сочетают на себе язык, работоспособность равным образом долговечность. Наша посланничество – предоставить посетителям отдельные заключения, созданные с учётом их пожеланий а также надобностей, чтобы каждая шакша встала приятным равным образом спокойным местом для животу и творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
T.me/s/mcatcasino – проекта Кэт казино телеграм-канал. Здесь найдете много полезной информации. Наша основная цель – это отличный игровой опыт для вас обеспечить. Cat – приличное казино, которое быстрые выплаты предлагает. Выбор игр хороший, все они загружаются быстро. Ищете cat casino зеркало официальный сайт? T.me/s/mcatcasino – тут узнаете, как играть в онлайн-казино Кэт и выигрывать. Вас ждут превосходные бонусные предложения. CAT CASINO – потрясающее, служба поддержки всегда на связи, обслуживание клиентов на высшем уровне. Осознанно играйте и наслаждайтесь каждым мгновением!
На сайте https://utepliteli-teploizolyaciya.ru/ вам предложен каталог теплоизоляционных материалов, которые отличаются высочайшим качеством. Откройте для себя широкий ассортимент теплоизоляционных решений и сделайте шаг к комфортному и экономичному жилью. Чтобы купить у нас продукцию, позвоните нам по телефону либо заполните на сайте форму онлайн-заказа. Предлагаем самые лучшие цены и удобную доставку. Делайте заказы уже сегодня. У нас все качественно и быстро.
https://telegra.ph/e-gitarre-spielen-lernen-powerchords-09-19
Компания «See Real» накопила большой потенциал в сфере наружной рекламы, а также светодиодных технологий. С удовольствием вашу самую смелую идею мы обсудим. Новые горизонты освещения откройте! Ищете освещение бизнес-центров? Iseer.kz/architect – сайт, где можете узнать больше информации, ознакомиться с ней можно в любое удобное время. Яркое событие в «жизни» любого здания – это архитектурная подсветка фасадов. Мы все сделаем, чтобы прекрасный внешний вид получила архитектура города. Узнать стоимость услуги можно по телефону. Отдайте нашей компании свое предпочтение!
На сайте http://allworldcars.ru специально для вас подберут подходящий под ваши запросы автомобиль, который будет полностью соответствовать предпочтениям, требованиям. Компетентные, знающие сотрудники выберут автомобиль из Китая либо Южной Кореи. Доставка из РФ всего за 14 дней. Организуется полное сопровождение, отсутствуют какие-либо скрытые платежи и комиссии. Оказывается вся необходимая помощь с логистикой. Регулярно устраиваются акции, чтобы вы сэкономили на покупке определенного автомобиля.
На сайте https://edu.vdgb.ru/ вы сможете найти любопытные, интересные и познавательные курсы: старт в 1С, программирование в 1С, 1С документооборот, комплексная автоматизация и многое другое. Изучите все имеющиеся онлайн-курсы, которые вы сможете приобрести в любое время. Все они реализуются по привлекательной стоимости, а потому у вас получится заказать все, что необходимо. Видео-курсы представляют собой оптимальный вариант повышения квалификации и получения необходимых знаний. К тому же, сформируется опыт работы.
На сайте https://t.me/s/vavada_zerkalo_sait вы сможете посмотреть рабочее зеркало на сегодняшнюю дату. Оно регулярно обновляется в целях безопасности. Зеркало даст возможность без блокировки и с тем же интерфейсом продолжить игру. Зеркало позволит получить доступ ко всем опциям и возможностям сайта, чтобы вы заработали деньги и получили огромное количество приятных эмоций. Зеркало позволяет получить максимально оперативный доступ к ресурсу. Следите за обновлениями, ведь оно меняется ежедневно.
Гадания | Онлайн https://xn--80aahfv3a1k.xn--80asehdb/ – сайт бесплатных онлайн гаданий! Гадание на картах Таро, Ленорман, цыганских и игральных картах! Гадания на Рунах, Зеркале, Кубиках и Домино! Астрология! Нумерология!
Познакомьтесь с нашим профессиональным коллективом, который формирует чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы на реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Наш инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный собрание мебели для кухонь. У нас ваша милость урвете все необходимое для учреждения уютного также многофункционального интерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
ПринтСервис – ваш надёжный партнёр в мире печати! Мы оказываем заправку картриджей высокого качества в Киеве и Вышгороде.
Наши спецы используют исключительно качественные компоненты для обеспечения наилучшего качества печати. Звоните, для того чтоб наполнить картриджи в Киеве и Вышгороде для того чтоб убедится в эффективности наших услуг! Ваше удовлетворение – наш главный приоритет.
Картриджи заправить Киев – https://printer.org.ua/ru/zapravka-kartridzhej/
На сайте https://tvoybroker.com/ вы найдете самую актуальную, ценную и полезную информацию, которая касается рейтинга брокеров и многого другого. Здесь представлены новости, финансы и обзоры инвестиционных проектов, технологии защиты, а также то, что обязательно вам пригодится. Прямо на этом портале у вас получится осуществить проверку предприятий на предмет обмана. Также находится и список мошеннических компаний. Кроме того, вы сможете задать все интересующие вопросы. Подпишитесь на рассылку писем прямо сейчас.
Топ критериев для выбора компании по утилизации строительного мусора на участке https://kuzrab.ru/partners_news/62/szhiganie-musora/
Aw, this was a really nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to produce a great article… but what can I say… I procrastinate a lot and never seem to get nearly anything done.
kayaking
клининг квартиры цена – [url=https://prostaya-uborka1.ru]http://prostaya-uborka1.ru/[/url]
Свой магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный собрание кухонь, которые помогут создать устроенность также благоустроенность в течение вашем обиталище http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Отечественный магазин НашаМебель приглашает широченный круг кухонь, коим посодействуют сделать устроенность (а) также уют в вашем жилье https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Интернет магазин мебли
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – профи тюмень
Меблі-24
Письменные столы Бровары
На сайте https://time1c.ru/ вы сможете воспользоваться демо 1С или арендой 1С. Кроме того, возможно и удаленное обслуживание. Перед тем, как сделать приобретение, у вас получится протестировать решение в облаке. А решив взять в аренду, вы сможете значительно сэкономить на покупке и дополнительно изучить все функции и возможности сервиса. В компании трудятся исключительно высококлассные, проверенные и надежные сотрудники, которые знают свое дело и выполняют его на профессиональном уровне.
Познакомьтесь маленький нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже создаёт уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечтания на явь https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Запчасти для автобусов
Обжалование решений юрист
мужские кроссовки адидас купить в москве
онлайн школы английского языка отзывы учеников
На сайте https://t.me/s/mcatcasino вы найдете большую коллекцию слотов, карточных игр и с живыми дилерами опции казино. Быстрый процесс регистрации, щедрая бонусная программа создадут для вас неповторимые ощущения от игры. При первом знакомстве казино CAT CASINO предлагает бонусы для новичков, захватывающие турниры и постоянные акции. Тут надежные методы финансовых операций. Саппорт работает круглосуточно. Присоединяйтесь к казино прямо сейчас и докажите всем свое превосходство.
На сайте http://allworldcars.ru заполните поля, чтобы узнать, во сколько вам обойдется автомобиль. После того, как заполните строчки, вам предоставят скидку 5 000 рублей. Компания строго соблюдает все возложенные на нее обязательства, чтобы гарантировать безупречный уровень сервиса. Автомобиль проходит обязательное страхование на всех этапах. Заказывайте автомобили из Китая и Кореи, ведь теперь качественная техника доступна каждому. В обязательном порядке подписывается договор на прозрачных условиях.
Ищите настоящего лидера в торговле бинарными опционами? Зайдите на сайт https://ru.binariumpro.online/ и при регистрации получите бонусы, а также, при необходимости бонусный демо счет. Вы можете управлять сделками с минимальными усилиями и максимальной эффективностью, доступ со всех ваших устройств, простота для начинающих, возможности для профессионалов, инструменты для глубокого анализа и точной торговли. Подробный мануал на сайте. Работайте с профессионалами!
Наша юкос «Сайт числом мебели для кухни» занимается организацией и перепродажей качественной кухонной мебели. Мы предлагаем широкий гарнитур(а) продукции, который расплачивается наиболее теперешним стандартам да направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Наш этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широченный коллекция кухонь, тот или другой помогут сделать устроенность да комфорт в течение вашем фамилии http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://skami-i-lavki.ru/ предлагаем вам купить недорогие скамейки и лавки высокого качества. Скамейки и лавки в ландшафтном дизайне выступают как композиционные элементы, и иногда такие предметы трудно подобрать, чтобы они красоту природы подчеркивали и при этом были многофункциональны и комфортны. Но мы с такой проблемой не знакомы, потому как все изделия выполнены из хорошего материала и качественно. Мастера все особенности и тонкости применения изделий учитывают.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш надежный участник в течение существе кухонных интерьеров. Мы работаем на разработке, фабрике равно установке высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или иной соединяют на себе стиль, функциональность а также долговечность. Наша миссия – дать клиентам отдельные решения, сотворенные из учётом их пожеланий равно надобностей, чтоб всякая кухня стала приятным равным образом спокойным местом для бытию (а) также творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – это чемодан фундаментальный участник на существе кашеварных интерьеров. Пишущий эти строки работаем на исследованию, производстве и установке высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, какие сочетают на себя стиль, функциональность а также долговечность. Наша задача – вручить посетителям личные резолюции, основанные не без; учётом ихний пожеланий и надобностей, чтобы любил шакша остановилась приятным а также удобным помещением чтобы бытью равным образом творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
T.me/mvavada – проекта Вавада официальный канал. Мы собрали всю необходимую информацию. Мы для вас стараемся! VAVADA казино славится тем, что без проблем выплачивает выигрыши. Отзывчивые менеджеры, отличная бонусная программа, условия отменные. Ищете vavada vip? T.me/mvavada – тут рассказываем, как играть правильно в казино. Casino VAVADA – душевное, каких еще поискать надо. Имеется большое количество игр. Подключены удобные системы платежа для вывода денежных средств. Вавада знает, как привлечь игроков!
На сайте https://t.me/s/igrovye_avtomaty_na_realny_dengi в огромном выборе представлены автоматы, в которые вы сможете сыграть на настоящие деньги. Все они представлены в режиме реального времени. При этом вы сможете получить настоящие деньги и потратить их на то, что необходимо. Воспользуйтесь бесплатной игрой, а для этого даже не нужно регистрироваться. Только для вас бесплатные фриспины, что позволит сыграть без минимальных рисков. А для того чтобы научиться играть, воспользуйтесь демо-версией, которая позволит не потерять средства.
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели для кухни» воспламеняется созданием и реализацией качественной кухонной мебели. Автор предлагаем широченный гарнитура продукта, который дает ответ самым современным трафаретам и еще тенденциям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://dush-tgc.shop вы сможете заказать высокотехнологичные, инновационные душевые ограждения, которые выполнены из закаленного стекла. Вся продукция производится в соответствии с вашими пожеланиями. Перед вами огромный ассортимент интересных вариантов самого разного дизайна, что позволит выбрать вариант в соответствии с целями, предпочтениями. При этом установлены привлекательные расценки, чтобы сделать заказ смогли многие. На всю продукцию есть гарантии. Вы сможете рассчитывать на надежную защиту от влаги.
В ЗАО «Техносвязь» трудится команда квалифицированных специалистов, нацеленная на то, чтобы приносить пользу своим клиентам. Изготавливаем печатные платы на заказ, придавая особое значение долговечности продукции. Гарантируем сжатые сроки и приемлемые цены. Ищете технология печатной платы? Techno-svyaz.ru – сайт, где можете узнать подробную информацию о нас, ознакомиться с ней можно прямо сейчас. Длительные отношения с партнерами – вот главное подтверждение нашей высочайшей квалификации. С удовольствием проконсультируем вас по любым вопросам, обращайтесь.
https://telegra.ph/poryadok-obucheniya-po-ohrane-truda-09-23
Покупка виртуального номера конкретно для привязки к Телеграмм-каналу имеет несколько достоинств, к числу которых относится одноразовый номер для тг
Запой развивается на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости, когда организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола. При отсутствии алкоголя у таких пациентов возникают абстинентные симптомы, включая тревогу, тремор, потливость и тахикардию.
[url=http://reabcentr-narko.ru]вывести человека из запоя на дому[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую медицинскую и социальную проблему, затрагивающую большое количество людей по всему миру. Одним из наиболее выраженных проявлений этой зависимости является запой, который характеризуется длительным и неконтролируемым потреблением алкоголя.
[url=http://alko-konsultaciya.ru/chto-takoe-zapoj]врач выводящий из запоя[/url]
Клинические проявления запоя разнообразны и зависят от стадии и тяжести состояния. На начальных этапах наблюдаются симптомы, такие как головные боли, тремор, повышенное потоотделение и тахикардия.
Узнать подробнее – [url=http://xn—-8sbbpb6asblledv7c.xn--p1ai]клиника выводящая из запоя[/url]
Выше- интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий номенклатура мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы найдете все необходимое для произведения приятного и еще высокофункционального интерьера https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
https://www.milliescentedrocks.com/board/board_topic/2189097/5709035.htm?page=18
custom balloons with inscription helium balloons price
На сайте https://t.me/s/frispiny_za_registraciyu_2024 вы сможете воспользоваться бесплатными фриспинами без регистрации. Перед вами только подборка самых свежих, актуальных и интересных предложений, которыми вы сможете воспользоваться уже сегодня. Фриспины выдаются всем, кто только что прошел регистрацию, а также на крупные праздники. Это возможность сэкономить собственные сбережения и потратить на игру те, что выдала администрация. Здесь вы найдете все, что необходимо, чтобы игра стала яркой, интересной и незабываемой!
AI Essay Writer is a free Chrome extension Ищете ChatGPT Essay Writer? chromewebstore.google.com/detail/ai-essay-writer/blcamfmkmjdbigcliokaebahmolamlfp?hl=en powered by ChatGPT that helps you write essays with a single click. Effortlessly generate well-structured documents in no time. We create tools for great productivity. Make original, structured and consistent content.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан надежный партнер в произведении кашеварных интерьеров. Мы работаем на разработке, изготовлении равно установке высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или иной сочетают в течение себе стиль, работоспособность равным образом долговечность. Наша цель – предоставить покупателям отдельные ответа, созданные начиная с. ant. до учётом их пожеланий и необходимостей, чтоб каждая шакша стало быть уютным равным образом спокойным районом для жизни а также творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Запой возникает из-за хронической алкогольной зависимости. Постоянное употребление алкоголя изменяет работу центральной нервной системы и приводит к физической зависимости. Алкоголь воздействует на нейротрансмиттерные системы мозга, что вызывает зависимость.
[url=http://xn—-7sbbdgsalifolh3ag.xn--p1ai]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую медицинскую и социальную проблему, затрагивающую большое количество людей по всему миру. Одним из наиболее выраженных проявлений этой зависимости является запой, который характеризуется длительным и неконтролируемым потреблением алкоголя.
[url=http://alko-konsultaciya.ru/vrach]врач выводящий из запоя[/url]
Важным компонентом клинической картины запоя является выраженный абстинентный синдром, проявляющийся после прекращения приема алкоголя.
[url=http://xn—-7sbzghhjoftt2h.xn--p1ai]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Запой – это состояние, характеризующееся непрерывным и длительным употреблением алкоголя, приводящим к значительным физиологическим и психологическим нарушениям. В состоянии запоя человек не способен контролировать количество выпитого алкоголя, что приводит к ухудшению его физического состояния, нарушениям в работе внутренних органов и психических расстройствам.
Подробнее – [url=http://narko-zakodirovan.ru]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Прихожая на заказ Бровары
Ремонт сельхоз техники
купить кроссовки найк в москве
Hey, I heard there’s a new platform set to launch, possibly called AFDAS (America’s First Digital Asset Society). Has anyone else come across this? Please send me the link if you have it.
Digital asset platform AFDAS, AFDAS launch, Investments AFDAS
онлайн курсы английского языка начальная школа
https://pobelka.su/ – предлагаем услуги по побелке животноводческих и производственных и складских помещений горячей известью. Работы выполняем быстро и качественно. Так же оказываем услуги по зачистке помещений от грибка и старой извести перед побелкой горячей известью. Услуги по побелке и ремонту крупногабаритных помещений горячей известью, в том числе с добавлением ядохимикатов, колеров.
https://massageivanteevka.ru/ – Массаж Ивантеевка
Познакомьтесь кот нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже учреждает чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты на реальность http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Hey there, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Firefox, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, great blog!
new retro casino регистрация
Ramenbet промокод зеркало
Выше- интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий гарнитур(а) мебели для кухонь. У нас вы урвете шиздец необходимое для создания уютного и еще функционального экстерьера https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
What’s up Dear, are you really visiting this site on a regular basis, if so then you will without doubt get good knowledge.
сайт new retro casino
https://salda.ws/f/topic.php?f=5&t=75962
На сайте https://shemi-otopleniya.ru/ вы сможете ознакомиться с особенностями, нюансами, характеристиками гибкой подводки, которая бывает различного дюйма, размеров. Также представлена информация по поводу того, для чего эти комплектующие используются. Вся продукция выполнена по ГОСТу, соответствует нормативам, что увеличивает эксплуатационные характеристики. При этом изделия точно никогда не покроются коррозией, ведь у них высокая степень износостойкости. На сайте находится вся важная информация, которая будет полезна каждому, кто планирует покупку.
Приобретайте виртуальные и временные номера телефонов для регистрации. Удобный и надежный сервис для получения смс-онлайн. Более 180 стран и тысячи сервисов купить виртуальный номер телеграм
Мебель Бровары
На сайте https://dooby.ru вы найдете предложения о продаже или покупке недвижимости, бытовой техники, различных вещей, которые имеют особую ценность. Для того чтобы выгодно реализовать что-то, необходимо просто заполнить поля, внести подробную информацию о том, что вы продаете. Далее покупатель найдется очень быстро, если вы установите привлекательную стоимость. О том, как передать вещь, договоритесь с покупателем лично. Постоянно на сайте выкладываются новые предложения, которые точно вас заинтересуют.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель призывает широченный комплект кухонь, что посодействуют сделать уют и еще благоустроенность в течение вашем доме http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широченный запас кухонь, кои посодействуют сделать уют и комфорт в течение вашем логове https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
pawno скриптинг
Чемпион казино зеркало
With over two thousand years of history, Saint – Laurent des Arbres invites you to discover its most beautiful features: the fortified Romanesque church, the narrow streets https://www.midilibre.fr/2011/07/22/nicole-rieu-en-concert,359465.php
Познакомьтесь небольшой нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже организовывает чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы в течение реальность https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте kreditbaza.ru собраны оптимальные предложения банков по потребительским кредитам. Ознакомьтесь с продуктами и оформите онлайн-заявку на кредит. О вашем времени мы заботимся. Не скрываем полные условия финансовых продуктов. Ищете моментальный кредит в Краснодаре? Kreditbaza.ru – ресурс, где вы найдете более детальную информацию. Здесь узнаете, как получить кредит в Краснодаре. Мы публикуем статьи, которые помогают лучше разобраться в банковских продуктах и повысить уровень финансовой грамотности. Вас специальные предложения ждут!
Ознакомьтесь с новыми предложениями на https://888starz.today
На сайте https://t.me/s/igry_na_dengi_onlajn_s_vyvodom ознакомьтесь с огромным количеством игр, в которые вы сможете сыграть на настоящие средства. Выигрыш выводится на карту, при этом отсутствует обман. Вы обязательно найдете огромное количество игр, которые вам понравятся своим интересным сюжетом и графикой. А самое важное, что вы действительно сможете заработать хорошие средства на своем умении. Выдаются интересные и любопытные бонусы, которые позволят сделать игру более зрелищной и интересной.
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается твореньем а также перепродажей лучшей кухонной мебели. Ты да я делаем отличное предложение широкий выбор продукта, яже расплачивается наиболее сегодняшним стандартам равно направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша юкос «Сайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» забирается формированием да перепродажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Наша сестра предлагаем широченный круг продукции, яже говорит наиболее современным шаблонам а также тенденциям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте http://polifarm-print.ru уточните всю необходимую информацию, которая касается работы типографии. Здесь вы сможете воспользоваться самыми разными услугами, включая офсетную, цифровую печать, производство коробок, постпечатную обработку и многое другое. Вы сможете ознакомиться с расценками прямо сейчас. Типография отличается безграничными возможностями, качественным и инновационным оборудованием для реализации проектов различной сложности. Применяются исключительно уникальные и инновационные технологии.
Компания АБК предлагает в прокат бытовки. Мы стараемся в сжатые сроки создать лояльные условия для людей. Выбор блок-контейнеров довольно большой. Бытовки отменного качества, стоимость аренды вас устроит. Доставка по Московской области и Москве выполняется. Ищете заказать бытовку? Arendabk.ru – портал, где опубликованы отзывы, посмотрите их уже сегодня. С удовольствием вас проконсультируем и подберем оптимальное решение, которое вашим потребностям соответствует. Вы точно останетесь довольны услугами компании.
На сайте https://paroochistiteli-shop.ru/ вы сможете подобрать пароочистители для домашнего использования или в офис. Они помогут поддержать чистоту в любом помещении. Устройства отличаются функциональностью, простотой использования, высоким качеством. Они созданы первоклассными брендами, которые дают на продукцию гарантии. Устройства отлично справляются с любыми пятнами, независимо от их интенсивности. Нет необходимости использовать чистящие средства, ведь приборы сами по себе работают эффективно. Их дополнительная функция – это дезинфекция предметов интерьера, мебели.
Официальный дилер Chery в Ростове-на-Дону https://chery-don.ru/ это большой выбор моделей и комплектаций автомобилей Chery в наличии. Chery центр на Каширской это полноценный модельный ряд, скидки, специальные предложения и различные акции. Зайдите на сайт и получите свою выгоду!
Zenless Zone Zero выделяется среди многих предложений уникальным подходом к игровому процессу, погружая игроков в интуитивно понятный и захватывающий мир. Игра предлагает завораживающий сюжет, в котором каждый элемент мира имеет значение. Игроки будут исследовать уникальные локации, которые наполняют атмосферу, включая разнообразные архитектурные стили и художественные концепции, что создает у игроков ощущение будто они действительно в другом мире. Выбор персонажей максимально широк и разнообразен, что позволяет каждому пользователю найти именно своего героя, с которым будут связаны как стратегические, так и эмоциональные моменты.
Mobile Legends представляет собой совершенно другую концепцию, сосредоточенную на командной работе и скоростных сражениях. Игра подчеркивает динамику и взаимодействие игроков, требуя от них мгновенных решений. Это великолепная возможность для любителей MOBA, в которой каждое сражение влияет на общее развитие команды. При этом различные уровни сложности и возможности кастомизации персонажей обеспечивают звонкую индивидуальность каждого игрового процесса, предоставляя игрокам возможность формировать свою уникальную стратегию.
Valorant, как народный шутер, сочетает в себе элементы тактики и атлетизма. Здесь акцент делается на умение стрелять и командную работу. Каждый агент обладает уникальными способностями, которые могут кардинально повлиять на ход матча. Эта игра завлекает игроков своей высокой степенью конкуренции и наличием тактических элементов, что позволяет каждому матчу быть совершенно уникальным и незабываемым. Поток обновлений и контента поддерживает интерес к игровому процессу и внушает доверие к разнообразному контенту.
PUBG Mobile известен своей реалистичностью и масштабными сражениями, где игроки могут испытать свои навыки выживания. Игра предлагает уникальные карты и режимы, что создает захватывающую атмосферу. Контент обновляется регулярно, что позволяет поддерживать интерес и увлечённость игроков. Возможность взаимодействия в команде, а также наличие боевой механики, подчеркивает как индивидуальные навыки, так и командный дух.
Honkai Star Rail и Genshin Impact погружают игроков в яркие и проработанные миры, где каждая деталь имеет значение. Эти игры выделяются своей нарративной структурой и захватывающими квестами, а также красивой графикой и редкими персонажами. Прекрасное сочетание RPG-элементов и подвижного сюжета позволяет игрокам глубже погрузиться в мир, исследуя его и открывая новые горизонты.
Каждая из игр обладает своей уникальной атмосферой, уровнем взаимодействия и стилистическими особенностями, делая каждое предложение уникальным и привлекательным для разных типов игроков.
гарантии сайт finargot’а
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – ремонт техники в волгограде
Слотика казино вход зеркало
Отечественный магазин НашаМебель приглашает широченный набор кухонь, тот или другой посодействуют сделать уют и удобство в течение вашем обители https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Medicines prescribing information. Brand names.
can you get generic proscar price
Everything news about medicine. Get information now.
그런가하면 뉴욕변호사사무소의 법무사가 우리나라에서의 절차 역시 그들 진행해 주기 덕에 손님은 대한민국에 갈 욕구도 없으며, 따로 국내의 법무사를 찾을 욕구도 없다. “짧게 바라는 것만 말씀하시면 되고, 나머지는 저희가 남들 처리해 드리겠습니다”라고 이 변호사는 힘주어 전했다.
[url=https://xn--vg1b88qc8c4zh5zv.com/]NY변호사[/url]
L-Glass – компания с многолетним опытом в области широкоформатной печати на стекле. Мы имеем все нужное оборудование. Успешно завершили сотни проектов разного масштаба: от отдельных квартир до крупных общественных зданий. Ищете стеклянные душевые кабины недорого? L-glass.ru – портал, где галерея декорированного стекла для интерьеров и экстерьеров представлена. Посмотреть ее можно уже сегодня. Гарантируем внимательный подход к каждому заказу. Бесплатно проконсультируем по вопросам и с удовольствием возьмемся за ваш проект, обращайтесь к нам.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервисные центры в красноярске
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
На сайте https://fynnews.ru/ почитайте экономические новости, которые будут интересны всем. Есть самые свежие и увлекательные новости на самую разную тему, а потому вы узнаете все, что интересно. В том числе, опубликованы мнения первых лиц государств о текущей обстановке. Только на этом портале представлены самые актуальные, честные новости, созданные настоящими профи. Добавляйте сайт в закладки, чтобы вернуться к нему в случае необходимости. Здесь также описаны и новые схемы мошенничества, то, какие выплаты положены пенсионерам.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – это ваш надежный участник в течение создании кашеварных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся сверху разработке, фабрике равно установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, каковые соединяют в течение себе язык, работоспособность а также долговечность. Наша посланничество – предоставить посетителям отдельные ответы, сделанные с учётом их пожеланий равно потребностей, чтоб всякая шакша стало быть уютным также спокойным местностью для бытие а также творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – это чемодан фундаментальный участник в образовании кухонных интерьеров. Наша сестра работаем на разработке, изготовлении а также установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, которые соединяют в течение себе язык, работоспособность также долговечность. Наша представительство – обеспечить посетителям личные ответы, организованные кот учётом их пожеланий а также необходимостей, чтоб всякая шакша стала приятным а также удобным местом для жизни да творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Перейти на сайт комета казино
здесь https://chl-heli.ru/catalog/richtraki/vysotnye/
Играйте в онлайн-казино, не выходя из дома! Огромный выбор игр и мгновенные выигрыши ждут вас!
лекс казино бонусы
hop over to these guys samourai wallet for iphone
Cast Iron Pipes in Iraq ElitePipe Factory is proud to be one of the leading suppliers of cast iron pipes in Iraq. Our cast iron pipes are manufactured to the highest standards, offering exceptional durability and reliability for various infrastructure projects. Ideal for both water and sewage systems, these pipes are known for their strength and longevity. ElitePipe Factory’s commitment to quality ensures that our cast iron pipes provide optimal performance and resilience, making us a preferred choice for contractors and engineers across the region. For more information about our cast iron pipes, please visit our website at ElitePipe Iraq.
navigate to this site bread wallet
трипскан топ – tripscan tor, tripscan
На сайте https://xn—–6kccjemwevfcqhwuxggufc2pwa.xn--p1ai/ воспользуйтесь ритуальными услугами, которые предлагаются по привлекательной цене. В компании работают первоклассные, опытные и компетентные сотрудники, которые проявят сочувствие, подберут все необходимые услуги и помогут с подготовкой к прощанию с близким человеком. В компании установлены доступные расценки, чтобы воспользоваться услугами смогли все. Здесь также можно приобрести и ритуальные товары, которые представлены в огромном количестве.
На сайте https://photo-cube.ru/ представлено огромное количество товаров для того, чтобы создать красивый, профессиональный контент. В разделе вы найдете микролинзы, штативы, а также фотобоксы, держатели и напольные штативы, которые произведены проверенными марками. По этой причине прослужат очень долго. На всю продукцию даются гарантии. Установлены привлекательные расценки, чтобы осуществить покупку смогли все желающие. Доставка происходит максимально оперативно. Если хотите отыскать что-то определенное, то используйте поиск.
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» вспыхивает сотворением а также перепродажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки делаем отличное предложение широченный ассортимент продукции, яже парирует наиболее сегодняшним стандартам а также тенденциям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
содержание R7 casino зеркало сайта
Casino Locowin en Espana –
casino locowin
На сайте http://prfavto.com получите консультацию абсолютно бесплатно. Проверенная, надежная компания рекомендует воспользоваться такими услугами, которые проводятся на профессиональном уровне, как: строительная экспертиза, экспертиза имущества с целью списания, товароведческая экспертиза, транспортная, таможенная экспертизы и многие другие. Все работы выполняются на высоком профессиональном уровне и в самые ограниченные сроки. Действуют привлекательные расценки. За все время работы огромное количество благодарных клиентов.
Выше- интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный инвентарь мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас вы посчитаете все необходимое для организации приятного да высокофункционального интерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
where can i get advair diskus without insurance
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий ассортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас вы обнаружите шиздец необходимое чтобы основания приятного да функционального экстерьера https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://inquisition.info/ вы найдете самые свежие новости о политике, экономике, преступности, бизнесе и обществе. Для поиска необходимой темы, воспользуйтесь удобным поиском на сайте. Мы предлагаем пользователям простой интерфейс для чтения и просмотра новостей. У нас вы найдете все самое интересное. Вся информация выделяется самым важным и предоставляется читателям в понятном виде. Если вас интересуют какие-либо вопросы, вы можете напрямую по почте связаться с редакцией.
Pin Up – это официальная платформа для ставок на спорт, которая получила лицензию в 2021 году и уже завоевала доверие среди бетторов в Казахстане pin-up-kz.online
Casino Locowin en Espana –
casino locowin espana
Whaddup, new bestie? I’m hella jazzed to kick it with you.
Despite my doubts, I came across a site that competes with your project Scrap Copper wire stripping machine
Goodbye for now
Физические последствия запоя включают повышенное артериальное давление, нарушения сердечного ритма, проблемы с печенью и почками, а также обезвоживание. Психологические последствия выражаются в тревоге, депрессии, галлюцинациях и психозах.
[url=http://narko-zakodirovan1.ru]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
УЗНАТЬ – [url=http://narko-zakodirovan2.ru]быстрый вывод из запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя обычно начинается с детоксикации организма, то есть удаления токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя. Этот процесс может сопровождаться рядом симптомов отмены, таких как тревога, дрожь, повышенная раздражительность, нарушения сна и даже галлюцинации или судороги.
Подробнее – [url=http://zavisim-alko.ru]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан фундаментальный партнер в течение произведении кухонных интерьеров. Автор этих строк специализируемся на разработке, фабрике (а) также аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые соединяют на себе стиль, функциональность равным образом долговечность. Наша миссия – вверить покупателям отдельные ответы, учрежденные один-два учётом ихний пожеланий равно потребностей, чтобы любая шакша застопорилась уютным и спокойным районом чтобы бытия также творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, яже создаёт уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания в течение реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Visite o site https://quotex-entrar.com/ e ganhe US$ 10.000 por uma conta demo para negociação de opções binárias para explorar todos os recursos da plataforma e experimentar todos os benefícios de trabalhar com nossa plataforma. Uma plataforma inovadora para investimentos inteligentes ao seu serviço.
T.me/mvavada – телеграм-канал проекта Вавада, который довольно популярный. Здесь вы отыщите актуальную информацию. Казино Вавада вам очень понравится, убедитесь лично. Здесь огромное разнообразие игр, скучно вам не будет! Ищете vavada бездепозитный бонус? T.me/mvavada – тут только интересное обсуждаем. Ознакомиться с информацией можете в любой момент. За все время работы, проект Вавада показала себя с отличной стороны. Превосходная бонусная программа и различные способы оплаты. Техподдержка также порадует и то, что быстро выводятся выигранные деньги.
На сайте https://vk.com/@promocodi.yandex.market вы найдете огромное количество свежих, актуальных промокодов для покупок на Яндекс Маркете в сентябре. Вы сможете приобрести все, что хотите и по небольшой стоимости. При этом воспользуйтесь возможностью неплохо сэкономить свой бюджет и приобрести все, что нужно. Есть возможность заказать что-то для дома, создания привлекательного интерьера, стильные вещи, которые никого не оставят равнодушным. С промокодом заказывают и косметику, парфюмерию. Воспользуйтесь и вы возможностью сэкономить.
Запой, характеризующийся длительным и неконтролируемым употреблением алкоголя, представляет собой опасное состояние, которое требует немедленного вмешательства.
https://gis-lab.info/forum/memberlist.php?style=1&g=121&sk=m&sd=d&mode=group&start=15550
Попробуйте себя в онлайн-казино! Рулетка, блэкджек и слоты с реальными выигрышами ждут вас на любой платформе.
лекс казино промокод
Medicament information sheet. Short-Term Effects.
where to get cozaar without prescription
All trends of medicine. Get now.
Статьи на различные темы на страницах сайта.
https://wilsoncountysource.com/outdoor-exercise-tips-for-breast-cancer-survivors-this-summer
Интересные статьи на данном сайте.
https://cheathamcountysource.com/traveling-with-breast-cancer-tips-for-safe-and-enjoyable-summer-vacations
Клининговая компания «Простая уборка» оказывает клининговые услуги и выполняет профессиональную уборку квартир, домов, офисов, коммерческих помещений. Если вам нужна мойка окон, химчистка мягкой мебели или другой клининг, звоните по телефону на сайте https://prostaya-uborka2.ru/
На сайте https://t.me/mvavada вы можете погрузиться в атмосферу казино с новыми слотами. Каждый слот – это неповторимое приключение. Для постоянных пользователей у нас есть VIP-программа, получайте привилегии и дополнительные бонусы с Вавада. Чтобы не пропустить эксклюзивные предложения и акции, подписывайтесь на обновления канала. Испытайте удачу уже сегодня в наших слотах. Предлагаем отменное обслуживание клиентов и щедрые бонусы. Играйте на Вавада с мобильного устройства и выигрывайте в любом месте и в любое время.
На сайте https://t.me/s/kometa_cazino_zerkalo вы сможете ознакомиться со всеми подробностями популярного онлайн-заведения «Комета». Здесь публикуются все актуальные и самые последние новости об этом онлайн-заведении. Также есть и промокоды, которые помогут вам существенно сэкономить. Вы сможете получить здесь всю необходимую информацию, которая важна вам. Если устраиваются какие-либо акции, то и в этом случае вы узнаете о них первым, если зайдете на этот канал. Все самое интересное, новое и актуальное публикуется именно здесь.
На сайте http://vitaminium.shop представлены эффективные, качественные витаминные комплексы, БАДы, минералы, которые принесут пользу. Есть витамины как для женщин, так и мужчин, которые помогут поддержать здоровье, улучшить состояние внутренних органов. Они подарят бодрость, энергию, тонус, отличное настроение. В разделе вы найдете и средства от кашля, для лечения болей в горле. Важным моментом является то, что все препараты абсолютно безопасные, а потому подарят лишь пользу. Все они реализуются по привлекательной стоимости.
Статьи на различные темы на страницах сайта.
https://robertsoncountysource.com/the-importance-of-hydration-for-breast-cancer-patients-during-hot-summer-months
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” зовет широченный номенклатура мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы нападете все нужное для создания приятного и еще функционального интерьера https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Домино33 – компания, которая осуществляет во Владимире качественные ремонты квартир. Бригада грамотных специалистов использует исключительно надежные отделочные материалы. Мы пожелания заказчиков всегда учитываем. Гарантируем быструю и качественную работу. Обращайтесь к нам и точно не пожалеете. Ищете предчистовая отделка квартир? Domino-33.ru – сайт, где можно детально ознакомиться с отзывами довольных клиентов. Получите по телефону бесплатную консультацию. Предлагаем самые выгодные условия сотрудничества. Готовы воплотить ваш ремонт в жизнь!
Интересные статьи на данном сайте.
https://rutherfordsource.com/outdoor-exercise-tips-for-breast-cancer-survivors-this-summer
Онлайн-казино открывает двери к большому количеству игр. Воспользуйтесь приветственными бонусами и начните играть сейчас!
зеркало casino lex официальное рабочее
Свой магазин НашаМебель призывает широкий ассортимент кухонь, кои помогут сделать устроенность и благоустроенность в течение вашем фамилии http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Как вам новый дедпул? https://xn—-btbkfl8ef.xn--p1ai/
На сайте http://ctgroup.kz вам предлагают по доступным ценам современное обучение. Образовательные программы рассчитаны на детей и взрослых с разным уровнем знаний языка. Преподаватели имеют большой опыт педагогической деятельности, поэтому учить язык с нами – это удобно и легко. Запишитесь на курсы уже сегодня. Заполните на языковое обучение форму и получите доступ к компетентным преподавателям и гарантированным результатам. На портале вы можете пройти онлайн-тестирование, которое дает возможность ваш уровень навыков определить.
Статьи на различные темы на страницах сайта.
https://fitnesshealthyoga.com/outdoor-exercise-tips-for-breast-cancer-survivors-this-summer-fitness-tips-of-the-day
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту парогенераторов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт парогенераторов москва
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Интересные статьи на данном сайте.
https://rutherfordsource.com/traveling-with-breast-cancer-tips-for-safe-and-enjoyable-summer-vacations
Pretty little village of the Gard, it is located 20 minutes from Avignon or Orange – Saint Laurent des Arbres is a typical village of the Gard Rhodanien in Provence. https://forum.saintlaurentdesarbres.com/en/infos-techniques
Дезинфекция квартиры от червей и мух одинокого умершего https://dezinfekciya-ot-smerti-msk.ru/
Medicament information leaflet. What side effects?
buying verapamil price
Best about medicines. Read here.
Познакомьтесь начиная с. ant. до нашим профессиональным коллективом, который творит чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NntCT5Wllvo/
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается созданием и перепродажей лучшей кухонной мебели. Наша сестра делаем отличное предложение широченный гарнитура продукции, который отвечает самым сегодняшним шаблонам и направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Наша юкос «Сайт по мебели чтобы кухни» загорается сотворением а также реализацией лучшей кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки делаем отличное предложение широченный круг продукции, который парирует самым сегодняшним эталонам а также направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Thank you for the good writeup. It actually was a amusement account it. Glance complicated to more delivered agreeable from you! By the way, how can we keep up a correspondence?
https://www.juntadeandalucia.es/averroes/centros-tic/14700626/helvia/bitacora/index.cgi?wIdPub=36
На сайте https://svoy-v-alfe.space пройдите регистрацию для того, чтобы воспользоваться партнерским проектом от Альфа-банка. Теперь каждый желающий получает возможность заработать, если будет рекомендовать возможности и продукты финансового учреждения друзьям, коллегам, знакомым. Банк предоставляет огромное количество возможностей для того, чтобы вы смогли заработать и расширить свои опции. Кроме того, получится расширить свой уровень знаний, кругозор. Начните свой бизнес под контролем наставника.
This allows you to maintain privacy and security, creating many opportunities for comfortable and safe communication https://voblakah.com/news/714-virtualnye-nomera-dlya-telegram
If you are looking for an alternative way to set up a new messaging app, WhatsApp, Signal, Line, Telegram or any other service that uses a mobile phone number https://wasp.kz/print.php?type=A&item_id=1958
центре “Остеодок” мы предлагаем услуги классического массажа спины, который подойдет как для профилактики, так и для лечения различных заболеваний. Классический массаж спины помогает снять напряжение, улучшить кровообращение и
Лечебный массаж спины Ростов
дезинфекция квартиры после смерти человека https://dezinfekciya-ot-smerti-msk.ru/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NntCT5Wllvo/
Наш этношоп НашаМебель предлагает широченный гарнитур кухонь, коие помогут создать устроенность равно удобства в вашем обиталище http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан надежный партнер в твари кашеварных интерьеров. Да мы с тобой работаем на исследованию, производстве равно аппарате первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, тот или иной сочетают в себя стиль, работоспособность равно долговечность. Наша посланничество – предоставить посетителям персональные вывода, разработанные с учётом их пожеланий а также необходимостей, чтоб любил кухня стало быть приятным и удобным местностью для бытья и творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
http://gribakov.com/news/advokat-gribakov-as-v-zhurnale-kriminal-i-nedvizhi
Medication information. Drug Class.
can i purchase cheap tamoxifen without insurance
Actual news about pills. Get here.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – это ваш надежный партнер на существе кухонных интерьеров. Пишущий эти строки работаем сверху разработке, фабрике и еще аппарате первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, какие сочетают на себя язык, функциональность равным образом долговечность. Наша миссия – отдать клиентам личные резолюции, сформированные не без; учётом ихний пожеланий а также потребностей, чтобы любил кухня замерзла приятным а также удобным помещением для жизни равным образом творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://teploeosteklenie.ru/ оставьте заявку для того, чтобы воспользоваться такой важной и нужной услугой, как замена холодного остекления на теплое. Важным моментом является то, что отсутствует необходимость изменять фасад. Здесь также вы сможете заказать и зимний сад. Для того чтобы ознакомиться с расценками именно вашего проекта, оставьте заявку на сайте. Менеджер произведет расчеты, после чего передаст вам для ознакомления. Для всех клиентов доступна такая услуга, как выезд замерщика.
защитить конструкции от воздействия влаги. Мембраны Дельта обеспечивают надежную защиту и долговечность, благодаря чему вы можете быть уверены в качестве своих строительных решений. На delta-msk.ru вы найдете дренажные мембраны и
Утеплитель
Авокадо FM предлагает всем слушателям большое разнообразие музыкальных стилей и жанров. Радио дарит хорошее настроение и не оставит вас равнодушным. Вы сможете открыть для себя новые группы и исполнителей, а также насладиться современными треками. От рабочего графика скорее отдохните. Исследуйте музыкальные направления, которые для вас раньше не были известны. Ищете русское радио онлайн слушать? Avocado-fm.ru – здесь каждый найдет что-то для себя. Погрузитесь уже сейчас в великолепный мир мелодий. Гарантируем великолепное качество звука. Откройте музыкальное путешествие для себя!
опорно-двигательным аппаратом, устраняя болевые синдромы и восстанавливая функции организма. Проблемы, с которыми мы часто сталкиваемся, включают боли в спине, головные боли, а также травмы и заболевания суставов. Мануальная
Классический массаж спины Ростов
[url=https://usa.alt.com]alt.com[/url]
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный сортимент мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость найдете все необходимое для учреждения приятного также функционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется учреждением равно продажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Наш брат делаем отличное предложение широкий гарнитура продукта, который парирует самым теперешним стереотипам и еще тенденциям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” зовет широченный инвентарь мебели для кухонь. У нас вы посчитаете шиздец необходимое чтобы сотворения уютного да многофункционального экстерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Тайвек позволяет избежать образования конденсата внутри конструкций, что помогает предотвратить повреждение утеплителей и других материалов. На delta-msk.ru вы найдете Тайвек и другие материалы для защиты вашего дома от
Герметик для мембран
can you buy cheap zetia without dr prescription
Интернет-магазин «Body-pit» предлагает купить высококачественное спортивное питание по оптимальным ценам. Мы стремимся обеспечить своих клиентов наилучшим сервисом. Сориентируем по вкусам, из ваших предпочтений исходя. Ищете казеиновый протеин купить? Ufa2.body-pit.ru – сайт, где у вас есть возможность об условиях оплаты узнать. Здесь представлены отзывы, можно ознакомиться с ними в любое удобное время. С удовольствием предложим вам грамотную помощь по выбору товаров. Выполняем быструю доставку спортпита. Вы точно не пожалеете, если к нам обратитесь!
JAECOO официальный дилер в Москве, купить автомобиль в автосалоне Jaecoo https://jaecoo-avtoport.ru/ – на сайте представлен полноценный модельный ряд в наличии. Уникальные условия приобретения, выгодные цены. Автохолдинг АВТОПОРТ – официальный дилер JAECOO.
На сайте https://t.me/s/igrovye_avtomaty_s_vyvodom_kartu вы найдете в огромном выборе игровые автоматы, которые предлагают получить реальные средства, чтобы потратить их на свои цели. Средства выводятся на любую карту. Специально для клиентов лучшие автоматы, которые работают в режиме реального времени. При этом у вас получится максимально оперативно и безопасно вывести весь выигрыш. Наслаждайтесь игрой и получайте средства максимально оперативно. Имеются слоты с максимально оперативным выводом средств.
loli
==> xzy.cz/2333 wts.la/wfelq <==
На сайте https://kino.tartugi.net вы найдете огромное количество любопытных и интересных фильмов, которые точно вам понравятся необычной актерской игрой, креативной постановкой. Есть как триллеры, так и драмы, мелодрамы, сериалы и все то, что поможет провести время с пользой для себя. Все фильмы в отличном качестве, с хорошим звуком. В них играют популярные и любимые многими актеры. Нет необходимости скачивать серию, ведь вы сможете посмотреть ее в режиме реального времени. Для этого используется комфортный плеер.
улучшить кровообращение, снять мышечное напряжение и ускорить процессы восстановления. Этот массаж подходит для людей с различными заболеваниями и состояниями, а также для профилактики. Наши специалисты тщательно подходят к
Остеопат Ростов
На сайте https://iz-medi.ru/ представлены фитинги, шаровые краны из нержавейки, РВД, гибкие подводки, трубы, многофункциональные рукава высокого давления. Ознакомьтесь с категориями товаров, которые выполнены из нержавейки. Для того чтобы лучше сориентироваться по каталогу, используйте специальный поиск. На сайте находится вся необходимая информация, которая станет решающей в выборе. На всю продукцию установлены доступные расценки. Ассортимент товаров постоянно расширяется. Все товары доставляются с быстрой доставкой.
Познакомьтесь небольшой нашим проф коллективом, яже созидает чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в реальность https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в Санкт-петербурге – это ваш надежный участник на существе кашеварных интерьеров. Наша сестра специализируемся сверху разработке, фабрике равным образом аппарате первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или иной сочетают в течение себя язык, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша роль – передать покупателям субъективные ответы, сотворенные с учётом их пожеланий а также необходимостей, чтобы любая шакша стало быть приятным и удобным местом чтобы бытие и творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Познакомьтесь всего нашим проф коллективом, который учреждает чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания на явь http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте https://t.me/s/Casino_x_m у вас есть возможность найти много настольных игр, слотов, а также живое казино с реальными дилерами. Простая навигация и удобный интерфейс делают игру приятной и комфортной, убедитесь в этом сами. Casino-X – это новейшее онлайн-казино, которое предлагает большой выбор игр от ведущих разработчиков. Окунитесь в мир азартных игр! Казино радует своих игроков выгодными акциями, бонусами и программой лояльности. Честность игр и безопасность данных – вот основные приоритеты этого казино.
Смотреть здесь https://chl-heli.ru/catalog/richtraki/
Visite el sitio web https://qxinfo.co/ y obtenga $10,000 para una cuenta de demostración para el comercio de opciones binarias para explorar todas las capacidades de la plataforma y experimentar todos los beneficios de trabajar con nuestra plataforma. Una plataforma innovadora para inversiones inteligentes. Quotex Colombia – Llevamos las opciones binarias al siguiente nivel.
delta-msk.ru и обеспечьте долговечность своих строительных объектов. Правильный выбор мембраны для кровли обеспечивает защиту от влаги и продлевает срок службы крыши. Мембраны Дельта подходят для различных типов кровель,
Скотч дельта
click here for more info brd wallet
На сайте http://www.tribal-tattoo.ru ознакомьтесь с телефоном популярного тату-салона «Tribal Tattoo», где работают настоящие профессионалы, которые смогут создать рисунок любой сложности и в самой разной цветовой гамме. Стоимость зависит от особенностей изображения, а также размеров картинки. Мастера смогут притворить в жизнь любые ваши идеи, чтобы вы остались довольны результатом. Татуировка может быть выполнена на любом участке тела. Используются только одноразовые инструменты и те, что прошли дезинфекцию, поэтому все манипуляции полностью безопасны.
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – выездной ремонт бытовой техники в уфе
go samourai crypto wallet
Лечение алкоголизма и наркомании – длительный и сложный процесс, в котором принимают участие врачи узких профилей и близкие зависимых. Собираясь привлечь к выздоровлению наркологическую клинику, больной должен осознать, что его состояние – заболевание, требующее серьезного медицинского подхода.
Подробнее – [url=https://ens-narkologia.ru/programmy-lecheniya/psihiatriya/lechenie-anoreksii]Лечение анорексии[/url]
Избавьтесь от алкоголизма с помощью эффективного и безопасного метода кодирования. Наша медицинская услуга предназначена для тех, кто стремится к здоровому образу жизни и желает вернуться к полноценной жизни без зависимости.
[url=https://nn.clinica-plus.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/kodirovanie]Кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Самым эффективным способом бросить пить является кодирование от алкоголизма. Оно представляет собой комплекс мер по «перепрограммированию» организма на трезвый образ жизни. Может происходить как на физиологическом, так и на психологическом уровне, проводится исключительно профильными специалистами.
Подробнее узнать – [url=https://kurovskoe.clinica-plus.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/kodirovanie]Кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
На сайте https://domashnie-koptilni.ru/ в большом ассортименте находятся домашние коптильни. Они созданы для приготовления вкусной, ароматной пищи, в которой не будет вредных ароматизаторов, красителей. Коптильни предназначены для того, чтобы обработать продукт горячим либо холодным дымом. Коптильня сможет приготовить курицу, рыбу холодного либо горячего копчения, копченые ребрышки либо сало, домашние сосиски, сыр, балыки. Современные материалы позволяют увеличить срок службы устройств.
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный сортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость откопаете шиздец необходимое чтобы тварей приятного (а) также многофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Наш этношоп НашаМебель предлагает широченный комплект кухонь, которые посодействуют сделать уют и уют в течение вашем здании http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Medicament information leaflet. Drug Class.
can i buy generic prevacid online
Some news about medicament. Get information now.
https tripscan – tripscan tor, tripscan tor
Нарколог на дом – это выездная медицинская услуга в Ростове-на-Дону. Врач приезжает на дом и может снять ломку, запой, интоксикациию, похмелье и др. Помощь оказывается круглосуточно, анонимно и быстро.
Подробнее – [url=https://ufa.narko-trezvost.ru/uslugi/vyzov-narkologa]Вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Помощь врача в домашних условиях – это наиболее удобный способ быстро получить медицинскую помощь в комфортных для человека условиях.
[url=https://lytkarino.narko-trezvost.ru/uslugi/vyzov-narkologa]Вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
здесь р7 казино
https://realtai.ru/forum/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=119638
Стационар наркологической клиники очень комфортный для проживания и лечения. Каждая палата оснащена современной мебелью, включая удобные кровати и функциональные шкафы для личных вещей, обеспечивая чувство уюта и приватности.
Подробнее – [url=https://istra.zapoy-clinic.ru]Анонимная наркология[/url]
Новая нейросеть Яндекса YandexGPT 2 уже в приложении Яндекс. YandexGPT помогает придумывать идеи, тексты на разные темы и многое другое гигачат купить
https://eventmoon.ru/
На сайте https://t.me/s/azino777_a вас ждет огромный выбор игровых автоматов, игр с реальными дилерами и карточных развлечений. AZINO CASINO – это для ценителей онлайн-игр на удачу верховное место. Быстрая регистрация, щедрые бонусы и простота в применении интерфейса, сделает ваш игровой процесс еще более интересным и продуктивным. Здесь проходят постоянные турниры и акции. Методы выполнения платежей надежные. Поддержка пользователей круглосуточная. Будьте уже сегодня частью AZINO CASINO!
https://www.terrapevtika.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=message&FID=1&TID=910&TITLE_SEO=910-aktualnye-anonsy-i-obzory-serverov-lineage-2&MID=1176&result=new#message1176
Наша компания «Сайт числом мебели для кухни» загорается образованием да перепродажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Автор предлагаем широченный ассортимент продукта, который расплачивается самым сегодняшним шаблонам и тенденциям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
перенаправляется сюда комета казино зеркало
Полный топ-Казино сайтов: нажмите здесь, чтобы получить бесплатный доступ к списку лучших Казино сайтов мира sykaaa зеркало
Компания «AXIONT» за 14 лет реализовала больше 80 проектов на платформе «1С:ERP Предприятие 8». Знаем, как повысить прибыльность бизнеса. Ценим всех своих клиентов, по статистике, большинство по рекомендациям к нам приходят. Сделаем все, чтобы нас вы тоже советовали. https://v8erp.ru – сайт, где у вас есть возможность прямо сегодня оставить заявку и посмотреть примеры наших решений. Помогаем внутри предприятия автоматизировать процессы. Если у вас возникли какие-либо вопросы, позвоните нам. Ждем ваших обращений, мы на связи всегда!
Drug prescribing information. Long-Term Effects.
how to buy warfarin price
Some news about drugs. Get information here.
На сайте https://fast-finans.ru/ получите деньги на развитие бизнеса. Это возможность выполнить быстрое пополнение оборотных средств. К важным достоинствам бизнес-кредита относят то, что он отличается гибкими условиями погашения, незначительной процентной ставкой, а также быстрым одобрением. При этом у вас получится потратить кредитные средства уже сразу же после получения, приобрести все, что нужно. Это доступно за счет быстрого рассмотрения заявки в самые короткие сроки. На портале ознакомьтесь и с тем, как правильно подобрать бизнес-кредит.
ремонт бытовой техники в самаре
Ищете возможность аренды профессионального оборудования? На сайте MedLight вы найдете выгодные условия аренды аппаратов для лазерной эпиляции https://medlight.com.ua/ru/orenda/ . Мы предлагаем широкий выбор современных аппаратов, которые помогут вам расширить свои услуги. Не упустите шанс повысить свой бизнес!
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – этто ваш надежный участник на сотворении кашеварных интерьеров. Пишущий эти строки специализируемся сверху исследованию, фабрике а также аппарате первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, кои сочетают в себе язык, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша делегация – вручить клиентам субъективные решения, основанные немного учётом ихний пожеланий а также потребностей, чтоб каждая кухня стала приятным а также удобным площадью чтобы животе а также творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Наш магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный гарнитур кухонь, коим помогут сделать уют равно удобства в вашем фамилии https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
стеклянные блоки для перегородок в интерьере
where to buy generic actos price
мобильные стеклянные перегородки
Итак, условия покупки спецтехники в лизинг могут быть разными, но выгодные условия лизинга всегда важны для юридических лиц и ИП спецтехника в лизинг для ип
узнать больше https://kp-inform.ru/catalog/hdd_and_ssd/zhestkiy_disk_dell_seagate_barracuda_es_st3750640ns_750gb_u300_7200_16mb_ncq_sataii_341_6321
стеклянная перегородка в комнату купить
Your Domain Name trustee plus
На сайте http://biburg.ru вы сможете пообщаться со своими друзьями, знакомыми, а также обменяться мнением и даже найти тех, с кем давно не общались. Здесь удобный интерфейс, а потому разобраться получится очень просто и быстро. Вы сможете обсудить самые последние новости, дать ценные рекомендации и обменяться новостями. Здесь выкладывают интересные факты, фотографии видеоматериалы и находят тех, с кем давно не общался. Такая социальная сеть дает возможность организовать круг по интересам. Заходите сюда каждый раз, как захотите пообщаться и рассказать что-то новое.
T.me/s/mcatcasino – телеграм-канал проекта Кэт казино. Тут вы много интересной информации отыщите. Наша цель – обеспечить вам положительный игровой опыт. Cat – достойное казино, предлагающее оперативные выплаты. Выбор игр отменный, они все мгновенно загружаются. Ищете cat casino регистрация? T.me/s/mcatcasino – здесь сможете узнать, как в онлайн-казино Кэт играть и выигрывать. Вас ждут превосходные бонусные предложения. CAT CASINO – потрясающее, служба поддержки всегда на связи, обслуживание клиентов на высшем уровне. Играйте и получайте удовольствие!
На сайте https://bfl-safina.ru пройдите тест для того, чтобы узнать, требуется ли вам абсолютно бесплатная процедура списания долгов. При этом вы сможете рассчитывать на получение 2 презентов. Вы освободитесь от долгов абсолютно законно. Также можно списать и штрафы, различные долги, кредиты. Практически не потребуется ваше участие, а заботы лягут на представителей компании. Все возможные риски сведены к минимуму. Прямо сейчас вы сможете пересмотреть свою жизнь и начать ее заново! Стоимость услуги остается на доступном уровне.
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный ассортимент мебели для кухонь. У нас вы выкопаете шиздец нужное чтобы создания приятного также многофункционального интерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» захватывается созданием (а) также реализацией качественной кухонной мебели. Да мы с тобой предлагаем широченный комплект продукции, яже откликается наиболее прогрессивным стандартам и тенденциям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Cryptoboss Casino: ваш путь к успеху и богатству
cryptoboss официальный криптобосс официальный сайт рабочее .
На сайте https://t.me/s/Joy_rus вас ждут заманчивые бонусы, которые вашей игре придадут новый уровень неповторимых ощущений. Вы можете забрать до 100% к вашему первому взносу и повысить свои возможность больших выигрышей. Собирайте за активную игру очки и на подарки и эксклюзивные бонусы обменивайте их. Гарантируем простоту применения сайта и скорость регистрации. Извлеките максимум пользы от всех бонусов JOY CASINO, играйте и с удачей побеждайте уже сейчас. Скорее регистрируйтесь и начните к успеху свое путешествие!
Trust SellAccs.net for your social media account needs. Our verified PVA accounts are created using diverse IPs, providing you with secure access to your favorite platforms.
Visit Here:
https://SellAccs.net
перегородка из стекла и металла купить
best site trustee crypto wallet
На сайте https://gamingvesty.online/ вы найдете интересную, качественную и любопытную информацию, которая касается не только самых популярных игр, но и железа, виртуальной реальности, компаний по производству софта, кино и релизов. На сайте выкладываются и любопытные слухи, которые будут интересны всем без исключения. Возможно, вам будет интересно узнать про консоли, игровую индустрию. Все новости из первых уст, а потому вы можете не сомневаться в правдоподобности и объективности. Регулярно выкладывается новое.
Drugs information leaflet. Short-Term Effects.
can i buy cheap coreg online
Best trends of drugs. Read now.
интернет https://kp-inform.ru/catalog/operativnaya_pamyat/operativnaya_pamyat_dell_512mb_1rx4_pc2_3200r_ddr2_400mhz_hys72t64001hr_5_a
Зарегистрируйтесь на cryptoboss casino и получите эксклюзивный бонус, Cryptoboss casino: регистрация проходит быстро и просто, Оформите аккаунт на cryptoboss casino и начните играть в любимые слоты, Присоединяйтесь к cryptoboss casino и станьте частью игрового сообщества, Станьте частью cryptoboss casino уже сегодня, Быстрая регистрация на cryptoboss casino – ваш шанс на удачу, Регистрация на cryptoboss casino – ваш ключ к миру азартных развлечений, Зарегистрируйтесь на cryptoboss casino и окунитесь в захватывающий мир азартных игр, Регистрация на cryptoboss casino – ваш первый шаг к большим выигрышам, Регистрация на cryptoboss casino – ваш билет в мир азартных развлечений, Присоединяйтесь к cryptoboss casino и получите шанс на крупный выигрыш, Присоединяйтесь к cryptoboss casino и начните выигрывать вместе с лучшими игроками, Cryptoboss casino приглашает вас стать его участником – зарегистрируйтесь сейчас, Уникальные бонусы ждут вас после регистрации на cryptoboss casino, Зарегистрируйтесь на cryptoboss casino и начните путь к успеху, Регистрация на cryptoboss casino – ваш шанс на удачу.
криптобосс промокод при регистрации hds5 cryptoboss регистрация cryptoboss ru casino .
Познакомьтесь раз-два нашим проф коллективом, который созидает чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты на явь https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров в Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш надежный участник в течение существе кухонных интерьеров. Мы работаем сверху исследованию, изготовлении и аппарате первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, что соединяют в течение себе стиль, работоспособность да долговечность. Наша представительство – обеспечить покупателям личные вывода, учрежденные капля учётом их пожеланий а также необходимостей, чтоб любая кухня стала приятным и удобным местом для века и творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Турагентство в Тюмени Акуна Матата Горящие туры https://akuna-matata72.ru/ – это поиск туров на сайте от всех надёжных туроператоров. Мы подберем Вам отдых по выгодным ценам. Туры в Турцию, Египет, Таиланд, ОАЭ, Китай (остров Хайнань), Вьетнам, Индонезию (остров Бали), Мальдивы, остров Маврикий, Шри-Ланка, Доминикану, Кубу и в другие страны. Туры из Тюмени и других городов. Мы расскажем Вам не только о пляжах, но и об особенностях безопасного и интересного отдыха в той или иной стране, про места, где лучше посетить экскурсии и любимые кафе.
Не упустите шанс, переходите на зеркало Cryptoboss Casino сейчас, выигрывайте без проблем!
Самое актуальное зеркало Cryptoboss Casino всегда под рукой, полный контроль гарантированы.
Официальное зеркало Cryptoboss Casino ждет вас прямо сейчас, пропустите другие варианты!
Новости и выигрыши ждут вас на зеркале Cryptoboss Casino, не пропустите свой шанс!
Без зеркала Cryptoboss Casino никуда!, получайте удовольствие без лишних хлопот!
криптобосс официальное зеркало криптобосс casino зеркало .
Выше- этношоп НашаМебель предлагает широченный выбор кухонь, какие помогут сделать устроенность также удобство на вашем доме https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Medicine prescribing information. Short-Term Effects.
generic sumatriptan prices
Actual trends of meds. Get information now.
держатель для рентгенпленки – магнитно порошковый дефектоскоп, пенетрант для контроля сварных купить
Выше- интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий перечень мебели для кухонь. У нас вы найдете все необходимое чтобы создания приятного (а) также функционального интерьера https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Omoda официальный дилер в Москве, купить новый автомобиль в автосалоне Омода https://omoda-avtoport.ru/ – посетите сайт и вы найдете необходимую модель в наличии. Также действуют акции, спец предложения, профессиональный сервис и обслуживание после приобретения. Подробнее на сайте.
набор для капиллярного контроля – контактная жидкость для ультразвукового контроля, дефектоскопист по магнитному и ультразвуковому контролю
Вывод из запоя на дому – это наркологическая услуга, которая оказывается наркологом в домашних условиях: врач приезжает на дом и проводит чистку организма для быстрого снятия запоя и следит за состоянием до конца процедуры.
Детальнее – [url=https://moscow.zapoy-clinic.ru/alkogolizm/vyvod-iz-zapoya/na-domu]Вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Прерывание запойного состояния на дому возможно только посредством постановки капельницы. Аппаратные методы применяются исключительно в условиях стационара. Врач составляет план лечения исходя из состояния пациента и результатов обследования.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://malahovka.zapoy-clinic.ru/alkogolizm/vyvod-iz-zapoya/na-domu]Вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Не всегда имеется возможность срочно посетить наркологический центр и получить необходимое лечение. Плохое физическое или психическое состояние наркозависимого или больного алкоголизмом может помешать встрече с врачом.
Детальнее – [url=https://voronezh.zapoy-clinic.ru/narcology]Вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
На ресурсе digi-keys.ru вы обнаружите широкий выбор проверенного программного обеспечения от Майкрософт, включая операционные системы Windows и офисные программы. Мы предлагаем доступные решения для тех, кто хочет найти надежное и лицензионное ПО для использования или персонального использования. На странице представлены версии как для профессионалов, так и для обычных пользователей, например, Windows 10 Pro и Office 2021 Pro Plus, с подробными инструкциями по инсталляции и активации.
Если вам нужно виндовс 10 скачать то у нас вы сможете получить лицензионную копию напрямую с официального сайта. Кроме того, вы найдете пошаговые указания по настройке системы на свой компьютер. Благодаря выгодным предложениям и системным обновлениям, ваши устройства будут функционировать надежно и безопасно.
Мы предлагаем долговечные решения для тех, кто хочет приобрести качественное ПО, с простым процессом лицензирования. Посетите digi-keys.ru, чтобы изучить полный ассортимент продуктов и найти необходимую версию Windows или Office, которая позволит вам комфортную работу.
датчик положения – модуль подготовки воздуха, блок подготовки воздуха camozzi
Очень полезно видеть, как мои привычки меняются со временем.
https://telegra.ph/dnevnik-programmy-pitaniya-09-26
Играйте бесплатно в Cryptoboss Casino с бездепозитным бонусом, воспользуйтесь шансом!
Заработайте крупный выигрыш без вложений в Cryptoboss Casino – шикарная возможность выиграть крупный джекпот.
Уникальные возможности для игры без вложений в Cryptoboss Casino – ваши шансы на победу увеличиваются.
Уникальное предложение от Cryptoboss Casino для новых игроков – заработайте крупный выигрыш без вложений.
Бездепозитный бонус доступен для всех в Cryptoboss Casino – возможность выиграть крупный джекпот без вложений.
Бездепозитный бонус в Cryptoboss Casino – это реальность – возможно, это ваш шанс выиграть крупный джекпот.
Cryptoboss Casino радует новых игроков щедрыми бонусами – шикарная возможность заработать без вложений.
Играйте без вложений и выигрывайте настоящие деньги в Cryptoboss Casino – шикарные призы и невероятные выигрыши ждут вас.
Начните играть бесплатно в Cryptoboss Casino с бездепозитным бонусом – новые призы и возможности для вас.
бонусы на пополнение cryptoboss cryptoboss casino промокод бездепозитный бонус .
Познакомьтесь один-другой нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже создаёт чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы в реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Как вам новые пансионаты? https://xn—-btbkfl8ef.xn--p1ai/
Pills information. Effects of Drug Abuse.
where to get effexor no prescription
Best news about drugs. Get information now.
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
Получить больше информации – [url=http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-11.ru]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Следует вызвать врача, рассказать о настораживающих симптомах, описать, что предшествовало их появлению. На основании полученной от пациента или его родственников информации нарколог посоветует, что можно предпринять на дому до его приезда.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://luhovicy.zapoy-clinic.ru/narcology]Вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность. В тяжёлых случаях могут развиться делирий, судороги и галлюцинации, что требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства.
Узнать больше – [url=http://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
проявитель – магнитно порошковый метод неразрушающего контроля, черная суспензия
Дневник питания помогает мне видеть связи между питанием и уровнем энергии.
https://telegra.ph/dnevnik-pitaniya-zapolnennyj-09-26
ремонт кондиционеров
дефектоскопист по ультразвуковому контролю – кассеты для рентгеновской пленки, контрастный грунт
Крутые игровые автоматы в казино Cryptoboss, для незабываемого времяпрепровождения.
Попробуйте свою удачу на автоматах в казино Cryptoboss, для любителей крупных выигрышей.
Играйте и выигрывайте на игровых слотах в казино Cryptoboss, для тех, кто ищет адреналин.
Попробуйте свою удачу на игровых автоматах в казино Cryptoboss, где каждый может стать победителем.
Развлекайтесь в казино Cryptoboss на лучших автоматах, для тех, кто мечтает о крупном выигрыше.
Играйте на популярных слотах в Cryptoboss Casino, где выигрыши ждут каждого.
Играйте на деньги на своих любимых слотах, для тех, кто мечтает о крупном выигрыше.
На сайте Cryptoboss ждут увлекательные слоты, для тех, кто ищет новые эмоции.
Уникальные автоматы в казино Cryptoboss, для ценителей азарта.
Играйте в казино Cryptoboss и выигрывайте крупные суммы, чтобы испытать настоящий азарт.
Играйте в лучшие игровые автоматы на сайте Cryptoboss, для тех, кто мечтает об успехе.
Лучшие игровые автоматы в казино Cryptoboss, для ценителей азарта.
Увлекательные слоты на сайте Cryptoboss ждут вас, для тех, кто мечтает о крупном выигрыше.
Игровые автоматы в казино Cryptoboss, которые порадуют вас выигрышами.
Играйте на деньги в казино Cryptoboss на лучших автоматах, для тех, кто мечтает о крупном выигрыше.
Попробуйте свою удачу в казино Cryptoboss, для азартных игроков.
Играйте в увлекательные слоты на сайте Cryptoboss Casino, где каждый может испыт
криптобосс игровые автоматы на деньги криптобосс автоматы зеркало .
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – это ваш фундаментальный партнер на твари кашеварных интерьеров. Наша сестра работаем на исследованию, изготовлении и аппарате высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, которые сочетают в течение себе язык, функциональность а также долговечность. Наша посланничество – передать покупателям персональные заключения, разработанные вместе с учётом ихний пожеланий равно необходимостей, чтобы любил шакша поделалась уютным также спокойным местом для бытию (а) также творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
T.me/mvavada – официальный телеграм-канал проекта Вавада. Здесь собрана вся актуальная информация. Мы для вас стараемся! VAVADA казино славится тем, что без проблем выплачивает выигрыши. Отзывчивые менеджеры, отличная бонусная программа, условия отменные. Ищете vavada рабочая ссылка? T.me/mvavada – тут рассказываем, как играть правильно в казино. Casino VAVADA – душевное, каких еще поискать надо. Имеется большое количество игр. Подключены удобные системы платежа для вывода денежных средств. Вавада умеет привлекать игроков!
Металлические входных двери двери в квартиру любого размера, конструкции и комплектации. Узнайте как правильно выбрать входную дверь для квартиры и частного дома https://totalarch.com/metallicheskie-vhodnye-dveri-v-kvartiru-sovety-po-vyboru
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
Детальнее – [url=http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-13.ru]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно[/url]
Свой этношоп НашаМебель предлагает широченный запас кухонь, коие посодействуют создать устроенность и еще удобство на вашем фамилии http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
T.me/s/azino777_a – проекта Azino777 телеграм-канал. Здесь исключительно достойная информация предложена. Азино777 – казино с безупречной репутацией. Множество игр позволят вам ощутить настоящий азарт. Ищете азино 777 официальный сайт? T.me/s/azino777_a – здесь рассказываем о самом главном, посмотрите прямо сейчас информацию. Быстрые выплаты, безопасность данных, круглосуточная поддержка клиентов делают Azino777 непревзойденным. Бонусы вас также порадуют. Посетите казино Азино777 и невероятное удовольствие от увлекательных игр получите.
На сайте https://t.me/s/izzi_russia вы найдете всю информацию, посвященную популярному проекту IZZI CASINO. Здесь вы сможете узнать актуальный и свежий промокод, про акции и многое другое. Регулярно появляется свежая и нужная информация, которая будет необходима всем, кто связан с азартными играми. Это заведение придает особое значение безопасности клиентов, а потому данные точно не попадут другим лицам. Перед началом игры необходимо определиться с тем, сколько сможете потратить. Игра поможет вам получить не только выигрыш, но и приятные эмоции.
Зависимость от наркотиков и алкоголя — одна из самых острых социальных проблем современности. Нарушение внутреннего равновесия, разрушение отношений, снижение производительности и здоровья — все это лишь малая часть негативных последствий, которые переживают зависимые люди и их близкие.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://ii4.ru/health/13358-sovremennye-metody-borby-s-alkogolizmom]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
проститутка новосибирск
Ищите найти проститутку в новосибирске? У нас есть лучшие индивидуалки этого города для наслаждения! Мы предлагаем только профессиональные девушки с безупречным внешним видом и безупречным сервисом. Планируете пригласить девушку на вечер? Свяжитесь с нами, и все ваши желания будут выполнены!
Не пропустите возможность встретиться с самыми горячими девушками города новосибирск. ??
https://humanlove.stream/wiki/User:RyderEaton65114
https://fbi.me/index.php?title=User:LuzSteiner
Обновленный курс валют в Казахстане
Способы отслеживания курса валют в Казахстане
Советы по обмену валют в Казахстане
Какой курс валюты в Казахстане будет завтра
Секреты выгодного обмена валюты в Казахстане
курс валют в павлодаре курс нб рк .
омск снять проститутку
Ищите вызвать проститутку в омске? Мы предлагаем топовые шлюхи этого города для наслаждения! У нас всегда проверенные девушки с безупречным внешним видом и лучшим сервисом. Планируете пригласить проститутку для встречи? Свяжитесь с нами, и все ваши желания будут выполнены!
Не пропустите возможность встретиться с самыми привлекательными индивидуалками города омск. ??
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” приглашает широченный подбор мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость выкопаете все необходимое чтобы сотворения приятного (а) также высокофункционального экстерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Процесс учебы в автошколах состоит из лекций и вождения. Стоимость обучения в автошколе варьируется от 20 до 25 тыс рублей стоимость курсов вождения автомобиля в москве
[url=https://kz.ndt.su]ультразвуковой контроль дефектоскопия[/url] – ультрафиолетовый фонарь купить, капиллярный метод контроля
На сайте https://iz-zala.ru/ в большом выборе представлены вешалки, а также настольные лампы различных модификаций, расцветок, а также размеров, самого разного предназначения. В разделе вы найдете огромное количество интересных, любопытных подарков, которые доставят радость каждому, подарят приятное настроение. И самое важное, что презенты нужные, ценные, поэтому точно будут вам полезны, независимо от пола, возраста. Также можно приобрести и столы, табуреты, созданные из надежных, современных материалов.
kometa casino официальный сайт komet casino buzz
Рады видеть тебя в КометаКазино!
Готов ли ты попробовать свою удачу и окунуться в мир незабываемых ощущений и больших выигрышей? В KometаCasino у каждого будет возможность выбрать игру по своему вкусу: от классических слотов до захватывающих игр с картами и рулетки!
Почему выбирают нас?
Дневные поощрения и специальные предложения – получай больше выигрышей с нашими эксклюзивными акциями!
Мгновенные выплаты – получай свой выигрыш в кратчайшие сроки!
Большое разнообразие игр – от слотов до реального казино с реальными дилерами!
Играй круглосуточно – играй в любом месте и когда угодно, прямо с твоего смартфона!
Вступай к нашей компании успешных игроков уже сейчас и начинай зарабатывать!
Для новичков у нас – уникальное предложение за регистрацию!
Нажимай на ссылку: KometаCasino и запусти своё путешествие к большим победам прямо сейчас!
Не упусти свой шанс стать следующим крупным призёром в KometаCasino! Твоя удача совсем рядом!
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» захватывается организацией также перепродажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Наш брат предлагаем широченный ассортимент продукции, который парирует самым современным стереотипам а также направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
магнитный метод контроля – крепления рентгеновских аппаратов паук у, контактная жидкость для ультразвукового контроля
Увлекательное казино Cryptoboss ждет вас, станьте победителем вместе с Cryptoboss, возможность выиграть крупный джекпот, попробуйте удачу в казино Cryptoboss, Cryptoboss casino – ваш путь к успеху, Cryptoboss casino – ваш лучший выбор, будьте боссом в мире криптовалютных игр с Cryptoboss casino, эксклюзивное казино для ценителей криптовалют, качественный сервис и безопасность с Cryptoboss casino, Cryptoboss casino – ваш путь к криптовалютному успеху, встречайте новый уровень криптовалютных ставок в Cryptoboss casino, большие выигрыши ждут вас в Cryptoboss casino, играйте и побеждайте с Cryptoboss casino, следуйте за лидером с Cryptoboss casino, выигрывайте крупные суммы с Cryptoboss casino, Cryptoboss casino – гарант криптовалютных побед.
скачать cryptoboss cryptoboss вход .
Это казино поражает своим ассортиментом слотов. С первого взгляда, когда заходишь на сайт, чувствуешь, что ты в мире азарта, где каждая ставка приносит волнение.
Интерфейс интуитивно понятный, что делает процесс приятным. Пополнение счёта проходят мгновенно, а переводы оперативен. Каждая деталь продумана, чтобы всё было на высшем уровне.
И конечно, поддержка клиентов всегда на связи, моментально реагируют и всегда на высоте. Для меня [url=https://selector-casino-igrat.tech/]Онлайн казино[/url] стал настоящим открытием, где каждая ставка приносит ощущения, которые сложно сравнить с чем-то!
проститутки москвы эскорт
Люкс премиум эскорт в столице: Мастерство роскоши и моды
Москва — город, где живут по высоким стандартам и ценят только лучшее. В сфере, где важна каждая мелочь, элитные эскорт-услуги становятся неотъемлемой частью успешных и требовательных людей. Наши профессиональные спутницы — это невероятно красивые и умные женщины, но и чудесные спутницы, которые понимают, как сделать ваш вечер невероятно запоминающимся.
Что заставит выбирать наши услуги?
Высокий уровень сервиса — обещаем абсолютную секретность и персонализированные услуги.
Безупречные дамы — любая наша спутница впечатляет внешностью, но и высоким интеллектом.
Шик и вкус — наши эскорт-спутницы сопровождают вас на любые события, независимо от того, светские мероприятия или бизнес-встречи.
Если вы цените комфорт, конфиденциальность и премиум сопровождение, то наша команда — именно то, что вам нужно. Погрузитесь в мир шика и изящества с нами!
купить кассовые чеки новосибирск
Оформление кассовых чеков
Требуются фискальные чеки для отчетности или подтверждения затрат? Мы обеспечиваем **достоверные и законные кассовые чеки для всех задач!
Тотальная приватность
Быстрая передача
Разные виды оплаты
Сэкономьте часы на лишние хлопоты — наши чеки позволят вам легко решить все задачи! Выйдите на связь с нами уже сейчас и заберите необходимую бумагу **без хлопот.
Оформить чек доступно незамедлительно в Telegram!
7к казино
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, яже учреждает уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы в течение явь https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
7к казино регистрация
На сайте https://otparivateli-odejdy.ru/ представлены в большом выборе отпариватели одежды. Они оказывают полноценный уход за одеждой, текстильными предметами. Высокотехнологичные изделия окажут необходимую помощь в том случае, если рекомендуется быстро вернуть вещам ухоженный и красивый вид, а также при условии, если необходимо поправить рюши, складки и выпрямить оборки. Устройства отличаются огромным набором важных функций, которые необходимы для ежедневного выполнения задач.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный участник на создании кухонных интерьеров. Автор этих строк работаем на исследованию, изготовлении равным образом установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, которые сочетают на себе стиль, функциональность и долговечность. Наша предназначение – предоставить клиентам персональные решения, построенные раз-два учётом ихний пожеланий и надобностей, чтоб любая кухня стала приятным и спокойным местностью чтобы существования равно творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.daytoday.hdwm вы сможете скачать HDWM 365. Уникальное приложение поможет вам спланировать свой день и не тратить время впустую. При этом будет заполнен каждый час вашего времени из 24 часов. Так нет необходимости в том, чтобы заводить бумажный дневник либо искать заметки в телефоне, ведь это приложение создано для вашего удобства. Теперь вы сможете отслеживать расписание в самом удобном для себя формате. С таким приложением вы сможете спланировать расписание тренировок, занятий в студии йоге и не пропустить важную встречу.
Наслаждайтесь играми с реальными крупье и живыми ставками в нашем онлайн казино.
лекс казино демо
набор для магнитопорошковой дефектоскопии – пенетрант для капиллярного контроля, муфта коллиматор
зарегистрироваться starda casino
сим карты мтс оптом
купить соленоидный клапан электромагнитный – пневмоостров festo, автоматический клапан воздуха
Сервисный центр предлагает мастер по ремонту сервера fujitsu отремонтировать сервера fujitsu
крепления рентгеновских аппаратов – набор для магнитопорошковой дефектоскопии, магнитная суспензия для магнитопорошкового контроля
Dive into high-precision GPS trail and topo maps of top global travel spots
Get hands-on with adventure maps of mountainous landscapes
Browse maps for global adventures
Выше магазин НашаМебель предлагает широченный гарнитур кухонь, кои посодействуют создать уют и удобства в течение вашем логове https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Шкаф купе недорого купить
работа девушкам в эскорте
На сайте https://kondicioneri-hisense.ru/ есть возможность приобрести качественные, функциональные, практичные кондиционеры проверенной марки Hisense. Она зарекомендовала себя с лучшей стороны благодаря тому, что создает технику высокого качества, оснащенную необходимым количеством важных опций. Есть такие модели, у которых встроенный Интернет. Все изделия отличаются огромным количеством важных и нужных опций, которые необходимы всем, кто хочет в доме приятную атмосферу и создать свой микроклимат.
Dleshka.org – сайт с множеством шаблонов на любой вкус. Наш сайт вебмастера любят. У нас найдете уникальные модули для DLE. Мы поделимся с вами полезными скриптами. https://dleshka.org – здесь можете скачать модули, шаблоны dle, DataLife Engine 17.2. Тут для вебмастеров представлены программы, которые в выполнении различных задач помогут. Постарались в одном месте все необходимое собрать. Публикуем исключительно высококачественные шаблоны. Будем рады видеть вас на нашем ресурсе. Процедура регистрации простая, и не займет много вашего времени.
[url=https://t.me/dostavka_moscow]доставка алкоголя москва alc0lux[/url]
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный набор мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы найдете шиздец нужное для формирования приятного и еще многофункционального интерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
colchicine side effects
Мебель недорого
стрип клуб женский – стриптиз бар кружева удмуртская ул., ижевск ночные клубы
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели чтобы кухни» захватывается организацией также реализацией качественной кухонной мебели. Автор делаем отличное предложение широченный ассортимент продукта, яже расплачивается самым современным стандартам да тенденциям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
интернет магазин шкафов купе
Попробуйте свои силы в казино от Cryptoboss, играйте и выигрывайте вместе с королем криптовалютных игр, криптовалютные ставки для настоящих боссов, освойте мир криптовалютных игр в казино Cryptoboss, Cryptoboss casino – ваш путь к успеху, играйте на крипто-максимуме вместе с Cryptoboss, будьте боссом в мире криптовалютных игр с Cryptoboss casino, Cryptoboss casino – ваша площадка для побед, качественный сервис и безопасность с Cryptoboss casino, Cryptoboss casino – ваш путь к криптовалютному успеху, революция в криптовалютных играх с Cryptoboss casino, большие выигрыши ждут вас в Cryptoboss casino, играйте и побеждайте с Cryptoboss casino, следуйте за лидером с Cryptoboss casino, попробуйте удачу вместе с Cryptoboss, наслаждайтесь азартом с Cryptoboss casino.
криптобосс игровые cryptoboss casino boss .
Познакомьтесь вместе с нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже образовывает чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте kreditbaza.ru собраны оптимальные предложения банков по потребительским кредитам. Посмотрите продукты и онлайн-заявку на кредит оформите. Мы заботимся о вашем времени. Не скрываем полные условия финансовых продуктов. Ищете совкомбанк? Kreditbaza.ru – ресурс, где вы найдете более детальную информацию. Как получить кредит в Краснодаре, здесь вы узнаете. Мы публикуем статьи, которые помогают лучше разобраться в банковских продуктах и повысить уровень финансовой грамотности. Специальные предложения ждут вас!
На сайте https://t.me/ramenbet_m вы найдете всю самую актуальную, интересную и полезную информацию, которая касается популярного проекта Ramenbet. Теперь всю самую важную, новую и честную информацию вы будете узнавать именно из этого канала. На нем, в первую очередь, публикуются новости, информация, которая понадобится всем, кто связан с этой темой. Здесь всегда публикуются промокоды, разные интересные и актуальные акции, которыми сможет воспользоваться каждый желающий. Заходите сюда регулярно!
Pills information leaflet. What side effects can this medication cause?
lisinopril heartburn
Actual news about medicines. Get now.
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-15.ru]вывод из запоя на дону[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это сложный и многоэтапный процесс, требующий комплексного подхода и поддержки. Важно обратиться за профессиональной помощью, получать психологическую поддержку и вести здоровый образ жизни. Только так можно добиться устойчивой ремиссии и улучшить качество жизни.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=http://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Хотя лучше всего проходить лечение под наблюдением специалистов, существуют также методы, которые можно использовать дома. Однако важно помнить, что самолечение может быть опасным, и перед началом любых процедур необходимо проконсультироваться с врачом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=http://narco-vivod.ru]вывод из запоя с выездом на дом[/url]
При правильном подходе и соблюдении всех рекомендаций можно не только успешно выйти из запоя, но и предотвратить его повторение, вернувшись к полноценной и здоровой жизни.
Подробнее тут – [url=http://alko-specialist.ru]вывод из запоя 24[/url]
площадки обслуживания мостовых кранов – грузоподъемное оборудование екатеринбург, кран балки подвесные
Выше этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широкий ассортимент кухонь, кои посодействуют сделать устроенность равно благоустроенность в вашем фамилии https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
обработка деталей на токарных станках – вакуумная формовка на заказ, изготовление изделий из полипропилена на заказ в спб
эскорт работа для девушек в красноярске
Drugs information. What side effects?
where buy generic valtrex without a prescription
Everything information about medicine. Get here.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:сервис центры бытовой техники ростов на дону
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Drugs information. Generic Name.
where to get ampicillin
Some about pills. Read here.
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
Узнать больше – [url=http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-16.ru]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
Узнать больше – [url=http://alko-lechebnica.ru]вывод из запоя с выездом на дом[/url]
Зависимость от наркотиков и алкоголя — одна из самых острых социальных проблем современности. Нарушение внутреннего равновесия, разрушение отношений, снижение производительности и здоровья — все это лишь малая часть негативных последствий, которые переживают зависимые люди и их близкие.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://mycistit.ru/lechenie/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya-spasenie-ili-vremennoe-oblegchenie]вызвать капельницу от запоя[/url]
Наш инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” зовет широкий прибор мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы посчитаете все необходимое для образования приятного и высокофункционального экстерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Запой — это состояние, при котором человек в течение нескольких дней или недель непрерывно употребляет алкоголь. Такое поведение сопровождается серьезными физическими и психологическими нарушениями, включая депрессию, тревожность, потерю аппетита, бессонницу и галлюцинации.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://alko-reabcentr.ru]доктор вывод из запоя[/url]
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели для кухни» занимается основанием да реализацией качественной кухонной мебели. Автор предлагаем широченный гарнитура продукта, яже парирует самым сегодняшним шаблонам и направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Зависимость от наркотиков и алкоголя — одна из самых острых социальных проблем современности. Нарушение внутреннего равновесия, разрушение отношений, снижение производительности и здоровья — все это лишь малая часть негативных последствий, которые переживают зависимые люди и их близкие.
Разобраться лучше – [url=http://facenewss.ru/obshhestvo/narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-tveri-put-k-zdorovyu-i-vosstanovleniyu]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
lucky jet
На сайте https://vestiok.ru/ ознакомьтесь с новостями, которые представлены здесь со всего мира. Это позволит вам узнать то, как обстоят дела не только с экономикой, но и политикой. Рассматриваются самые важные вопросы на злободневную тему. Есть интересные, увлекательные статьи, посвященные теме спорта, бизнеса, культуры, экологии. Имеются публикации, представленные на тему будущего и всего того, что нас окружает. А если хотите обсудить какие-либо новости, темы, которые особенно беспокоят, то заходите на форум, где вы обязательно найдете единомышленников.
строительство кирпичного дома под ключ цена – клееный брус купить, монтаж водоснабжения
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-17.ru]срочный вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=http://alko-lechebnica.ru/chto-takoe-zapoj]частный вывод из запоя[/url]
Medicines information leaflet. What side effects can this medication cause?
buy robaxin pill
All news about drug. Read here.
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели для кухни» воспламеняется образованием равным образом реализацией качественной кашеварной мебели. Автор делаем отличное предложение широкий гарнитура продукции, который отвечает самым передовым шаблонам равно тенденциям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Зависимость от наркотиков и алкоголя — одна из самых острых социальных проблем современности. Нарушение внутреннего равновесия, разрушение отношений, снижение производительности и здоровья — все это лишь малая часть негативных последствий, которые переживают зависимые люди и их близкие.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://justwoman.club/metody-lecheniya-alkogolizma/]https://justwoman.club/metody-lecheniya-alkogolizma/[/url]
Первый этап вывода из запоя – это детоксикация организма. Она включает в себя удаление токсинов, накопившихся в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Этот процесс должен проводиться под наблюдением медицинских специалистов, так как резкое прекращение употребления алкоголя может вызвать серьезные осложнения, такие как алкогольный делирий (белая горячка), судороги и другие острые состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=http://narko-reabcentr.ru]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
AI Essay Writer is a free Chrome extension Ищете AI Essay Writer? chromewebstore.google.com/detail/ai-essay-writer/blcamfmkmjdbigcliokaebahmolamlfp?hl=en powered by ChatGPT that helps you write essays with a single click. Create easily and well-structured documents in no time. Our tools are designed to improve productivity. Create consistent, well-structured and original content.
купить детские часы с сим картой
Ньючип – компания, коллектив которой уже более 14 лет успешно работает в сфере поставок надежной компьютерной техники. Широкий список продукции на постоянной основе пополняется новинками. Предлагаем удобную систему скидок и индивидуальные условия для крупных заказчиков. Ищете моноблоки недорого, с рассрочкой от тбанка? Newchip.ru – портал, где вы найдете о товарах блог. У нас свыше 50000 наименований представлено. Сотрудничаем с поставщиками техники популярных брендов напрямую. Корпоративные и оптовые клиенты извлекают максимальную выгоду от партнерства.
На сайте https://lordkino.net/ вы найдете огромное количество интересных фильмов самых разных жанров: мелодрамы, драмы, комедии, детективы, аниме, а также аниме сериалы, которые погрузят вас в удивительный и разнообразный мир. Изучите топ для того, чтобы быстрее определиться с выбором. Все кино в хорошем качестве, интересное, с отличным звуком, а потому точно вам понравится. Играет приятная музыка, обрадует актерский состав. Подобрать то, что нужно поможет специальный фильтр. Регулярно добавляются новинки.
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – это ваш фундаментальный участник в течение образовании кашеварных интерьеров. Да мы с тобой работаем на исследованию, производстве и аппарате первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, коим соединяют в течение себя стиль, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша посланничество – отдать посетителям персональные заключения, основанные раз-два учётом их пожеланий а также надобностей, чтобы любая кухня стала приятным и еще удобным местом чтобы существования равно творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Medicament information. Cautions.
cost cheap coumadin without a prescription
Everything information about drug. Get information here.
can you get generic bystolic pills
доставка алкоголя на дом москва alcolux7
На сайте https://t.me/mvavada представлен официальный канал уникального проекта VAVADA, который теперь будет и в вашем мобильном телефоне. Именно здесь выкладываются самые последние интересные новости, которые точно понравятся всем гемблерам без исключения. Здесь публикуются не только новости, но и информация о предстоящих акциях, а также промокоды, которые позволят сэкономить собственные сбережения. А если вы проиграете, то потратите средства клуба. Он предлагает ознакомиться с огромным количеством развлечений, что позволит отыскать решение на свой вкус.
Kraken представляет собой революцию в мире цифровой безопасности, где приватность и защита данных становятся важнейшими аспектами вашего цифрового присутствия. Сеть под названием “Kraken” ассоциируется с бесконечными возможностями и технологическими прорывами. Эта система обеспечивает доступ к миру цифровой свободы, в котором обычные правила интернета не действуют.
Ссылка на сайт: Кракен даркнет ссылка
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – это чемодан надежный участник в течение основании кухонных интерьеров. Да мы с тобой работаем на исследованию, фабрике и установке высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или иной соединяют на себя стиль, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша миссия – предоставить посетителям субъективные заключения, сделанные маленький учётом их пожеланий и потребностей, чтоб любая кухня сковаться льдом приятным и еще спокойным районом для бытья равно творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
http://fabnews.ru/forum/showthread.php?p=82088#post82088
http://center-2.ru/forum/?mingleforumaction=viewtopic&t=14929#postid-29409
Хотите зарядиться энергией и избавиться от усталости? Парвеник сделает ваш отдых незабываемым и предложит для вас покупку банных веников. Доступные цены гарантируем. Если у вас возникнут вопросы, мы с радостью поможем. https://www.parvenik.ru – портал, посетите его, для ознакомления со всем перечнем товаров, а также на доставку стоимостью. У нас представлены такие веники: дубовые, липовые, хвойные, эвкалиптовые, березовые. Также тут вы найдете травы в мешочках и пучках, эфирные масла, чаи, шапки, подушки, матрасы, рукавицы и коврики.
Хотите скачать приложение 1вин и начать зарабатывать деньги онлайн? У нас вы найдете подробную инструкцию и полезные советы по использованию этой платформы для ставок и азартных игр.
Наш магазин НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широкий прибор кухонь, кои помогут создать уют также комфорт в течение вашем доме http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Прокачайся по полной на https://tunebody.ru/ Спорт, питание, мысли.
Dleshka.org – сайт с множеством шаблонов на любой вкус. Наш портал любят вебмастера. У нас вы отыщите для DLE уникальные модули. Поделимся полезными скриптами с вами. https://dleshka.org – тут можете скачать DataLife Engine 17.2, шаблоны dle, модули. Здесь представлены программы для вебмастеров, которые помогут в выполнении разных задач. Постарались собрать в одном месте все необходимое. Публикуем исключительно высококачественные шаблоны. Будем рады вас видеть на нашем портале. Процедура регистрации простая, и не займет много вашего времени.
В статье рассматривается функционал и особенности мобильной версии сайта [url=https://1winvv.xyz/]1win[/url], а также преимущества использования данной версии для пользователей.
lucky jet демо
Quotex Philippines https://qxinfo-ph.online/ is binary options at a new level. Over 100 different global trading assets are available, as well as a mobile app for all devices for easy trading from anywhere in the world. Find out on the website all the advantages of trading with us on the website, and also, if necessary, get a free demo account.
Купить кухню мдф
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный коллекция мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы найдете все нужное чтобы формирования уютного (а) также функционального экстерьера https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
вакансии в кружевах – вакансии в клубах, приватные танцы для мужчин
На сайте https://right-well.ru закажите такую важную услугу, как рытье колодца под ключ. Оплачивается работа и сам колодец. Для того чтобы воспользоваться услугой, просто оставьте заявку. Прямо сейчас вы сможете узнать стоимость услуги, чтобы заранее спланировать бюджет. Колодцы эффективны и надежны. А все потому, что их конструкция очень простая. Во время установки колодцев применяются железобетонные кольца. Они невосприимчивы к агрессивному воздействию среды. Именно поэтому колодцы наделены длительным сроком эксплуатации.
mailsco.online
профилированный брус киров – vk. comlesstroyproekt, построить каркасный дом
проекты одноэтажных домов из газобетона – готовые проекты жилых домов, дом из керамических блоков
hellcase free case code in Germany
Medication information sheet. Brand names.
where to get generic sumatriptan tablets
Actual news about medicines. Read information now.
Выше- интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный прибор мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость посчитаете все необходимое чтобы сотворения приятного да высокофункционального экстерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
https://thebraai.co.za/kvartiry-na-sutki-v-gomele-tenancy-by-11/
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется созданием равно продажей лучшей кухонной мебели. Наш брат предлагаем широченный коллекция продукта, яже дает ответ наиболее сегодняшним шаблонам (а) также направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
шлюхи омск
Хотите узнать, где вызвать девушку легкого поведения в омске? У нас есть топовые шлюхи омска для наслаждения! Мы предлагаем только надёжные девушки с безупречным внешним видом и лучшим сервисом. Планируете пригласить девушку для встречи? Обращайтесь к нам, и ваши мечты осуществятся!
Не теряйте возможность провести время с самыми горячими девушками омска. ??
Cryptoboss Casino – ваш шанс на большой выигрыш
cryptoboss официальный сайт cryptoboss casino официальный сайт .
работа эскорт
https://lamisionsalta.com.ar/kvartiry-na-sutki-v-gomele-snjat-kvartiru-4-2/
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, который создаёт уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы в течение реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Medication information leaflet. Drug Class.
can i order ziprasidone prices
All trends of pills. Read now.
Зайдите на сайт https://avtobus-nn.ru/ и вы сможете ознакомиться с главными событиями и новостями автоиндустрии в России. На сайте свежие новости, статьи и обзоры о последних новинках автоиндустрии. Статьи постоянно добавляются, что позволит получать интересную информацию ежедневно.
lucky jet игра с выводом
контейнер для оборудования ижевск – грузоподъемное оборудование екатеринбург, краны на железнодорожном ходу
работа для девушек
вакуумная формовка пластика спб – вакуумная формовка санкт петербург, вакуумформовка санкт петербург
https://www.mejorhosting.cl/8-objavlenij-arenda-kvartir-na-sutki-v-gomele-na-9/
Зарегистрируйтесь на cryptoboss casino и получите эксклюзивный бонус, Cryptoboss casino: регистрация проходит быстро и просто, Оформите аккаунт на cryptoboss casino и начните играть в любимые слоты, Уникальная атмосфера cryptoboss casino для зарегистрированных пользователей, Регистрация на cryptoboss casino – ваш первый шаг к увлекательному миру азартных игр, Быстрая регистрация на cryptoboss casino – ваш шанс на удачу, Пройдите регистрацию на cryptoboss casino и откройте доступ к лучшим играм, Присоединяйтесь к cryptoboss casino и начните выигрывать большие суммы денег, Не упустите шанс зарегистрироваться на cryptoboss casino и получить эксклюзивные бонусы, Зарегистрируйтесь на cryptoboss casino и получите доступ к лучшим игровым автоматам, Станьте участником cryptoboss casino – зарегистрируйтесь и начните играть сегодня, Регистрация на сайте cryptoboss casino – ваш первый шаг к азартным приключениям, Регистрация на cryptoboss casino – ваш путь к финансовой независимости, Уникальные бонусы ждут вас после регистрации на cryptoboss casino, Зарегистрируйтесь на cryptoboss casino и начните путь к успеху, Присоединяйтесь к cryptoboss casino и получите бонус за регистрацию.
криптобосс регистрация cryptoboss casino2 one криптобосс регистрация cryptoboss casino2 one .
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный участник на сотворении кашеварных интерьеров. Автор этих строк специализируемся сверху исследованию, производстве а также аппарате первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или другой соединяют в течение себя стиль, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша организация – оделить. ant. взять посетителям индивидуальные вывода, образованные небольшой учётом ихний пожеланий а также надобностей, чтобы любая шакша стала приятным равно удобным помещением для живота и еще творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Petryaj – это динамично развивающаяся компания. Мы успешно специализируемся на производстве и оптовых поставках амуниции для животных. Вся продукция надежностью в применении и отменным качеством отличается. Ищете petryaj.ru? Petryaj.ru – тут есть возможность в любое время с условиями оплаты ознакомиться. Сотрудничая с нами, будьте уверены в выгодных ценах и высочайшем качестве. Чтобы приобрести лучшие товары для животных отправьте заявку на e-mail, указанный на сайте. Будем рады рассмотреть ваши предложения!
Pills information sheet. What side effects?
cost olmesartan prices
Everything news about medicament. Read information now.
Medicament prescribing information. What side effects?
buy lryica on line no presciption
Actual news about meds. Get here.
https://www.fieranazionalecarciofo.com/2024/09/23/kvartiry-na-sutki-v-gomele-tenancy-by-4/
Наш магазин НашаМебель призывает широкий комплект кухонь, какие посодействуют создать уют (а) также удобство в течение вашем доме https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Попробуйте свои силы в казино от Cryptoboss, играйте и выигрывайте вместе с лучшим криптовалютным казино, возможность выиграть крупный джекпот, попробуйте удачу в казино Cryptoboss, стать криптобоссом легко с Cryptoboss casino, играйте на крипто-максимуме вместе с Cryptoboss, ипотека доверия с Cryptoboss casino, эксклюзивное казино для ценителей криптовалют, взломай банк с Cryptoboss casino, Cryptoboss casino – ваш путь к криптовалютному успеху, встречайте новый уровень криптовалютных ставок в Cryptoboss casino, играйте на криптовалютных волнах вместе с Cryptoboss, Cryptoboss casino – ваш ключ к фортуне, следуйте за лидером с Cryptoboss casino, выигрывайте крупные суммы с Cryptoboss casino, наслаждайтесь азартом с Cryptoboss casino.
скачать cryptoboss casino криптобосс cryptoboss .
На сайте https://t.me/s/azino777_a изучите информацию, которая касается популярного заведения Azino777. Если вы не можете зайти на сайт, то в этом случае используйте зеркало. Необходимо лишь перейти по ссылке, после чего вы окажетесь в этом заведении, где получите возможность сыграть без ограничений. Вас ожидает бонус в 500%, а также кэшбек. Все новички смогут рассчитывать на более выигрышные условия. А регистрация проходит всего в пару минут. На этом канале выкладываются самые последние новости, акции, которые будут интересны всем без исключения.
На сайте https://zenno.club/discussion/threads/prodazha-akkauntov-google-play-console-developer.112933/ вы сможете приобрести аккаунты Google Play Console. Стоимость уточните на сайте. Но в любом случае она будет для вас доступной и привлекательной. Возраст – 1 год, предоставляется гарантия – неделя. Качество фарминга остается на высоком уровне. Аккаунт фармится в течение 7 дней и только человеком. В случае если с аккаунтом что-то происходит, то производится его оперативная замена.
Свой этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широкий ассортимент кухонь, тот или другой посодействуют создать уют равным образом комфорт в течение вашем семье http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
https://ihelpuride.com/2024/09/18/snjat-kvartiru-v-gomele-na-sutki-arenda-kvartir-36-2/
где взять ссылку на кракен – kraken площадка, кракен сайт
Meds information leaflet. Generic Name.
buying generic acyclovir without prescription
Actual news about pills. Read information here.
Выше- инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий сортамент мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость улучите все необходимое для формирования приятного и многофункционального внутреннего убранства https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Компания «СпецДорТрак» регулярно развивается и внимательно следит за новыми тенденциями в своей отрасли. Если вам нужны на спецтехнику качественные запасные части, обращайтесь к нам. Грамотно вас проконсультируем и подберем все необходимое. Ищете купить сервомеханизм? Trak74.ru – портал, на котором ориентироваться просто. Тут каталог товаров представлен. У нас большой выбор для спецтехники запчастей. Мы высоко ценим наших клиентов и надеемся на долгосрочное сотрудничество в будущем. Обеспечим вам лучший сервис!
kraken20 at – kraken маркетплейс официальный сайт, кракен darknet ссылка
Натяжные потолки под ключ в Москве на сайте https://potolki-pk.ru/ с бесплатным выездом замерщика. Монтаж натяжных потолков от профессионалов по лучшим ценам. Ознакомьтесь на нашем сайте с портфолио и прайсом – он вас приятно удивит. Даем 25 лет гарантии на материалы и 10 лет на монтажные работы!
https://www.camminodiaronte.it/bez-rubriki/snjat-kvartiru-na-sutki-v-gomele-onlajn-12/
На сайте https://elektrogrili-dlya-doma.ru/ вы найдете качественные, надежные и функциональные электрогрили, которые различаются техническими характеристиками, формой, размерами и другими особенностями. Это позволит подобрать такую модель, которая точно подойдет вам под определенные цели. Электрогрили станут оптимальным решением в том случае, если хочется приготовить мясо, курицу, рыбу на природе, но нет возможности выехать. По вкусовым характеристикам блюда не будут уступать тем, что приготовлены на костре.
рабочий тор мега – мега даркнет маркет, мега платформа мориарти
Наша компания «Сайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется основанием также реализацией лучшей кашеварной мебели. Наша сестра предлагаем широкий набор продукта, яже дает ответ наиболее современным стандартам а также тенденциям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
http omg gl – omg market ссылка, сайт omgomg
Medicament information for patients. Generic Name.
can you get esomeprazole for sale
All about meds. Get now.
На сайте http://xn--e1afncgmffocf.xn--p1ai вы узнаете много интересного про то, как питаться правильно, разнообразно, интересно и каждый день по-новому. А самое главное, что при помощи таких рецептов вы обретете талию мечту, избавитесь от живота, а заодно получите заряд положительных эмоций. Также имеется информация, которая касается того, как спланировать свои тренировки и какие упражнения лучше всего делать на определенную группу мышц, чтобы добиться определенных результатов. Вы узнаете много интересных советов, полезных рекомендаций, которые помогут обрести идеальное тело.
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» загорается сотворением и еще реализацией лучшей кухонной мебели. Мы делаем отличное предложение широченный ассортимент продукта, яже начинает говорить наиболее прогрессивным эталонам и направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте gamingoff.ru мы составили известные квесты Elden Ring, а также способы их решения. Прохождение части из них существенно упростит вашу жизнь, а другие поразят необычной историей либо представят совершенно нового персонажа. Ищете знак радагона? Gamingoff.ru/solutions/akademiya-rayi-lukarii-v-elden-ring-gayd-i-prohozhdenie-lokatsii-na-100 – тут узнаете, как в Академии Райи Лукарии побывать. Расскажем, как волшебный ключ академии найти. Посмотреть информацию можете в любое время. Пишите вопросы в комментарии. Удачной вам игры!
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, который созидает чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы на реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Платформа онлайн бронирования жилья для отдыха и путешествий https://brony24.com/ – это возможность забронировать квартиру, апартаменты, дома, отели по лучшим ценам. Найти жилье очень просто – вводите даты и выбираете город, а система подберет для вас варианты, который можно забронировать в 1 клик. На сайте тысячи вариантов во всех популярных направлениях для путешествий!
Medicines prescribing information. Effects of Drug Abuse.
can i order fosamax price
Actual news about medicine. Get now.
omg рабочая ссылка – ссылка на гидру http omg onion, омг
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – это ваш фундаментальный партнер в учреждении кухонных интерьеров. Ты да я работаем сверху исследованию, производстве да аппарате первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, каковые сочетают на себе стиль, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша миссия – позволить клиентам личные ответы, образованные с учётом ихний пожеланий и потребностей, чтоб всякая шакша выходила уютным также спокойным площадью для жизни и творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Ивенты на мероприятиях подарят заряд вам интерактивные позитивные переживания. Театральные представления вдохновляют на получить заряд бодрости. Сетевые вечеринки в семейном кругу вдохновляют на свершения. Планируйте для потрясающих ивентов без лишних забот!
https://festivalguru.ru/
Woman.pub предлагает массу полезной информации. Здесь вы найдете такие категории, как: психология, мода и стиль, красота и уход, саморазвитие, здоровье, отношения. Узнаете, чем полезна растяжка, как создать стильный образ и модно выглядеть в любое время года, что такое цифровой детокс. Ищете саморазвитие женщин? Woman.pub – сайт, где можете воспользоваться удобным поиском. Мы расскажем, как спасти брак, добиться успеха и независимости в современном мире. Заходите прямо сейчас на наш портал. Тут вы найдете только все самое интересное!
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – это чемодан фундаментальный партнер на образовании кашеварных интерьеров. Ты да я специализируемся на разработке, изготовлении равно аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, что соединяют в течение себе стиль, функциональность а также долговечность. Наша миссия – предоставить клиентам персональные решения, основанные кот учётом их пожеланий и необходимостей, чтобы всякая шакша принялась приятным а также удобным районом чтобы века равным образом творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Наш этношоп НашаМебель предлагает широкий прибор кухонь, которые помогут создать уют и комфорт в течение вашем фамилии http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Medicines information sheet. Brand names.
where can i buy cheap benicar without dr prescription
All information about medicament. Get information here.
http omg 4 gl – omg1 gl ссылка omg, омг сервис
На сайте https://t.me/mvavada изучите всю самую нужную информацию, которая касается популярного проекта VAVADA. Теперь самое увлекательное, популярное заведение в вашем смартфоне. Важным моментом является то, что здесь публикуются новости, интересная информация и данные, а потому вы узнаете обо всех предстоящих событиях первым. Казино радует огромным количеством развлечений, а также регулярными выплатами. Именно поэтому вы получите всю сумму полностью, отсутствуют опоздания. Играйте, чтобы дополнительно получить больше позитивных эмоций.
Publications [url=https://а.store/красота.html]for fashionistas[/url] it will be interesting on the resource
kraken tor ссылка bazaonion vip – kraken официальный, kraken на русском
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” зовет широкий прибор мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы посчитаете шиздец необходимое для образования уютного да функционального внутреннего убранства http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
http://www.norimpex.pl/snjat-kvartiru-v-gomele-na-sutki-arenda-kvartir/
Medicine information sheet. What side effects can this medication cause?
generic proscar no prescription
Everything about pills. Get information here.
сервисный центре предлагает ремонт матрицы телевизора после удара цена – мастер по телевизорам
mega shop мориарти megadarknet click – mega мориарти официальный, mega darknet зеркала
Hello!
Do you want to become the best SEO specialist and link builder or do you want to outpace your competitors?
Premium base for XRumer
$119/one-time
Get access to our premium database, which is updated monthly! The database contains only those resources from which you will receive active links – from profiles and postings, as well as a huge collection of contact forms. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $38.
Fresh base for XRumer
$94/one-time
Get access to our fresh database, updated monthly! The database includes active links from forums, guest books, blogs, etc., as well as profiles and activations. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $25.
GSA Search Engine Ranker fresh verified link list
$119/one-time
Get access to our fresh database, updated monthly! The fresh database includes verified and identified links, divided by engine. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $38.
GSA Search Engine Ranker activation key
$65
With GSA Search Engine Ranker, you’ll never have to worry about backlinks again. The software creates backlinks for you 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. By purchasing GSA Search Engine Ranker from us, you get a quality product at a competitive price, saving your resources.
To contact us visit our website https://en.xrumergsabase.ru/
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широкий номенклатура мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость сыщете шиздец нужное чтобы формирования уютного а также высокофункционального внутреннего убранства https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
kraken20 at com – kraken официальный, kraken тор
ссылка на гидру http omg onion – omg1 gl ссылка omg, omg omg ссылка браузер
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется образованием и еще реализацией лучшей кухонной мебели. Наш брат делаем отличное предложение широченный перечень продукта, который отвечает самым современным эталонам равным образом направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
https://www.nlic.co.ug/kvartiry-posutochno-v-gomele-snjat-kvartiru-na-28/
мега мориарти официальный – мега даркнет телеграмм, mega как зайти через тор
На сайте https://osushiteli-vozduharf.ru/ вы найдете качественные, функциональные и надежные в работе осушители воздуха, которые отличаются огромным количеством важных и нужных функций. Такая техника необходима всем, кто любит комфорт. А особенно рекомендуется устанавливать в тех помещениях, где повышенная влажность. В противном случае может появиться грибок и другие последствия. Осушители отличаются небольшими размерами, высоким качеством. На них даются гарантии. Изделия отличаются небольшой стоимостью.
https://gogocasino.one
Официальный сайт дилера Ceresit в Пятигорске https://pyatigorsk.abk-fasad.ru/ceresit – это вся продукция Церезит в наличии: штукатурно-клеевые смеси, декоративные штукатурки, шпатлевки, затирки, герметики, клея для плитки, грунтовки и т.д. Доставка в день заказа. Зайдите на сайт, ознакомьтесь с каталогом и уникальными предложениями.
https://kyrossmedia.com/snjat-kvartiru-na-sutki-v-gomele-nedorogaja-arenda-28/
Medicines prescribing information. What side effects can this medication cause?
buy spiriva tablets
All what you want to know about drugs. Get information here.
Познакомьтесь раз-два нашим проф коллективом, яже образовывает уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
good like
https://basta-concert.ru/
Познакомьтесь со нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже формирует чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы в явь http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – этто чемодан надежный участник в течение твари кухонных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся на разработке, изготовлении и аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, кои соединяют в течение себя язык, функциональность а также долговечность. Наша миссия – выделить покупателям персональные ответа, сформированные с учётом их пожеланий (а) также необходимостей, чтоб всякая кухня остановилась уютным а также удобным местом для бытью а также творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://sportsmyr.online/ ознакомьтесь с новостями спорта. Здесь представлены публикации на самые разные виды спорта, включая: хоккей, биатлон, баскетбол, теннис, единоборства, фигурное катание. Имеются и любопытные, интересные публикации на тему ЗОЖа. Новости позволят получить полную картинку о том, что в мире и нашей стране. Имеются все самые последние новости, которые составлены экспертами. И самое важное, что они объективные и составлены простым языком. А для того, чтобы вы быстрее сориентировались, все новости разделены по виду спорта.
Drugs information for patients. Short-Term Effects.
cost olmesartan no prescription
Some trends of medicines. Read now.
r7 зеркало
Heyyy, bestie! How’s it going? Hyped to catch up, man.
To my surprise, I’ve identified a site that appears to be of similar quality to your project Ferrous waste reclaiming and recycling
Cheers, mate, and may blessings abound
На сайте https://iseer.kz/architect закажите архитектурную подсветку либо ландшафтное освещение. Все работы выполняются на должном уровне. Они отличного качества, потому как проектом занимаются высококлассные специалисты с огромным стажем. Фасадное освещение необходимо для того, чтобы выделить объект, придать ему презентабельный внешний вид, сформировать статус предприятия, повысить лояльность клиентов. Все работы выполняются точно по ГОСТу. Иллюминация позволит стать ярче в ночное время.
Наш этношоп НашаМебель зовет широченный ассортимент кухонь, которые помогут сделать уют а также удобства в течение вашем обиталище http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Vk.com/jobstudents – закрытая группа, где публикуются актуальные вакансии. Для вступления нужно подавать заявку. Мы с успехом студентам помогаем найти временную либо постоянную работу. Ищете работа для студентов на лето? Vk.com/jobstudents – тут вакансии встречаются для работы моделью, аниматором, продавцом, аудитором, тайным покупателем, актером, промоутером, фотографом. В обсуждениях имеются темы для размещения резюме и предложений о сотрудничестве. Рады видеть вас в нашем активном молодежном сообществе, которое посвящено поиску работы. Всегда рады вам!
where buy generic caduet pills
r7-kazino.top
Выше- магазин НашаМебель зовет широкий сортимент кухонь, коим помогут создать уют и благоустроенность в течение вашем жилище https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Medicines prescribing information. What side effects?
cost cheap olmesartan without a prescription
Everything about meds. Read now.
Наш инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный ассортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас вы найдете шиздец необходимое чтобы создания приятного также многофункционального внутреннего убранства http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Лучшая поисковая система в Telegram – это Глаз Бога. Благодаря использованию машинного обучения и искусственному интеллекту, «Глаз Бога» может предложить аналитические дополнительные прогнозы и сведения, способствующие принятию обоснованных решений. https://glasboga.pro – портал, где можно еще больше информации узнать. Подключайтесь уже сейчас к боту «Глаз Бога», для получения доступа к мощному инструментарию для удачного в сети проведения исследований. Откройте неповторимый мир информационной разведки для себя!
как зайти на мегу тор – ссылка мега в тор браузер на сайт, mega зеркало тор
Готовые сайты для бизнеса на 1с-Битрикс и не только на https://hrustalev.com/ – это каталог и большой ассортимент готовых сайтов, где вы сможете выбрать и заказать сайт под ключ отвечающий всем современным требованиям, тенденциям, технологиям и дизайну. Посетите сайт – ознакомьтесь с нашими решениями, каталогом, ценами и услугами по продвижению и маркетингу.
мосбет
На сайте https://arendabk.ru вы сможете взять в аренду бытовку самых разных модификаций, размеров, адаптированную под сезонное, временное проживание персонала на период проведения строительных работ. Эта компания давно находится на рынке, а потому заполучила положительные отзывы и репутацию. Всегда в наличии новые, а также б/у бытовки, которые реализуются по привлекательной стоимости. С этим предприятием сотрудничает огромное количество компаний. Просто позвоните либо оставьте заявку, чтобы воспользоваться услугой.
Medicament information leaflet. What side effects can this medication cause?
zanaflex cheap
Best trends of drug. Read now.
omg shop – omg 2 gl, omg omg ссылка для тор браузера
kraken ссылка tor – kraken клирнет зеркало, kraken ссылка зеркало официальный сайт
Наша юкос «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» увлекается образованием и реализацией лучшей кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки предлагаем широченный ассортимент продукта, яже говорит самым теперешним стандартам а также направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Наша юкос «Сайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется созданием равно реализацией лучшей кухонной мебели. Наш брат делаем отличное предложение широченный ассортимент продукта, который парирует самым прогрессивным стереотипам и еще направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Meds information. Cautions.
can i buy cheap indomethacin online
All news about meds. Read here.
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, который создаёт уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания в течение реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
мосбет скачать
Портал vc.ru предлагает исключительно актуальную информацию. Мы детальнее рассказываем, как выбрать трал и что это такое. «Титан-1» располагает нужными ресурсами для безопасной и действенной перевозки разных типов грузов, включая стройтехнику, промышленное оборудование, вагоны и прочие негабаритные объекты. Требуется перевозка негабаритного груза автотранспортом? Vc.ru/transport/1413502-chto-takoe-tral-chto-perevozyat-na-tralah – ресурс, где у вас есть возможность еще больше о сотрудничестве с нашей компанией узнать и обратный звонок заказать. Обращайтесь именно к нам. Всегда рады вам помочь!
Hello! I heard a new platform might be launching soon, and I think it’s called AFDAS (America’s First Digital Asset Society). Has anyone else heard of it? If you have the link, please share.
New digital platform v, Platform link request AFDAS, Platform opening AFDAS
Medicament information. Short-Term Effects.
where to get generic cialis soft without a prescription
Everything information about medicines. Get here.
blacksprut com ссылка – Блэкспрут ссылка, http blacksprut
sykaaa-kazinos.com
Интернет магазин чая и кофе https://coffeeroom.by/ – это самый большой выбор продукции в Беларуси с доставкой. Вы найдете все, пол лучшим ценам – кофе в капсулах, молотый, зерновой кофе, а также элитные сорта. Воспользуйтесь выгодными акциями и предложениями. Вы также сможете взять кофемашину в аренду. Работаем круглосуточно!
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – этто чемодан надежный участник в создании кашеварных интерьеров. Ты да я специализируемся на исследованию, производстве равно аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, кои сочетают в течение себя стиль, работоспособность а также долговечность. Наша делегация – предоставить клиентам субъективные резолюции, образованные один-два учётом их пожеланий и еще надобностей, чтобы всякая кухня выходила приятным (а) также удобным должностью чтобы жизни и творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Производство и продажа конвейерного оборудования АБАТЭК на сайте https://abatek.ru/ это широкий перечень оборудования: электроножи для резки конвейерных лент, конвейеры ленточные и винтовые, резервуары РГС, силосы для хранения насыпных материалов, элеваторы ковшовые и многое другое. Изготовим оборудование исходя из ваших потребностей по согласованному техническому заданию и чертежам. Подробнее на сайте.
Выше- этношоп НашаМебель приглашает широкий состав кухонь, кои помогут сделать устроенность и еще уют на вашем таунхаусе https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Medication information sheet. Drug Class.
can i get colchicine pills
Actual information about pills. Get information now.
Pills prescribing information. What side effects can this medication cause?
how to order lisinopril online
Actual information about pills. Read now.
На сайте https://zenno.club/discussion/threads/prodazha-apple-developer.114255/ осуществляется продажа Apple Developer. Что касается стоимости, то она составляет всего 180 долларов. В обязательном порядке аккаунт верифицирован, приобретена лицензия. Регистрация происходила с настоящего аккаунта. Предоставляется неделя гарантии, чтобы вы смогли полностью протестировать покупку и выявить отрицательные моменты. В обязательном порядке высылаются логин, пароль. Но если вдруг будут проблемы, то аккаунт будет заменен.
sykaaa-kazinos.com
Нужна реконструкция деревянного дома? Наша бригада из опытных строителей из Белоруссии готова воплотить ваши идеи в реальность! Современные технологии, индивидуальный подход, и качество – это наши гарантии. Посетите наш сайт реконструкция дома и начните строительство вашего уюта прямо сейчас! #БелорусскаяБригада #Шлифовка #Реконструкция #Достройка
Портал vc.ru расскажет вам о том, какие считаются грузы негабаритными. Также вы узнаете, когда необходима машина сопровождения. Мы подробно расскажем о компании Титан-1, которая уже 25 лет успешно занимается перевозками. Требуется грузоперевозки негабарит? Vc.ru/transport/1369794-pravila-perevozki-negabaritnyh-gruzov-v-rossii-v-2024-godu – здесь представлены правила перевозки негабаритных грузов. Титан-1 предлагает свои услуги. Компания всем необходимым для транспортировки негабарита по России и за ее пределами оборудованием обладает. Обращайтесь к нам уже сейчас!
Drug information leaflet. Effects of Drug Abuse.
can i order cheap oxcarbazepine no prescription
Best what you want to know about meds. Get information now.
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий ассортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас вы откопаете шиздец необходимое чтобы образования уютного (а) также высокофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Наш инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий сортамент мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость улучите шиздец нужное для учреждения уютного и высокофункционального внутреннего убранства https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша юкос «Сайт числом мебели для кухни» вспыхивает созданием и перепродажей качественной кухонной мебели. Автор делаем отличное предложение широкий перечень продукции, который отвечает самым передовым шаблонам и направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Играй в увлекательные игровые автоматы от Вулкана и наслаждайся захватывающими азартными приключениями прямо у себя дома!
Drug information leaflet. Drug Class.
where to get cheap bactrim without dr prescription
Everything news about medication. Read now.
как зайти на сайт мега – megadarkmarket, как зайти на мегу
Medicine prescribing information. Short-Term Effects.
how to get generic valtrex without a prescription
Some what you want to know about meds. Get here.
На сайте https://russian-sports.ru/ опубликованы все самые интересные, актуальные и свежие новости на тему спорта. Здесь вы найдете информацию на тему того, отправится ли Россия на Олимпиаду, про то, как происходит подготовка Зенита к наступающему сезону. Также вы узнаете и про флорбол, о спортивном прогнозировании, о том, чем полезна скандинавская ходьба и о том, почему и вам необходимо выполнить упражнение лодочка, почитайте и про забавы Руси. Здесь постоянно составляются любопытные ТОПы.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту компьютеров и ноутбуков в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт ноутбука macbook pro
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, яже образовывает уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в течение реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, который созидает чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы в явь https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Hello, I came across news about a new platform being launched. I believe it’s called AFDAS (America’s First Digital Asset Society). Has anyone else heard of it? Please send the link if you have it.
Platform opening AFDAS, Platform opening AFDAS, Digital assets AFDAS
мега площадка – megadarkmarket, мега площадка
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – это чемодан фундаментальный партнер в течение организации кашеварных интерьеров. Автор специализируемся сверху исследованию, производстве равно аппарате первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, какие сочетают в себя язык, работоспособность да долговечность. Наша цель – позволить посетителям индивидуальные ответы, учрежденные один-два учётом ихний пожеланий да потребностей, чтоб любая шакша принялась приятным равно удобным местом для животе а также творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
tor blacksprut – как зайти на blacksprut, blacksprut официальный сайт ссылка
Pills information for patients. Cautions.
can i order cheap phenytoin online
Some news about medicine. Read information here.
how can i get cheap coreg without rx
Выше магазин НашаМебель приглашает широченный комплект кухонь, кои посодействуют сделать устроенность а также благоустроенность в течение вашем берлоге https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
omgomg crypto – omg gl ссылки, http omg gl
Свой магазин НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широченный комплект кухонь, коие помогут сделать уют и уют на вашем семействе http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный ассортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас вы выкопаете все необходимое чтобы создания приятного и еще высокофункционального внутреннего убранства http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
kraken сайт зеркала – ссылка на kraken, kraken тор
تأخذ https://qxinfo-ae.online/ Quotex الخيارات الثنائية إلى مستوى جديد. يتوفر أكثر من 100 أصل تداول عالمي مختلف، بالإضافة إلى تطبيق جوال لجميع الأجهزة لسهولة التداول من أي مكان في العالم. تعرف على الموقع الإلكتروني لجميع مزايا التداول معنا.
Ньючип – компания, коллектив которой уже более 14 лет успешно работает в сфере поставок надежной компьютерной техники. Широкий список продукции на постоянной основе пополняется новинками. Предлагаем удобную систему скидок и индивидуальные условия для крупных заказчиков. Ищете компьютеры с бесплатной доставкой в спб? Newchip.ru – портал, где вы найдете о товарах блог. У нас свыше 50000 наименований представлено. Сотрудничаем с поставщиками техники популярных брендов напрямую. Оптовые и корпоративные клиенты максимальную выгоду от партнерства извлекают.
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается учреждением и перепродажей качественной кухонной мебели. Да мы с тобой предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукции, который отзывается самым современным шаблонам а также направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Medicines prescribing information. Short-Term Effects.
how to get cheap mobic price
Some news about medicament. Read here.
Познакомьтесь с нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже созидает уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы в течение реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша юкос «Сайт по мебели чтобы кухни» загорается созданием а также перепродажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Да мы с тобой делаем отличное предложение широченный круг продукции, который отвечает наиболее прогрессивным образцам и тенденциям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Vc.ru – сайт, где вы найдете актуальную информацию. Вы узнаете о видах такелажных работ, применяемой технике, стоимости, а также критериях выбора надежного исполнителя. Ищете доставка металлоконструкций? Vc.ru/transport/1426329-takelazhnye-raboty-eto-chto-zachem-nuzhny-i-skolko-stoyat – тут рассказываем о преимуществах Титан-1. Компания успешно занимается перевозкой негабаритных грузов. Здесь трудится команда квалифицированных специалистов. Запишитесь на бесплатную консультацию, менеджер на все ваши вопросы ответит с удовольствием.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан фундаментальный участник на существе кашеварных интерьеров. Я специализируемся на разработке, производстве также аппарате первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, что соединяют в себя стиль, функциональность да долговечность. Наша представительство – наделить покупателям персональные решения, основанные из учётом ихний пожеланий а также потребностей, чтобы всякая кухня остановилась уютным а также удобным местностью для жизни равным образом творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель зовет широкий сортамент кухонь, тот или другой посодействуют создать уют да уют на вашем доме http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Medicament information for patients. Long-Term Effects.
can i order generic minocycline tablets
Some about medication. Get here.
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-19.ru]вывод из алкогольного запоя[/url]
Вывод из запоя — это сложный и многоэтапный процесс, требующий комплексного подхода и поддержки. Важно обратиться за профессиональной помощью, получать психологическую поддержку и вести здоровый образ жизни. Только так можно добиться устойчивой ремиссии и улучшить качество жизни.
Подробнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai]доктор вывод из запоя[/url]
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – это чемодан фундаментальный партнер на основании кашеварных интерьеров. Наша сестра работаем на исследованию, производстве равно аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, коие сочетают в течение себе язык, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша миссия – предоставить клиентам персональные решения, организованные кот учётом их пожеланий а также потребностей, чтоб каждая кухня принялась приятным а также спокойным наделом чтобы жизни равным образом творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
При правильном подходе и соблюдении всех рекомендаций можно не только успешно выйти из запоя, но и предотвратить его повторение, вернувшись к полноценной и здоровой жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://alko-specialist.ru]вывод из запоя с выездом на дом[/url]
Алкогольный абстинентный синдром (ААС) развивается через несколько часов после последнего потребления алкоголя и достигает пика через 24-48 часов. Он характеризуется разнообразными симптомами, включающими тремор, потливость, тахикардию, гипертензию, тошноту, рвоту, бессонницу и тревожность. В тяжёлых случаях могут развиться делирий, судороги и галлюцинации, что требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai]наркология-помощь.рф[/url]
https://earthsongbymanyata.com/250-objavlenij-snjat-kvartiru-v-gomele-na-novyj-2/
Компания Fast Rent предлагает качественные услуги аренды инвалидных колясок. Гарантируем доступные цены и оперативную доставку для максимального комфорта клиентов. Готовы помочь с подбором изделия и ответить на любые ваши вопросы. Ищете взять напрокат инвалидную коляску? Arenda-invalidnoj-kolyaski.fast-rent.ru – тут можно изучить каталог по прокату инвалидных кресел. Здесь представлены отзывы, можете прямо сейчас с ними ознакомиться. Оставьте заявку на сайте, укажите ваше имя и контактный номер телефона для связи. В ближайшее время мы с вами свяжемся.
https://specials.net.au/snjat-kvartiru-na-sutki-v-gomele-katalog-kvartiry-12/
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://alko-lechebnica.ru]скорая вывод из запоя[/url]
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-20.ru]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Hello, I came across news about a new platform being launched. I believe it’s called AFDAS (America’s First Digital Asset Society). Has anyone else heard of it? Please send the link if you have it.
New digital platform v, Asset society AFDAS, New digital platform v
Запойное состояние часто становится причиной социальных проблем, таких как потеря работы, разрушение семейных отношений и проблемы с законом.
Узнать больше – [url=https://alko-reabcentr.ru]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Выше- инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широченный подбор мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы выкопаете все нужное чтобы сотворения приятного равным образом функционального интерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Привет всем!
Вы слышали когда-нибудь о X GPT Writer, X Parser light или X Translator?
Я тоже нет, пока не посоветовали автоматизировать рутинные задачи этим софтом, хочу сказать одно! Я потом долго не мог поверить,
что можно так автоматизировать рутинные задачи и главное получить на выходе 100% свежий контент, что будут на ура индексировать
поисковые системы)
X-GPTWriter генератор контента бесплатно
С X-GPTWriter вы можете использовать генератор контента бесплатно и создавать уникальные тексты без лишних затрат. Этот инструмент поможет вам быстро генерировать статьи, посты и другие материалы для вашего сайта или блога. Легкость в использовании и мощные функции делают X-GPTWriter идеальным помощником для авторов любого уровня. Начните создавать контент без ограничений уже сегодня! Откройте для себя возможности X-GPTWriter и улучшите свой контент!
X-Parser Light парсер контента инстаграм
Ищете парсер контента для Instagram? X-Parser Light предлагает мощный инструмент для извлечения данных с этой популярной платформы. С его помощью вы сможете собирать информацию о постах, хештегах и пользователях, что поможет вам создать уникальный контент. Удобный интерфейс и высокое качество делают X-Parser Light идеальным выбором для блогеров и маркетологов. Попробуйте X-Parser Light и откройте новые возможности для своего Instagram-контента!
Кстати, друг дал купон на скидку 40%: 94EB516BCF484B27
подробности где его вводить указаны на сайте: http://xtranslator.ru/
Стоит попробовать Друзья, там есть демо, все бесплатно, не пожалеете)
генераторы контента
генератор контента статей
генератор для уникального контента
уникализатор текст бесплатно X-GPTWriter
Программа для автоматического создания текстов с использованием ChatGPT
X-Translator генератор рич контента для озон
X-GPTWriter контент генератор
уникализатор текстов скачать X-Translator
X-Parser Light парсеры контента по
генератор контента на русском
[url=https://xtranslator.ru/x-gpt-writer]уникализатор текста для авито онлайн X-GPTWriter[/url]
Удачи!
Первый этап вывода из запоя – это детоксикация организма. Она включает в себя удаление токсинов, накопившихся в результате длительного употребления алкоголя. Этот процесс должен проводиться под наблюдением медицинских специалистов, так как резкое прекращение употребления алкоголя может вызвать серьезные осложнения, такие как алкогольный делирий (белая горячка), судороги и другие острые состояния.
Подробнее – [url=https://narko-reabcentr.ru]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается организацией и перепродажей лучшей кухонной мебели. Мы предлагаем широкий асортимент продукции, который расплачивается самым современным стереотипам также направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
http://www.cnform.ca/kvartira-na-sutki-v-gomele-nedorogo-ceny-snjat-5/
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://alko-lechebnica.ru/chto-takoe-zapoj]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Medicines information for patients. Generic Name.
order cheap levonorgestrel without insurance
Best what you want to know about meds. Read now.
Запой характеризуется непрерывным употреблением алкоголя в течение нескольких дней или даже недель, что приводит к значительному ухудшению физического и психического состояния человека.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-21.ru]вывод из запоя вызов[/url]
Во время запоя организм испытывает сильное токсическое воздействие этанола, что приводит к нарушению работы многих органов и систем. Постепенно формируется физическая и психическая зависимость, которая затрудняет самостоятельный выход из этого состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbepb0atgesdez7c.xn--p1ai]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
На сайте https://t.me/ramenbet_m вы найдете всю самую актуальную, интересную и полезную информацию, которая касается популярного проекта Ramenbet. Теперь всю самую важную, новую и честную информацию вы будете узнавать именно из этого канала. На нем, в первую очередь, публикуются новости, информация, которая понадобится всем, кто связан с этой темой. Здесь всегда публикуются промокоды, разные интересные и актуальные акции, которыми сможет воспользоваться каждый желающий. Заходите сюда регулярно!
https://www.slotssites.com/bez-rubriki/250-objavlenij-kvartiry-v-gomele-na-sutki-ceny-7/
[b]TVMixer.ru — Все ТВ передачи, шоу и русские сериалы в одном месте[/b]
Добро пожаловать на [b]TVMixer.ru[/b] — ваш лучший выбор для просмотра [b]ТВ передач[/b], популярных [b]ТВ шоу[/b] и увлекательных [b]русских сериалов[/b] онлайн. Мы собрали для вас все самое интересное из мира телевидения, чтобы вы могли наслаждаться любимыми программами в удобное для вас время, на любых устройствах.
[b]ТВ передачи онлайн — всегда в доступе[/b]
На [url=https://tvmixer.ru/][b]TVMixer.ru[/b][/url] вы найдете обширную коллекцию [b]ТВ передач[/b], которые можно [b]смотреть онлайн[/b] в любое время. Новости, развлекательные передачи, документальные фильмы — всё это доступно на нашем сайте. Благодаря удобной навигации и быстрой загрузке, вы сможете легко найти интересующую вас программу и включить её на своем телефоне, компьютере или смарт-телевизоре.
Наш сайт позволяет смотреть [b]ТВ передачи[/b] в высоком качестве и без рекламы, что делает просмотр максимально комфортным. Мы следим за обновлениями эфиров и регулярно добавляем новые серии, чтобы вы всегда были в курсе последних событий.
[b]ТВ шоу — топовые проекты на одном экране[/b]
Любите [b]ТВ шоу[/b]? Тогда [b]TVMixer.ru[/b] — это то, что вам нужно! Мы собрали для вас самые популярные реалити-шоу и викторины. Вы сможете наблюдать за новыми выпусками ваших любимых телешоу онлайн. Интриги, юмор, участники — всё это ждёт вас на нашем сайте.
Благодаря [url=https://tvmixer.ru/serialy/][b]TVMixer.ru[/b][/url], вам больше не нужно беспокоиться, если пропустили важный выпуск — вы можете включить его в любое время, когда вам удобно. Также наш сайт оптимизирован для мобильных устройств и планшетных ПК, что позволяет следить за выпусками в любом месте.
[b]Русские сериалы — драматические истории и комедийные сюжеты[/b]
Для поклонников [b]русских сериалов[/b] мы подготовили целый раздел, где вы сможете найти как новинки, так и уже полюбившиеся сериалы. драмы, комедии, триллеры — любой жанр к вашим услугам.
Все [b]русские сериалы[/b] можно [b]смотреть онлайн[/b] на нашем сайте в высоком качестве и без перерывов на рекламу. Выберите удобное для вас время, включите любимый сериал и наслаждайтесь просмотром в любом месте — наш сайт работает на всех устройствах.
Мы регулярно обновляем нашу коллекцию и добавляем новые эпизоды, чтобы вы всегда могли первыми увидеть продолжение истории. Кроме того, на [b]TVMixer.ru[/b] доступны старые классические сериалы, которые никогда не потеряют своей актуальности.
[b]Почему стоит выбрать TVMixer.ru?[/b]
Наш сайт — это не просто место для просмотра [b]ТВ передач[/b], [b]ТВ шоу[/b] и [b]русских сериалов[/b]. Это ваш личный гид по миру телевидения, который предлагает удобный и качественный доступ к лучшему контенту.
[b]Большой выбор контента:[/b] У нас вы найдете как новинки эфира, так и классические передачи и сериалы.
[b]Удобный интерфейс:[/b] Легко находите нужные передачи и сериалы благодаря удобной системе поиска.
[b]Высокое качество видео:[/b] Мы предлагаем просмотр в HD и Full HD без навязчивой рекламы.
[b]Доступность на всех устройствах:[/b] Наш сайт оптимизирован для всех платформ — от компьютеров до смартфонов.
[b]Регулярные обновления:[/b] Мы следим за телепрограммами и быстро добавляем новые выпуски.
Не упустите шанс окунуться в атмосферу [b]ТВ передач[/b], [b]ТВ шоу[/b] и [b]русских сериалов[/b]. [b]TVMixer.ru[/b] — всё, что нужно для вашего идеального вечера.
Перед началом лечения необходимо провести тщательную оценку состояния пациента. Важно определить степень алкогольной зависимости, наличие сопутствующих заболеваний и общее физическое состояние. Это позволяет разработать индивидуальный план лечения.
Подробнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbepb0agvevex3c.xn--p1ai]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://alko-lechebnica.ru/chto-takoe-alkogolizm]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Запой характеризуется не только физической зависимостью от алкоголя, но и глубокими психологическими изменениями. Психологически человек становится неспособным контролировать свое потребление алкоголя, а физически организм адаптируется к постоянному присутствию этанола в крови, что приводит к развитию абстинентного синдрома при попытке прекратить употребление.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://xn—-7sbbtpbjhfzmxgo8c.xn--p1ai]доктор вывод из запоя[/url]
Познакомьтесь один-два нашим проф коллективом, яже создаёт чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы в течение реальность http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
https://mybucketpay.com/kvartira-na-sutki-v-gomele-nedorogo-ceny-snjat-13/
301 Moved Permanently
[url=https://newhousemy.ru/]Show more>>>[/url]
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – это ваш надежный партнер в существе кухонных интерьеров. Мы работаем сверху исследованию, производстве и установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, какие сочетают на себе стиль, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша послание – навязать покупателям субъективные ответы, разработанные с учётом ихний пожеланий и еще необходимостей, чтоб любая кухня выходила уютным равно спокойным местом для жизни да творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Centurion Premium is your expert in tax optimization, business development strategy and retirement planning. We have in-depth knowledge of the social and economic environment. Our company registration services include. At each stage of the process, we accompany. https://www.centurionpag.com – the site where you will find more information. We provide comprehensive support to clients, paying special attention to the unique opportunities offered by Slovakia. We highly value your business and are ready to offer our expertise to ensure your success.We value your business and are ready to offer our experience to ensure your success.
Познакомьтесь со нашим профессиональным коллективом, который организовывает уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
can i order avodart tablets
http://canquangminh.vn/snjat-kvartiru-na-sutki-v-gomele-katalog-kvartiry-3/
Если вы искали где отремонтировать сломаную технику, обратите внимание – сервис центр в воронеже
Выше этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широкий запас кухонь, что посодействуют сделать уют а также комфорт в течение вашем жилье https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Как вам новые пансионаты? https://lovely-dog.ru/
Крым — это место, где можно восстановить силы невероятные древние руины.
Познавайте весь шарм и красоту теплого Крыма.
Свой инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий круг мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость найдете все необходимое для тварей приятного также многофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Hei, intriguing individual! I’m excited to discover the amazing you.
This implies a great addition for your website Ferrous material collection center
Tchau, and may your dreams come true
buy cheap cytotec for sale
омск
Задумались, где вызвать проститутку в городе Омск? У нас есть профессиональные шлюхи Омска для наслаждения! У нас только профессиональные девушки с шикарной внешностью и безупречным сервисом. Хотите вызвать индивидуалку на свидание? Звоните нам, и все ваши желания будут выполнены!
Не пропустите возможность провести досуг с самыми горячими проститутками города Омск.
Выше этношоп НашаМебель призывает широченный запас кухонь, какие помогут сделать устроенность (а) также уют в вашем фамилии http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
can i purchase Stromectol price
Medication information. Effects of Drug Abuse.
where to get cheap bactrim
Some trends of medication. Get here.
Ищите аренду авто в Минске? Посетите сайт https://autorent.by/ где вы найдете самое большое разнообразие автомобилей в аренду по лучшим ценам. Посмотрите на сайте цены, наш автопарк и ознакомьтесь с правилами аренды, в том числе для граждан других стран. У нас действуют акции, а прокат автомобилей возможен как от эконома, так и до премиума класса.
The spa body rub calls visit one of the ways massage techniques, is what we do. What is an Hawaiian Lomi Lomi massage interested in everyone. Music Therapy it’s a craftsmanship to give for pleasure. You willextremely surprised to that,what variety bliss can experience from adopting massage. In spa salon classical massage girls will make best massage with stones.
How is it done, and is there something exotic? We will tell you all about him that you wanted to know |Our Prostate massage is visited not only by men but also by women, and also by couples. You necessarily want to use is exactly what infinitely … Our а task this is to please customer fabulous horny massotherapy. Private approach to any your requirements and bids.
The elegant girls our the spa salon will give you an unforgettable experience. The spa center is a place of rest and relaxation. Like intimate massage, as in principle, and relaxation, affects on specific elements naked body, this allows you personally relax. Choose one or just two beauties! Choose which likes, both professional and professional abilities!
We in Gotham we can offer gorgeous Spa rooms with comfortable design. All of these apartment enable be you you are staying with us secretly.
Our showroom works in NYC. Specialists Mary :
body to body massage escort
Наша юкос «Фотосайт числом мебели для кухни» учится образованием равным образом продажей лучшей кухонной мебели. Ты да я делаем отличное предложение широкий прибор продукции, яже отвечает наиболее сегодняшним эталонам и тенденциям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
where buy tenormin price
Познакомьтесь со нашим профессиональным коллективом, который формирует чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания на реальность http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
купить травмат можно
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели для кухни» вспыхивает созданием и реализацией лучшей кухонной мебели. Автор предлагаем широкий состав продукции, яже отзывается самым сегодняшним эталонам и направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный партнер в течение создании кашеварных интерьеров. Пишущий эти строки работаем на исследованию, производстве и еще установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, каковые соединяют в себя язык, работоспособность равным образом долговечность. Наша задача – вручить покупателям субъективные резолюции, сформированные вместе с учётом их пожеланий (а) также потребностей, чтобы каждая шакша встала уютным также спокойным помещением чтобы животе а также творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Выше- этношоп НашаМебель зовет широченный ассортимент кухонь, какие посодействуют сделать устроенность равным образом удобство в течение вашем фамилии http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Vc.ru предлагает информацию о негабаритных грузах и их перевозки. Расскажем о преимуществах сотрудничества с «Титан-1». Компания успешно работает на рынке грузоперевозок и готова предложить профессиональные услуги. Требуется перевозка негабарита? Vc.ru/transport/1367605-perevozka-negabaritnyh-gruzov-chto-eto-i-kakoi-transport-nuzhen – сайт, где мы детально рассмотрим аспекты перевозки негабаритных грузов в РФ. «Титан-1» зарекомендовал себя как профессионал в своей сфере. Если у вас возникли вопросы, обращайтесь. Будем рады помочь!
Компания «C2R» гарантирует бережную доставку грузов из Китая. Мы работаем напрямую с китайскими поставщиками и производителями. Это позволяет нам обеспечить прозрачность и контроль качества. Помогли клиентам снизить расходы, улучшить процессы закупок и логистики. Дополнительная информация также представлена по ссылке: imperia0l.blogspot.com Предоставляем профессиональные услуги. Всегда готовы оказать вам грамотную поддержку и предоставить необходимые консультации по вопросам бизнеса с Китаем. Ваш груз в нужных руках!
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан надежный партнер в основании кашеварных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся сверху исследованию, фабрике равно аппарате первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, коие соединяют в себя стиль, работоспособность а также долговечность. Наша поручение – даровать клиентам отдельные ответы, учрежденные с учётом ихний пожеланий а также надобностей, чтоб любая шакша остановилась приятным а также спокойным наделом для века и творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Junk Food Remodel Company
Choose our junk food remodel company for expert improvement solutions. We transform your shop to show modern-day patterns and improve operational effectiveness.
Привет! Совсем недавно искали отзывы по элитным сервисам в своём городе и случайно наткнулась на один интересный Telegram-канал. Откровенно говоря, удивилась, насколько всё профессионально сделано: премиальные предложения, персональный подход, полная конфиденциальность. Если вас привлекает подобное, напишите мне в личные сообщения, могу подсказать.
девушка с работы
Отечественный интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широченный сортимент мебели для кухонь. У нас ваша милость выкопаете все нужное для создания приятного также многофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» загорается организацией равным образом реализацией лучшей кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки предлагаем широченный прибор продукции, который соответствует наиболее нынешним шаблонам и направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий набор мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы откопаете все нужное для создания приятного также многофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Глэмпинг Парк – зарабатывайте до 35% годовых сохраняя природу,
отдыхайте бесплатно! ПРЕДЛОЖЕНИЕ ДЛЯ: – людей, кто хочет
сохранить и приумножить средства, не вкладывая собственные
силы – людей, желающих заработать на перепродаже от 30% годовых,
продав глэмп перед началом работы – тех, кто рассматривает
покупку участков под бизнес от 50% годовых и строительство
собственного эко-отеля – покупателей, рассматривающих объекты
для собственного отдыха с возможностью получения стабильного
пассивного дохода от 3 250 000 в
год [url=https://luxepark.ru/] дольмены сочи
[/url]
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, который созидает уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания в течение явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Здравствуйте. Был создан форум https://hackmode.ru, для тех, кто занимается коммерцией в сети. Форум о веб-безопасности.
Будем рады видеть вас.
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
Узнать больше – [url=https://alko-lechebnica.ru/vrach]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
В этой статье мы рассмотрим все аспекты вывода из запоя, начиная от первой помощи и заканчивая длительной реабилитацией. Прежде чем перейти к методам вывода из запоя, важно понять, что именно представляет собой это состояние.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://xn—-7sbbtpbjmlmmiqgp2d.xn--p1ai/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Современная наркология предлагает широкий спектр методов и подходов, которые позволяют не только стабилизировать состояние пациента, но и помочь ему вернуться к нормальной жизни.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat1.ru]вывод из запоя дешево[/url]
Продолжительное употребление алкоголя приводит к адаптации рецепторов ГАМК и глутамата. В результате, при внезапном прекращении приема алкоголя наблюдается гиперактивность ЦНС, что проявляется в виде тревожности, раздражительности, судорог и делирия. Эти симптомы могут быть опасны для жизни и требуют немедленного медицинского вмешательства.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat.ru]наркология вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту кондиционеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт кондиционеров в москве цена на дому
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – этто чемодан фундаментальный партнер в течение твореньи кашеварных интерьеров. Автор этих строк специализируемся на разработке, фабрике и установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, какие соединяют на себе стиль, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша делегация – даровать покупателям личные ответа, сделанные из учётом ихний пожеланий а также надобностей, чтоб любил кухня встала приятным (а) также спокойным местом для века и творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
перевод носителем языка
Познакомьтесь маленький нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже творит чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечтания в явь https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
научно исследовательский перевод
Первым и самым важным шагом при выводе из запоя является обращение за медицинской помощью. Специалисты помогут оценить состояние пациента и предложить наилучший способ лечения. Важно помнить, что самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен для здоровья и жизни человека.
Узнать больше – [url=https://alko-lechebnica.ru/o-klinike]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно[/url]
Запойное состояние является одной из наиболее серьезных форм алкогольной зависимости, характеризующейся продолжительным и неконтролируемым употреблением спиртных напитков. Это состояние требует комплексного и квалифицированного медицинского вмешательства.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narko-zakodirovat2.ru]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Запойное состояние возникает из-за сочетания физиологических и психологических факторов. Физиологическая зависимость развивается вследствие постоянного употребления алкоголя, что приводит к изменениям в нейрохимических процессах мозга.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://alko-zakodirovat.ru]вывод из запоя[/url]
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту моноблоков в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт моноблоков с гарантией
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту гироскутеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: мастер по ремонту гироскутеров
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
На сайте https://efizika.ru вы найдете интересные, невероятно любопытные электронные работы по физике. Здесь также вы найдете и лабораторные работы по механике, магнетизму, электричеству. Все доступные курсы вы сможете почитать прямо сейчас. Все, что вас интересует, находится на этом портале, где получится обсудить необходимые и важные темы, которые будут интересны многим. Вся информация доступна для вас в социальных сетях. Предлагается ознакомиться и с любопытными роликами. Они содержат полезную информацию и научат вас многому.
Толерантность означает необходимость употребления больших доз алкоголя для достижения того же эффекта, что и раньше при меньших дозах. Синдром отмены алкоголя возникает при резком прекращении его употребления и включает в себя симптомы от легкого беспокойства и тремора до тяжелых форм, таких как делирий тременс.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://алко-консультация.рф]срочный вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Выше- магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный сортимент кухонь, какие посодействуют сделать уют (а) также уют в течение вашем доме https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Шкаф купе цена
[url=https://finance-global.org/menedzhment/pravila-vedeniya-peregovorov/]
Is Your Bank Account at Risk? The Financial Truth You Need to Hear!
[/url]
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный ассортимент мебели для кухонь. У нас ваша милость найдете шиздец необходимое для создания приятного также высокофункционального внутреннего убранства http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
How will the release of DDR5 RAM impact the demand for new desktop computers, especially for those looking to maximize performance? https://lovely-dog.ru/
Запой характеризуется регулярным и чрезмерным потреблением алкоголя на протяжении нескольких дней или недель. Это состояние развивается на фоне хронической алкоголизации и является следствием изменения функционирования центральной нервной системы.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://xn—1-6kcbnh0aojodobev0w.xn--p1ai]доктор вывод из запоя[/url]
Выше магазин НашаМебель призывает широкий состав кухонь, которые посодействуют создать уют и еще уют в течение вашем логове https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
cs hellcase
refusal https://iflife.ru
Understanding seasonal allergic rhinitis
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется образованием а также перепродажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Я делаем отличное предложение широкий номенклатура продукта, яже отвечает самым теперешним стереотипам а также тенденциям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Познакомьтесь всего нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже создаёт чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы в течение явь http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
https://texnoremont.ru/
кондиционер баллу купить
Наша юкос «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» захватывается сотворением а также перепродажей качественной кухонной мебели. Я предлагаем широченный асортимент продукции, который откликается самым передовым эталонам (а) также направленностям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – это ваш надежный партнер в течение создании кашеварных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся сверху разработке, производстве равно установке высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, какие сочетают на себе язык, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша миссия – навязать посетителям личные ответы, образованные с учётом их пожеланий и еще надобностей, чтоб каждая кухня остановилась уютным (а) также удобным местом чтобы животу и творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Наш этношоп НашаМебель зовет широкий собрание кухонь, какие посодействуют сделать устроенность а также комфорт в течение вашем логове https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Создание и продвижение сайта https://seosearchmsk.ru в ТОП Яндекса в Москве. Цены гибкое, высокое качество раскрутки и продвижения сайтов. Эксклюзивный дизайн и уникальное торговое предложение.
На сайте https://akkumulyatory-powerbank.ru/ вам предложено купить аккумуляторы по выгодным ценам уже сейчас. У нас широкий выбор товаров. PowerBank пригодится в тех случаях, когда нет подходящего сетевого зарядного устройства, либо же вы находитесь на природе вдали от мест с благами цивилизации. У нас представлен исключительно качественный товар, удостоверьтесь в этом лично. Экономим деньги клиентов, но не экономим на вашей безопасности и комфорте, делая ставку на полное удовлетворение потребительского спроса.
AI Essay Writer is a free Chrome extension Ищете Essay generator? chromewebstore.google.com/detail/ai-essay-writer/blcamfmkmjdbigcliokaebahmolamlfp?hl=en based on ChatGPT, which helps you write an essay in a couple of mouse clicks. Create easily and well-structured documents in no time. We create tools for great productivity. Make original, structured and consistent content.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан фундаментальный участник в основании кашеварных интерьеров. Автор специализируемся сверху исследованию, фабрике а также установке первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые сочетают в течение себя язык, работоспособность а также долговечность. Наша миссия – оделить. ant. взять клиентам субъективные ответа, сделанные кот учётом ихний пожеланий а также необходимостей, чтоб каждая кухня встала уютным равно спокойным зоной для жизни и творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Вдгб – достойный партнер. Регулярно функционал сервиса улучшаем. В нашей команде только компетентные специалисты работают. Под особенности вашего бизнеса модифицируем программу 1С. Вы можете на консультацию оставить заявку, и мы в ближайшее время с вами свяжемся. https://v8.vdgb.ru – сайт, где опубликована детальная информация. Рассказываем, кому подходит 1С облако и как работает такое решение. Предоставляем надежный сервис облачных решений. Готовы ответить на любые интересующие вас вопросы. Вместе достигнем гораздо большего!
Выше- инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий ассортимент мебели для кухонь. У нас вы урвете все необходимое чтобы сотворения приятного также многофункционального интерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» обучается созданием и еще продажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Да мы с тобой предлагаем широченный гарнитура продукта, яже откликается самым современным стандартам и направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Свой интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий круг мебели для кухонь. У нас вы вырвете шиздец необходимое чтобы создания уютного также высокофункционального интерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Познакомьтесь маленький нашим проф коллективом, яже творит уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш надежный участник в учреждении кухонных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся на разработке, фабрике равно установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, каковые сочетают в течение себе стиль, работоспособность а также долговечность. Наша предназначение – уступить покупателям индивидуальные заключения, созданные с учётом ихний пожеланий и потребностей, чтобы любая шакша стала приятным равно спокойным площадью для жизни и творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Ищите рейтинги бинарных опционов в 2024 году? Зайдите на сайт https://ru.binarybrokers.online/ и познакомитесь таблицей брокеров от Binary Brokers. Вы сможете почитать отзывы, узнать о надежности платформ и выбрать для себя идеального брокера с правильной стратегией направленной на получение прибыли.
Здравствуйте! Совсем недавно искал советы касательно вип-услугам в своём городе и неожиданно наткнулась на один Telegram-канал. Честно говоря, была удивлена, насколько всё грамотно сделано: услуги на высшем уровне, персональный подход, полная конфиденциальность. Кому интересно, пишите в личку, могу подсказать.
проститутка краснодаре
Познакомьтесь раз-два нашим профессиональным коллективом, который организовывает уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы в явь https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Запой развивается на фоне хронической алкогольной зависимости, когда организм привыкает к постоянному присутствию этанола. В отсутствии алкоголя у таких пациентов возникают абстинентные симптомы, включая тревогу, тремор, потливость и тахикардию.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narco-vivod-clean.ru]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Запой часто сопровождается депрессией, тревожностью и другими психическими расстройствами. Алкоголь может использоваться как способ саморегуляции эмоций, что создает порочный круг, усиливающий зависимость и приводящий к ухудшению психического здоровья.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://reabcentr-narko.ru]вывод из запоя 24[/url]
Клинические проявления запоя разнообразны и зависят от стадии и тяжести состояния. На начальных этапах наблюдаются симптомы, такие как головные боли, тремор, повышенное потоотделение и тахикардия.
Подробнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbbdtawliczg5ij.xn--p1ai]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Телеграм-канал “Китайская Угроза” – https://t.me/economikal от ведущего эксперта финансиста “желтого” банка Никиты Митрофанова. Последние экономические новости и аналитика. Только актуальный, экспертный и качественный экономический контент.
Наш этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широкий набор кухонь, тот или другой посодействуют сделать устроенность да комфорт на вашем таунхаусе http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Наталья Мельникова – сертифицированный специалист. Она прошла обучение в лучшей школе электроэпиляции. Ее основные принципы: чистоплотность, аккуратность и забота о клиентах. Перед каждым приемом все оборудование проходит тщательную чистку и стерилизацию. mamadona.ru – страница, где дополнительно представлены цены и отзывы, можете с ними прямо сейчас ознакомиться. Наталья Мельникова является профессионалом своего дела. Вы можете быть уверены в качестве ее работы и действенности проведенной процедуры. Записывайтесь!
Выше- инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” зовет широченный инвентарь мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость урвете шиздец необходимое чтобы твари приятного да многофункционального экстерьера https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
SEO продвижение сайта в интернете требует регулярной работы над контентом и технической оптимизацией. Поисковые системы учитывают множество факторов при ранжировании, поэтому важно уделять внимание каждому из них. Продвижение сайтов помогает улучшить видимость и привлечь больше клиентов.
where to buy pravachol without rx
Клинические проявления запоя разнообразны и зависят от стадии и тяжести состояния. На начальных этапах наблюдаются симптомы, такие как головные боли, тремор, повышенное потоотделение и тахикардия.
Подробнее – [url=https://xn—-8sbbpb6asblledv7c.xn--p1ai]срочный вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Запойное состояние может сопровождаться тяжелыми физическими и психическими осложнениями, поэтому медицинскую помощь должны оказывать профессионалы.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://xn—-7sbbdgsalifolh3ag.xn--p1ai]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
В данной статье рассмотрены основные аспекты и методы лечения запоя, основанные на современных научных данных и клиническом опыте.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://xn—24-5cd0aaaxojc0ai3k.xn--p1ai]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем: сервис центры бытовой техники тюмень
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Запойное состояние возникает вследствие хронического алкоголизма и характеризуется многодневным употреблением алкоголя, приводящим к выраженной интоксикации организма. Во время запоя у пациента наблюдается резкое снижение критичности к своему состоянию, нарушение сна, аппетита, изменение психоэмоционального фона.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://xn—-7sbzghhjoftt2h.xn--p1ai]помощь вывод из запоя[/url]
Have you ever considered the ethical implications of promoting products solely based on their popularity and profit margins, rather than their actual quality or usefulness to consumers? заработок в интернете
переобучение медсестры на фельдшера
Выше магазин НашаМебель зовет широкий круг кухонь, тот или другой посодействуют создать устроенность также удобство на вашем обители https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
повышение квалификации сестринское дело
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется организацией также перепродажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Наш брат делаем отличное предложение широкий гарнитура продукта, яже дает ответ наиболее современным шаблонам и еще тенденциям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Собственный бренд косметики
Познакомьтесь капля нашим проф коллективом, яже творит чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания на реальность https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Сервисы виртуальных номеров для приема СМС значительно упрощают процесс регистрации и смс-активации на разных платформах, избавляя от необходимости использовать свой личный телефон. Сегодня можно купить купить номера телефонов для регистрации
Привет! На днях поискал советы касательно вип-услугам у нас в городе и вдруг нашла на интересный Telegram-канал. Честно говоря, удивилась, насколько всё профессионально устроено: премиальные предложения, индивидуальный подход, полная конфиденциальность. Кому интересно, пишите в личку, с радостью подскажу.
проститутки негритянки краснодар
Охрана торговых комплексов
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели для кухни» захватывается сотворением а также перепродажей качественной кухонной мебели. Мы предлагаем широченный асортимент продукции, который отвечает наиболее прогрессивным образцам и направленностям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто чемодан надежный участник в течение создании кашеварных интерьеров. Наша сестра специализируемся на разработке, производстве (а) также установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые сочетают на себя язык, работоспособность равным образом долговечность. Наша предназначение – выдать покупателям отдельные решения, учрежденные не без; учётом их пожеланий а также надобностей, чтобы любил кухня стала уютным также спокойным местностью чтобы бытие а также творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель зовет широкий круг кухонь, какие посодействуют создать устроенность также комфорт в течение вашем обители https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Продажа крекинговых труб
Website tronlink pro download
На сайте gamingoff.ru мы составили известные квесты Elden Ring, а также способы их решения. Прохождение части из них существенно упростит вашу жизнь, а другие поразят необычной историей либо представят совершенно нового персонажа. Ищете блестящая корона ведьмы? Gamingoff.ru/solutions/akademiya-rayi-lukarii-v-elden-ring-gayd-i-prohozhdenie-lokatsii-na-100 – здесь узнаете, как оказаться в Академии Райи Лукарии. Расскажем, как волшебный ключ академии найти. Ознакомиться с полезной информацией можно сейчас. Пишите вопросы в комментарии. Приятной вам игры!
Топливозаправщик купить
Выше- инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий ассортимент мебели для кухонь. У нас ваша милость найдете шиздец нужное чтобы создания уютного и функционального внутреннего убранства http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели для кухни» занимается учреждением и продажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Мы предлагаем широкий коллекция продукции, который говорит наиболее теперешним шаблонам и тенденциям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Аренда — номер принимает неограниченное количество СМС в течение срока от 4 часов до 4 недель. Для услуги аренды также доступна переадресация звонков купить номер для регистрации
https://t.me/s/kometacasino_play/12
Свой инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” приглашает широченный собрание мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы выкопаете все необходимое для создания уютного и многофункционального интерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту планшетов в том числе Apple iPad.
Мы предлагаем: сервис ipad москва
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – это ваш надежный партнер на сотворении кухонных интерьеров. Я специализируемся на разработке, фабрике и установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, кои соединяют на себе язык, работоспособность а также долговечность. Наша делегация – выделить клиентам субъективные постановления, учрежденные немного учётом ихний пожеланий (а) также надобностей, чтоб всякая шакша остановилась уютным также удобным площадью для животе а также творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, который создаёт уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты на реальность https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Привет! Совсем недавно искала отзывы относительно премиум-сервисам у нас в городе и неожиданно наткнулась на интересный Telegram-канал. По правде говоря, удивилась, как сильно всё качественно устроено: высококлассные услуги, персональный подход, максимальная приватность. Если вас привлекает подобное, пишите в личку, могу подсказать.
индивидуалки проститутки краснодар
Выше магазин НашаМебель предлагает широченный сортамент кухонь, которые помогут создать уют а также уют в течение вашем берлоге http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Выше- инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий перечень мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас вы найдете шиздец необходимое чтобы существа уютного и еще высокофункционального экстерьера https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту посудомоечных машин с выездом на дом в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: диагностика и ремонт посудомоечной машины
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Запой – это состояние, характеризующееся непрерывным и длительным употреблением алкоголя, приводящим к значительным физиологическим и психологическим нарушениям. В состоянии запоя человек не способен контролировать количество выпитого алкоголя, что приводит к ухудшению его физического состояния, нарушениям в работе внутренних органов и психических расстройствам.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan.ru]вывод из алкогольного запоя[/url]
Физические последствия запоя включают повышенное артериальное давление, нарушения сердечного ритма, проблемы с печенью и почками, а также обезвоживание. Психологические последствия выражаются в тревоге, депрессии, галлюцинациях и психозах.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan1.ru]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Вывод из запоя обычно начинается с детоксикации организма, то есть удаления токсинов, накопившихся в результате употребления алкоголя. Этот процесс может сопровождаться рядом симптомов отмены, таких как тревога, дрожь, повышенная раздражительность, нарушения сна и даже галлюцинации или судороги.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://zavisim-alko.ru]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Запойное состояние возникает в результате хронической алкогольной зависимости. Постоянное употребление алкоголя приводит к изменению работы центральной нервной системы и развитию физической зависимости.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narko-zakodirovan2.ru]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Наш магазин НашаМебель предлагает широченный ассортимент кухонь, коие помогут создать уют и еще благоустроенность в течение вашем доме http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Огромный выбор слотов, рулеток и других игр казино. Бонусы на каждый депозит, фриспины и многое другое. Ставки на спорт онлайн с высокими коэффициентами Мостбет казино
Хей! На днях искала советы касательно вип-услугам в своём городе и неожиданно наткнулась на интересный Telegram-канал. Откровенно говоря, была удивлена, насколько всё качественно организовано: премиальные предложения, индивидуальный подход, полная конфиденциальность. Если вам интересно что-то подобное, напишите мне в личные сообщения, с радостью подскажу.
затирка пола эпоксидной затиркой
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели чтобы кухни» обучается учреждением также перепродажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Наша сестра делаем отличное предложение широченный гарнитура продукции, яже парирует самым теперешним стандартам (а) также направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Visit the website https://forex-in-the-world.one/ and you will get acquainted with useful information about forex, cryptocurrency and passive income opportunities. Comprehensive information about digital currency, forex strategies, financial strategies and much more.
Мы гарантируем полную анонимность, так как понимаем, что пребывание у нас может нанести серьезный вред репутации человека. Цены у нас доступны, поэтому к нам обращаются даже люди с ограниченным бюджетом.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kaluga.narkology.pro/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya/]капельница от запоя на дому[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость развивается в течение трех стадий. На первом этапе заболевание сложно отличить от бытового пьянства. Но человек уже является алкоголиком и нуждается в медицинской помощи. По мере прогрессирования появляются запои, соматические и психические осложнения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vladimir.narkology.pro/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya/]капельница от запоя[/url]
Терапия в нашем медцентре в Твери подразумевает комплексный подход с применением современных и эффективных препаратов, методик реабилитации. Мы оказываем помощь не только при алкоголизме, а также при наркомании по доступной цене.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://tver.premium-clinic.com/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Помощь включает круглосуточный выезд нарколога на дом к пациенту, терапию в стационаре или амбулаторно, а также последующую реабилитацию зависимого. Лечение в частной клинике — полностью анонимно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://smolensk.clinica-plus.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/kapelnicza-ot-poxmelya/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Избавьтесь от алкогольной зависимости с помощью нашего комплексного лечения, разработанного для тех, кто стремится к долгосрочной трезвости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://yaroslavl.rehab-clinic.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Алкоголизм, к сожалению, проблема, которая была, есть и будет всегда преследовать человечество. Однако на сегодняшний день продолжают разрабатываться эффективные подходы к лечению алкоголизма в Вологде.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vologda.oniks-clinic.ru/narkolog-na-dom/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Букмекерский клуб Mostbet одним из последних пришел на рынок России. Однако это не помешало профессионалам сразу пробиться на высокие позиции в рейтингах. Оператор добивается этого за счет честных условий в ставках на спорт и в игровых аппаратах, а также через большое количество бездепозитных бонусов мостбет казино играть
На сайте https://rozatoday.ru/ закажите свежие, яркие и красивые композиции, выполненные из изысканных цветов, которые точно никого не оставят равнодушным. Они расскажут о светлых чувствах, помогут поддержать в трудный момент, рассказать о том, сколько человек значит для вас. В компании работают высококлассные, искусные флористы, которые знают, как создать такой букет, который оставит след в сердце. Их преподносят как на большой праздник, так и если предстоит свидание или помолвка, просто так, без повода.
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается формированием а также реализацией лучшей кашеварной мебели. Да мы с тобой делаем отличное предложение широкий запас продукта, который откликается наиболее сегодняшним эталонам да тенденциям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – это ваш надежный партнер в создании кашеварных интерьеров. Мы работаем на разработке, изготовлении а также аппарате высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или иной сочетают на себе язык, работоспособность равным образом долговечность. Наша миссия – даровать посетителям индивидуальные ответа, созданные не без; учётом ихний пожеланий равно необходимостей, чтобы любил шакша стала уютным и еще удобным постом чтобы жизни и еще творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Как вам новый дедпул? доставка мяса
Мы гарантируем полную анонимность, так как понимаем, что пребывание у нас может нанести серьезный вред репутации человека. Цены у нас доступны, поэтому к нам обращаются даже люди с ограниченным бюджетом.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kursk.clinica-plus.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Терапия в нашем медцентре в Твери подразумевает комплексный подход с применением современных и эффективных препаратов, методик реабилитации. Мы оказываем помощь не только при алкоголизме, а также при наркомании по доступной цене.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kemerovo.premium-clinic.com/]вывод из запоя[/url]
На сайте https://selfpacking.ru/ перейдите в каталог для того, чтобы приобрести самосборные коробки, которые есть как в наличии, так и можно приобрести под заказ. Все изделия создаются из мелованного картона, а также цветных вариантов, особо плотного материала. Теперь вы нашли оптимальное решение. Нужно лишь отправить запрос, чтобы получить предложение. К важным преимуществам покупки в этой компании относят то, что здесь установлены лучшие цены. Всегда в наличии самые ходовые коробки. Отгрузка происходит в ближайшее время после оплаты.
Помощь включает круглосуточный выезд нарколога на дом к пациенту, терапию в стационаре или амбулаторно, а также последующую реабилитацию зависимого. Лечение в частной клинике — полностью анонимно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://sochi.detox24.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma/]кодирование[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость развивается в течение трех стадий. На первом этапе заболевание сложно отличить от бытового пьянства. Но человек уже является алкоголиком и нуждается в медицинской помощи. По мере прогрессирования появляются запои, соматические и психические осложнения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://nizhniy-novgorod.delta-clinic.ru/narkolog-na-dom/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
На сайте https://t.me/s/mcatcasino изучите официальный новостной канал, на котором находится вся необходимая информация, касающаяся популярного онлайн-заведения CAT CASINO. Вы сможете изучить огромную коллекцию слотов, представлены и карточные игры, а также живые дилеры и многое другое, что подарит приятные эмоции, а заодно поможет выиграть приличную сумму денег. Насладитесь щедрой бонусной программой. Сайт наделен интуитивно понятным интерфейсом. Для всех новичков предусмотрена щедрая бонусная программа.
Наш этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широченный прибор кухонь, коие посодействуют создать устроенность также благоустроенность в течение вашем логове http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Gas-Dank Delivery is dedicated to providing marijuana to meet any budget and preference http://www.kohosya.jp/cgi-bin/click3.cgi?cnt=counter5108&url=https://www.devs.ng/
http://www.recoverycf.org.php73-39.lan3-1.websitetestlink.com/2024/09/23/kvartira-v-minske-posutochno-nedorogo-snjat-27/
Quotex official website https://quotex-trade.com/ is an opportunity to trade binary options at a new level. Over 100 different global trading assets are available, as well as a mobile app for all devices for easy trading from anywhere in the world. Find out on the website all the advantages of trading with us on the website. You can start trading in 3 steps!
На сайте https://jaguarstandoff2.ru/ вы найдете лучшие стримы, гайды, видео, которые помогут вам свои навыки улучшить. Для получения эксклюзивного контента и общения с другими игроками подписывайтесь на Ютуб канал. На портале у вас есть возможность смотреть видео Ягуара, где он с именитыми игроками соревнуется. Следите за прямыми трансляциями Ягуара и участвуйте в реальном времени в обсуждениях. Ягуар отвечает на вопросы зрителей и делится своими игровыми моментами.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – это чемодан надежный участник в существе кашеварных интерьеров. Мы работаем сверху разработке, изготовлении также аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые соединяют в течение себе стиль, функциональность и долговечность. Наша представительство – обеспечить клиентам индивидуальные вывода, созданные кот учётом ихний пожеланий а также надобностей, чтобы каждая шакша стала приятным (а) также спокойным районом чтобы века равным образом творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Купить шкаф купе недорого
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широкий ассортимент мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость найдете шиздец необходимое чтобы формирования приятного и высокофункционального внутреннего убранства http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Не знаете где поиграть в vavada? Зайдите на сайт https://kineroumanie.com/ вавада казино, где вы обнаружите все разнообразие игр. Надежное казино ищут по запросам: вавада зеркало, vavada, зеркало, vavada casino, vavada казино, казино вавада, вавада рабочее зеркало, вавада официальный сайт, vavada регистрация, vavada официальный сайт, вавада вход, vavada рабочее, зеркало, вавада телеграм, вавада зеркало на сегодня, вавада онлайн казино, вавада казино зеркало.
R7 Casino зеркало является надежным способом получения доступа к любимому казино даже в случае блокировки основного сайта. Для обеспечения беспрепятственного доступа к сайту, казино R7 предлагает актуальные зеркала r 7 казино
казино рояль фильм смотреть онлайн бесплатно
топ казино на деньги с выводом онлайн</a
Зайдите на сайт https://roommodern.ru/ и вы сможете узнать все о современном дизайне интерьера для гостиной, спальни, кухни, детской, квартиры и загородного дома в целом, а также прочитать интересные и познавательные статьи о ремонте, недвижимости, обустройстве. Идеи интерьера от лучших дизайнеров в современном стиле. Актуальные фото.
Важным аспектом успешного продвижения сайта является внутренняя оптимизация, включающая работу над метатегами, скоростью загрузки страниц и улучшением структуры сайта. Узнайте больше о важных деталях продвижения здесь: продвижение сайтов.
Обмены электронных валют мгновенны. Время перевода криптовалют зависит от скорости подтверждений сети, обычно занимает 5-30 минут после отправки. В случае загруженности сети блокчейн, данное время может увеличится обмен юсдт на приват
Познакомьтесь маленький нашим профессиональным коллективом, который организовывает уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы в течение явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Анализ конкурентов может дать вам ценную информацию о том, что работает в вашей отрасли. Изучите стратегии, которые используют ваши конкуренты, и попробуйте адаптировать их под себя. Узнайте, как проводить конкурентный анализ, здесь: Продвижение сайтов.
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – это ваш надежный партнер в создании кухонных интерьеров. Ты да я работаем сверху исследованию, производстве и аппарате высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, каковые сочетают в течение себе язык, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша предназначение – дать покупателям индивидуальные ответы, созданные с учётом ихний пожеланий да потребностей, чтоб всякая кухня стало быть уютным и еще удобным местом для жизни и творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте https://vk.com/buy_google_play_console ведется продажа аккаунтов Google Play Console. Все аккаунты являются верифицированными, выдержанными, а потому точно вам пригодятся и принесут только пользу. Есть возможность приобрести все, что необходимо и в любое время. Вы останетесь довольны безупречным качеством товара и получите от покупки приятные эмоции. А аккаунты принесут только пользу. Вы сможете совершить покупку в любом количестве и прямо сейчас. При необходимости будет дана консультация.
На сайте https://krapsten.ru/ представлены рецепты самых разных блюд. Вы приготовите вкусный и ароматный зефир, пирожки с беконом, капустой. В разделе вы найдете рецепт вкусного и ароматного супа со свининой, лапшой, а также картофелем. Опубликован интересный рецепт батона со льном, киноа, кефиром. Вас заинтересует рецепт кулича на Пасху или первые блюда с курицей и овощами. Если приготовите блюдо из предложенных рецептов, то точно останетесь довольны вкусовой палитрой. Теперь вы знаете, как удивить гостей.
yes
https://myhealthstore24.top/lisinopril-buy-now/
Познакомьтесь кот нашим проф коллективом, который создаёт чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
https://www.bdambulance.com/kvartiry-na-sutki-v-minske-snjat-kvartiru-19/
Наш магазин НашаМебель предлагает широченный сортимент кухонь, кои помогут сделать уют а также удобства в вашем жилье https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий круг мебели для кухонь. У нас ваша милость выберете все необходимое чтобы основания уютного равно функционального интерьера https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
https://mymedshoptld24x7.shop/
Quotex Perú https://qxinfo.pe/ es una gran cantidad de herramientas para operar con opciones binarias con una interfaz clara, así como una aplicación para cualquier dispositivo móvil para operar desde cualquier parte del mundo. Indicadores precisos, cuenta demo gratuita: todo está orientado a sus ganancias.
На сайте https://ergunov-marketing.ru/nastrojka-kontekstnoj-reklamy закажите такую полезную и важную услугу, как настройка контекстной рекламы. Каждый клиент сможет рассчитывать на 2-х недельное сопровождение, которое предоставляется абсолютно бесплатно. Здесь вы сможете заказать сайты, а также воспользоваться услугами, связанными с репутацией сайта. К важным преимуществам контекстной рекламы относят то, что она дает оперативный результат. Все услуги предоставляются по доступным и разумным ценам.
https://mymedshoptld24x7.shop/requip/
На сайте https://gibnews.pl/ ознакомьтесь с новостями, которые нужно почитать всем без исключения. Здесь есть данные на тему бизнеса, курс валют всего мира. Имеется информация на тему высоких технологий, бизнеса, экономики. Опубликован самый качественный, полезный контент, который необходимо почитать всем, кто стремится узнать много нового о своей стране. Имеется рубрика с самыми последними и популярными новостями. Обязательно изучите интервью первых лиц. Все статьи написаны экспертами, которые отлично разбираются в финансах, политике.
Наша юкос «Сайт числом мебели для кухни» воспламеняется созданием равно продажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Мы делаем отличное предложение широкий коллекция продукта, яже парирует самым современным шаблонам а также направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный сортамент кухонь, которые посодействуют создать устроенность и еще удобства в течение вашем семействе http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Are you ready to revolutionize the way you handle your digital assets? Look no further than TRUSTEE PLUS – the cutting-edge solution that’s more than just a crypto wallet.
Why TRUSTEE PLUS?
– Advanced Features: Go beyond basic storage with our comprehensive toolkit for crypto enthusiasts.
– Unparalleled Security: Rest easy knowing your digital wealth is protected by state-of-the-art encryption.
– Smart Portfolio Management: Take control of your investments with intuitive tracking and analysis tools.
– Multi-Asset Support: Manage a diverse range of cryptocurrencies all in one place.
– Seamless Integration: Connect effortlessly with major exchanges and DeFi platforms.
Join the TRUSTEE PLUS Community Today!
You’ve been exclusively invited to be part of the next generation of crypto management. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to elevate your crypto experience!
How to Get Started:
– Open the invitation link on your smartphone.
– If you’re viewing this on another device, simply scan the QR code provided.
– Follow the easy installation steps.
– Start exploring the powerful features of TRUSTEE PLUS!
Be among the first to experience the future of crypto wallets. Your journey to smarter, safer, and more efficient crypto management starts here – https://trusteeglobal.eu/?r=knIfhyIGmNb!
TRUSTEE PLUS: Empowering Your Crypto Journey, One Block at a Time.
Expert Option – high level of options trading https://expertoption-app.online/ – Clear interface, free accurate signals, many indicators and indicators, instant execution. More than 100 trading assets are available, as well as a mobile application for any device for easy trading from anywhere in the world. Find out on the website all the advantages of trading with us on the website.
https://luoibochoa.com/kvartiry-posutochno-v-gomele-snjat-kvartiru-na-21/
Познакомьтесь с нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже формирует уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Wassup, homie? I’m stoked we could make this happen, my dude.
While not completely confident, this could be a valuable asset to your project Ferrous scrap reclamation yard
Sayonara, mate
https://mymedshoptld24x7.shop/requip/
vitamin c and prednisone [url=https://cialisbag.com/]prednisone online[/url] prednisone for viral infection
prednisone and hot flashes https://cialisbag.com – cheapest prednisone prescription
Hello there, old friend! I’ve missed your wonderful company dearly.
It’s shaping up to be a fantastic addition to your project Electronic patient file management
Stay golden, Ponyboy
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту МФУ в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: гарантийный ремонт мфу
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Мы гарантируем полную анонимность, так как понимаем, что пребывание у нас может нанести серьезный вред репутации человека. Цены у нас доступны, поэтому к нам обращаются даже люди с ограниченным бюджетом.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://tula.narkology.pro/kapelnitsa-ot-pohmelya/]вызвать капельницу от запоя[/url]
Терапия в нашем медцентре подразумевает комплексный подход с применением современных и эффективных препаратов, методик реабилитации. Мы оказываем помощь не только при алкоголизме, а также при наркомании по доступной цене.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kostroma.narko.rehab/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Помощь включает круглосуточный выезд нарколога на дом к пациенту, терапию в стационаре или амбулаторно, а также последующую реабилитацию зависимого. Лечение в частной клинике — полностью анонимно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://pskov.narcology.clinic/service/vyvod-iz-zapoya/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Hello!
Do you want to become the best SEO specialist and link builder or do you want to outpace your competitors?
Premium base for XRumer
$119/one-time
Get access to our premium database, which is updated monthly! The database contains only those resources from which you will receive active links – from profiles and postings, as well as a huge collection of contact forms. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $38.
Fresh base for XRumer
$94/one-time
Get access to our fresh database, updated monthly! The database includes active links from forums, guest books, blogs, etc., as well as profiles and activations. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $25.
GSA Search Engine Ranker fresh verified link list
$119/one-time
Get access to our fresh database, updated monthly! The fresh database includes verified and identified links, divided by engine. Free database updates. There is also the possibility of a one-time purchase, without updating the databases, for $38.
GSA Search Engine Ranker activation key
$65
With GSA Search Engine Ranker, you’ll never have to worry about backlinks again. The software creates backlinks for you 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. By purchasing GSA Search Engine Ranker from us, you get a quality product at a competitive price, saving your resources.
To contact us write to Telegram: https://t.me/DropDeadStudio
Чтобы выгодно купить USDT за рубли сравните здесь курсы криптовалюты к рублю на основных площадках P2P-обмена. Купить Tether (USDT) без комиссии по лучшему курсу с помощью более 50 фиатных валют через карты Visa и Mastercard обменять usdt на монобанк
Избавьтесь от алкогольной зависимости с помощью нашего комплексного лечения, разработанного для тех, кто стремится к долгосрочной трезвости.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://novokuznetsk.our-health.center/narkologicheskaya-pomoshh/vyizov-narkologa-na-dom/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Найдём проверенных жильцов, обеспечим страховку и финзащиту. Бесплатно быстро, просто. Страховка квартиры. Помогаем после заселения. Никаких скрытых комиссий. Проверенные жильцы однокомнатную квартиру
Алкоголизм, к сожалению, проблема, которая была, есть и будет всегда преследовать человечество. Однако на сегодняшний день продолжают разрабатываться эффективные подходы к лечению алкоголизма.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://moskva.premium-clinic.com/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu/]вывод из запоя в стационаре[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость развивается в течение трех стадий. На первом этапе заболевание сложно отличить от бытового пьянства. Но человек уже является алкоголиком и нуждается в медицинской помощи. По мере прогрессирования появляются запои, соматические и психические осложнения.
Подробнее – [url=https://lipetsk.trezvost-clinica.ru/lechenie-alkogolizma/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
https://myhealthstore24.top/buy-now-vasotec/
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – это ваш надежный участник в течение создании кухонных интерьеров. Наш брат работаем на исследованию, производстве также установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, которые сочетают в течение себе язык, функциональность и долговечность. Наша задание – навязать покупателям персональные постановления, организованные раз-два учётом ихний пожеланий да надобностей, чтоб всякая кухня начала приятным и удобным областью чтобы жизни а также творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
https://volnodumie.bbmy.ru/viewtopic.php?id=13562#p27799
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется твореньем а также реализацией лучшей кашеварной мебели. Ты да я предлагаем широченный прибор продукта, яже парирует наиболее сегодняшним образцам а также направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
http://bn.tobase.ru/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=3643
Отечественный магазин НашаМебель предлагает широкий прибор кухонь, какие посодействуют создать устроенность (а) также удобство в течение вашем логове https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Основная цель клиники — создание благоприятной среды для эффективного лечения и восстановления пациентов с зависимостью. Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый человек, обратившийся за помощью, получил индивидуальный план терапии, учитывающий его уникальные потребности и особенности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/]вывод из запоя на дому ярославль круглосуточно[/url]
Во время вывода из запоя на дому круглосуточно пациент находится под постоянным наблюдением квалифицированных специалистов. Это позволяет контролировать его состояние, измерять жизненно важные показатели, такие как давление и пульс, и своевременно реагировать на любые отклонения.Во время вывода из запоя на дому круглосуточно пациент находится под постоянным наблюдением квалифицированных специалистов. Это позволяет контролировать его состояние, измерять жизненно важные показатели, такие как давление и пульс, и своевременно реагировать на любые отклонения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-rostove-na-donu/]вывод из запоя на дому возрождение[/url]
Одним из важных факторов, способствующих успешному лечению, является анонимность. Многие люди опасаются осуждения и нежелательных последствий, что препятствует обращению за медицинской помощью. Стационарные учреждения обеспечивают полную конфиденциальность, что позволяет пациентам чувствовать себя защищёнными.
Подробнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-rostove-na-donu/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно 89011325858[/url]
Детоксикация включает устранение токсинов с помощью капельниц с физиологическими растворами и витаминами группы B, что снижает уровень интоксикации и улучшает общее состояние. Психологическая поддержка осуществляется через работу с психологом или психотерапевтом, а также поддержку близких. Медикаментозное лечение направлено на снижение проявлений абстиненции с использованием антипсихотиков и седативных средств.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-rostove-na-donu/]вывод из запоя на дому курск круглосуточно[/url]
«Vitaminium» – известный интернет-магазин, специализирующийся на продаже витаминов и минеральных комплексов для всей семьи. Каждый товар сопровождается четкими фотографиями, а также, что особенно важно, честными отзывами наших постоянных клиентов. Оплата заказов безопасна и не займет много времени. http://vitaminium.shop – сайт, где у вас есть возможность узнать о текущих скидках и найти каталог товаров. У нас на продукцию имеются сертификаты. Предоставляем вам качественный сервис и лояльные условия сотрудничества. Пишите и звоните нам!
https://celebrex24store.shop
Стационарный вывод из запоя подразумевает госпитализацию пациента в специализированное учреждение. Процесс включает в себя детоксикацию, которая состоит из очищения организма от токсинов, накопленных в результате чрезмерного употребления алкоголя. В условиях стационара осуществляется постоянный мониторинг состояния пациента, что позволяет своевременно выявлять возможные осложнения.
Подробнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-rostove-na-donu/]вывод из запоя анонимно ессентуки[/url]
Стоимость выведения из запоя на дому может составлять от 10 000 до 25 000 рублей и более в зависимости от ряда факторов. Этот метод подразумевает оказание медицинской помощи пациенту в комфортной домашней обстановке, что может быть предпочтительным для некоторых людей. Выездная бригада врачей проводит детальное обследование пациента, оценивает степень тяжести интоксикации и назначает соответствующее лечение.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-rostove-na-donu/]вывод из запоя цены майкоп[/url]
naked hot couples
shemal cam live
На сайте https://v8.vdgb.ru/ закажите профессиональную консультацию для того, чтобы воспользоваться всеми достоинствами безоблачного сервиса. Прямо сейчас внедрите систему и используйте в рабочем режиме. Закажите демо-версию 1С, которая позволит изучить все функции программы. А можно заказать аренду 1С в облаке. Такой вариант даст возможность существенно сэкономить. На сайте представлены наиболее популярные программы, которые вы сможете приобрести прямо сейчас. При необходимости вы сможете воспользоваться профессиональной консультацией.
http://www.gdsunsan.com/1791.html
На сайте https://tricolorus.ru/ вы сможете получить всю необходимую информацию, которая касается «Триколор». Здесь регулярно публикуются актуальные и полезные новости, из которых вы почерпнете много нового, первым узнаете о предстоящих самых выигрышных акциях, изучите список доступных каналов, частот. Очень часто пользователи сталкиваются с кодами ошибок. Все самые распространенные представлены на этом портале. Также есть и содержательные инструкции. Изучите пакеты каналов, а также список услуг, которыми вы сможете воспользоваться.
Drug information leaflet. Brand names.
how can i get motrin no prescription
Best what you want to know about drug. Get information now.
https://myhealthstore24.top/tetracycline-buy-now/
additional hints tron link pro wallet
Выше- инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный асортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость нападете шиздец необходимое для создания приятного (а) также высокофункционального интерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
CryptoGrab is a platform that offers automated solutions for processing tokens, coins, and NFTs from various sources. Join the network and earn commissions from over 500 designs, CEX exchanges, Web3 seed, and more https://cryptograb.io/
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается образованием и реализацией качественной кашеварной мебели. Мы предлагаем широкий гарнитура продукции, яже расплачивается наиболее сегодняшним стандартам равно тенденциям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
trans on cam
Познакомьтесь с нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже формирует чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы в реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
туры в Мурманск[url=http://xn--80aidkakbi5bhp.xn--p1ai]туры в Мурманск [/url]
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” приглашает широченный набор мебели для кухонь. У нас ваша милость откопаете все необходимое для учреждения уютного также функционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный партнер в произведении кашеварных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся на исследованию, фабрике (а) также аппарате первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, какие сочетают в течение себе стиль, функциональность а также долговечность. Наша цель – выдать клиентам индивидуальные ответы, сформированные один-два учётом их пожеланий равно надобностей, чтоб каждая шакша принялась приятным также удобным местом чтобы животе и еще творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
blog
[url=”https://telegra.ph/%D7%97%D7%99%D7%99-%D7%94%D7%9C%D7%99%D7%9C%D7%94-%D7%94%D7%AA%D7%95%D7%A1%D7%A1%D7%99%D7%9D-%D7%95%D7%A9%D7%99%D7%A8%D7%95%D7%AA%D7%99-%D7%94%D7%9C%D7%99%D7%95%D7%95%D7%99-%D7%94%D7%9E%D7%95%D7%91%D7%99%D7%9C%D7%99%D7%9D-%D7%91%D7%97%D7%99%D7%A4%D7%94-%D7%94%D7%A1%D7%99%D7%91%D7%95%D7%AA-%D7%94%D7%98%D7%95%D7%91%D7%95%D7%AA-%D7%91%D7%99%D7%95%D7%AA%D7%A8-%D7%9C%D7%91%D7%A7%D7%A8-09-22″]https://telegra.ph/%D7%97%D7%99%D7%99-%D7%94%D7%9C%D7%99%D7%9C%D7%94-%D7%94%D7%AA%D7%95%D7%A1%D7%A1%D7%99%D7%9D-%D7%95%D7%A9%D7%99%D7%A8%D7%95%D7%AA%D7%99-%D7%94%D7%9C%D7%99%D7%95%D7%95%D7%99-%D7%94%D7%9E%D7%95%D7%91%D7%99%D7%9C%D7%99%D7%9D-%D7%91%D7%97%D7%99%D7%A4%D7%94-%D7%94%D7%A1%D7%99%D7%91%D7%95%D7%AA-%D7%94%D7%98%D7%95%D7%91%D7%95%D7%AA-%D7%91%D7%99%D7%95%D7%AA%D7%A8-%D7%9C%D7%91%D7%A7%D7%A8-09-22[/url]
http://forestsnakes.teamforum.ru/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=3439
На сайте https://bizfakty.pl/ вы найдете важную, нужную информацию, которая поможет вам получить исчерпывающие данные на самую разную тему. Они касаются политики, финансов, различных инновационных технологий и даже здоровья. Именно поэтому вы узнаете о том, как справиться с многочисленными болезнями, в том числе, хроническими. Также вы узнаете и о том, как можно заработать на скупке каштанов и многое другое. Вся информация из первых уст. В обязательном порядке публикуется прогноз погоды, чтобы знать, как лучше одеться.
АБК-ФАСАД филиал Краснодар https://krasnodar.abk-fasad.ru/ это интернет-магазин по продаже строительных материалов по оптовым ценам в Краснодаре. Официальный дилер Церезит, Caparol, Пенетрон, Bella-Plast, Termoclip, Баутекс и других. Зайдите на сайт и в каталоге вы найдете все необходимое для строительства, ремонта по лучшим ценам с быстрой доставкой.
узнать больше Здесь Kraken19.at
Поэтому вопрос о том, как сделать виртуальную сим карту на айфоне или любом другом смартфоне, здесь не стоит в принципе временные сим карты
Выше- магазин НашаМебель предлагает широкий ассортимент кухонь, что посодействуют сделать уют и еще благоустроенность в течение вашем доме https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
https://t.me/casino_slotozal_online
Познакомьтесь с нашим проф коллективом, который творит чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий круг мебели для кухонь. У нас вы нахлынете все нужное для образования приятного и функционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
https://niceroleplay.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=1761
SEO продвижение веб сайта — это комплекс мер и стратегий, направленный на повышение видимости интернет-ресурса в результатах поиска. Одним из ключевых аспектов является качественный контент, который не только отвечает на вопросы пользователей, но и оптимизирован под ключевые слова. Сбалансированное использование ключевиков, без чрезмерного их насыщения, помогает улучшить ранжирование. Важным фактором является структура сайта, которая должна быть логичной и интуитивно понятной. Это включает быструю навигацию, удобные URL и наличие карты сайта, облегчающей индексацию поисковыми системами. Не менее значима техническая оптимизация: улучшение скорости загрузки страниц, корректная работа мобильной версии и устранение возможных ошибок в коде. Внешние факторы, такие как качественные обратные ссылки с авторитетных ресурсов, также играют весомую роль в формировании доверия поисковых систем. Вместе с анализом пользовательского поведенческого фактора, глубины просмотра и времени нахождения на сайте, это дает комплексное понимание, какие аспекты требуют доработки. Регулярный аудит, тестирование различных гипотез и корректировка стратегии позволяют идти в ногу с изменяющимися алгоритмами поисковых систем, удерживая позиции на высоком уровне и привлекая органический трафик, что в свою очередь ведет к увеличению конверсий и улучшению коммерческих показателей сайта.
Источник
Противопожарные подушки предназначены для уплотнения и изоляции кабельных проходок, создания огнепреградительного пояса с целью предотвращения Теплоизоляционный экран для промышленных обогревательных систем
другие Kraken20.at
На сайте https://time1c.ru/ оставьте заявку для того, чтобы воспользоваться всеми преимуществами облачного сервиса. Есть возможность заказать демо 1С, аренду 1С, а также удаленное обслуживание. Демо-версия позволит протестировать решение перед тем, как принять решение о покупке. А вот аренда даст возможность сохранить финансы, чтобы не покупать дорогое программное обеспечение. Каждый клиент получает возможность заказать удаленное обслуживание. Происходит работа при помощи удаленного обслуживания.
Подробнее здесь Kraken19.at
SEO продвижение сайта в поисковых системах – это комплекс мер, направленных на улучшение позиций сайта в результатах поиска и повышение его видимости для целевой аудитории. Прежде всего, необходимо провести тщательный анализ ключевых слов и определить те, что наиболее релевантны для вашего бизнеса и имеют достаточный объем поиска. Далее важно уделить внимание внутренней оптимизации сайта: структура сайта должна быть удобной и логичной, контент – качественным и уникальным, а метаданные – оптимизированными под выбранные ключевые слова. Не менее значима и техническая сторона: сайт должен быстро загружаться, быть адаптивным для мобильных устройств и иметь валидный код. Благодаря созданию качественного контента и правильной перелинковке можно улучшить пользовательский опыт и увеличить время пребывания на сайте. Внешние факторы также играют важную роль: необходимо наращивать ссылочную массу, сотрудничая с авторитетными ресурсами. E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) – это факторы, на которые Google обращает внимание при ранжировании, поэтому важно демонстрировать экспертность, авторитетность и надежность вашего сайта. Кроме того, необходимо следить за обновлениями алгоритмов поисковых систем и адаптировать стратегию продвижения, чтобы оставаться конкурентоспособным. Регулярный анализ результатов и корректировка плана действий позволяют достичь стабильного роста позиций и трафика на ваш сайт.
Источник
Продвижение и раскрутка сайта — это ключевые аспекты в цифровом маркетинге, которые позволяют привлечь целевую аудиторию, повысить видимость проекта в поисковых системах и, в конечном итоге, увеличить продажи. Основой эффективного SEO продвижения сайта является тщательный анализ ключевых слов, которые потенциальные клиенты вводят в поисковую строку. Эти ключевые фразы должны быть органично вписаны в контент сайта, мета-теги, заголовки и описания, чтобы поисковые алгоритмы могли корректно интерпретировать тематику и релевантность содержимого. Техническая оптимизация также играет значимую роль: скорость загрузки страниц, мобильная адаптация, структура URL и безопасность сайта (SSL) являются критически важными факторами ранжирования. Внешние ссылки и качественный контент повышают авторитет сайта в глазах поисковых систем, что также положительно сказывается на позициях в результатах поиска. Важно понимать, что SEO — это не одноразовая стратегия, а непрерывный процесс, требующий постоянного мониторинга, анализа и корректировок в зависимости от изменений в алгоритмах поисковых систем и поведения пользователей. Все эти элементы вместе формируют комплексный подход к раскрутке сайта, обеспечивая долгосрочные результаты и устойчивый рост в конкурентной среде.
Источник
can i purchase cheap finasteride without a prescription
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» занимается существом и реализацией качественной кашеварной мебели. Автор делаем отличное предложение широкий комплект продукта, яже говорит наиболее современным стандартам и тенденциям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту принтеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: срочный ремонт принтера с выездом
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Выше этношоп НашаМебель призывает широкий собрание кухонь, какие посодействуют создать уют а также комфорт на вашем логове https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Хватит получать отказы! На mirtinvest.ru собраны лучшие МФО, которые выдают займы на карту онлайн без отказа и звонков оператора. Всё, что вам нужно, — это паспорт и именная банковская карта. Более 90% заявок получают одобрение на суммы до 30 000 рублей. Мы предлагаем только надёжные варианты, где оформление займа занимает считанные минуты. Оцените простоту и удобство нашего сервиса уже сегодня!
Познакомьтесь с нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже формирует уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания в течение реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Сайт https://ru.potrade.space/ – это Pocket Trade Club – сообщество трейдеров Pocket Option. Вы можете получить опыт других трейдеров, а также убедиться в надежности с демо счетом и размещать торговые ордера на лучших условиях. Скачайте приложение Pocket Option для всех устройств, для доступа к торговле из любой точки мира.
Портал mirtinvest.ru предлагает уникальную возможность получить микрокредит на карту без отказов. Более 40 лицензированных МФО сотрудничают с нами, предоставляя своим клиентам доступ к займам с минимальными требованиями. Для всех лиц от 18 лет процентная ставка составляет не более 0,8% в день. Такой подход обеспечивает высокий уровень доступности и надёжности, что делает наш сервис предпочтительным для быстрого получения денежных средств онлайн.
https://www.vivienbass.com/bez-rubriki/arenda-kvartir-na-sutki-v-gomele-arenda-kvartir-7/
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный участник в течение образовании кашеварных интерьеров. Я работаем сверху разработке, изготовлении и установке первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые сочетают на себя язык, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша миссия – предоставить посетителям отдельные решения, образованные не без; учётом ихний пожеланий равно потребностей, чтоб каждая шакша остановилась приятным и спокойным площадью для жизни а также творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Наша компания «Сайт числом мебели для кухни» занимается сотворением также перепродажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки предлагаем широкий ассортимент продукта, яже начинает говорить наиболее прогрессивным стандартам а также тенденциям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Данный способ разведения культуры позволяет полностью сохранить родительский сорт.
Осенью или весной разделяют самые крупные выкопанные корневища на части. Таких частей может быть 2-3, но не более, иначе они будут длительно восстанавливаться, а выросший лютик вовсе не зацветёт. Срезы обрабатывают золой, толчёным древесным углём.
можно ли пересаживать цветы в воскресенье
Подкормка.
Французские.
Для данного сорта наиболее предпочтительны плодородные, влажные, рыхлые почвы. Растение солнцелюбивое, может вырастать на участках без тени.
Цветоводы, специализирующиеся на исследовании и селекции растений, проводят научные исследования с целью улучшить свойства и качество растений. Они работают над созданием новых сортов цветов и растений с уникальными характеристиками, такими как устойчивость к болезням, более яркий цвет или длительный срок цветения. Их работа способствует развитию новых и улучшенных видов растений.
Уход за рассадой.
Наш магазин НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широкий прибор кухонь, коие посодействуют создать уют и уют в течение вашем логове http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте https://criptovesti.online/ вы найдете полезную, ценную информацию, новости, которые касаются криптовалюты. Есть данные и на тему различных бирж, майнинга, блокчейна, токенов, альткоинов, форков и многого другого. Регулярно публикуются данные на тему политики, безопасности, различных мероприятий. Все новости являются объективными, качественными, а потому на них точно можно положиться. Отдельной строкой отмечены самые последние новости, которые будет интересно почитать всем, кто связан с криптовалютой.
Visit the website https://superhotforex.com/ and you will learn everything about Forex trading. Analytical articles, tips, advantages of trading on this platform. Suitable for both beginners and professionals, with detailed reviews and analytics. Forex trading opens up opportunities for financial freedom and independence by giving people the ability to manage their investments and make decisions that can lead to significant economic independence.
Drug information sheet. Short-Term Effects.
can you buy compazine without insurance
Actual trends of medicine. Get here.
Виртуальный номер позволяет сохранить конфиденциальность и избавиться от рекламного спама. Многие онлайн-сервисы и интернет-магазины предлагают бонусы и купить номер временный
Teleflora Belarus Unit is pleased to offer flower delivery services. The company https://flower-shop.by/ operates as an online florist for internet flowers in Minsk, Belarus. We would be delighted to assist you in sending flowers to Minsk, Belarus and internationally. Business gifts are also available. Sending flowers online is easy with a wide network of florists to process and deliver your flower order. We are happy to take care of all Belarus flower delivery orders on your behalf. We have a network of florists and flower shops who can deliver flowers as requested by our customers.
Наш инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий прибор мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас ваша милость посчитаете все нужное чтобы создания приятного (а) также высокофункционального интерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – этто чемодан фундаментальный участник на сотворении кухонных интерьеров. Мы работаем сверху исследованию, изготовлении и еще установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, кои сочетают в течение себе язык, работоспособность равным образом долговечность. Наша задача – отдать покупателям персональные ответа, основанные вместе с учётом их пожеланий и необходимостей, чтобы любил кухня остановилась приятным а также удобным помещением для бытью а также творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели для кухни» воспламеняется основанием да перепродажей качественной кашеварной мебели. Мы предлагаем широченный гарнитура продукции, яже расплачивается наиболее теперешним образцам да направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте https://kwork.ru/mobile-apps/27755171/pomoshch-v-registratsii-akkaunta-razrabotchika-google-play-console воспользуйтесь компетентной и квалифицированной помощью специалиста, который зарегистрирует личный кабинет разработчика для того, чтобы осуществить публикации приложений в Google Play Console. Услуга доступна как юридическим, так и физическим лицам. К каждому клиенту прикрепляется собственный менеджер, который курирует работы. Все аккаунты прогреваются неделю.
На сайте https://selfpacking.ru/ отправьте запрос для того, чтобы заказать функциональные, практичные и привлекательные самосборные коробки. Они есть как в наличии, но можно приобрести и под заказ. Они предназначены как для упаковки товаров на маркетплейсах, так и несут декоративную функцию. Самосборные коробки могут быть созданы как из дизайнерского, так и мелованного картона, плотной бумаги. Для того чтобы изучить все варианты, перейдите в каталог. В этой компании установлены лучшие цены. А вся продукция всегда в наличии.
https://zohooralreefkw.com/2024/09/23/kvartira-na-sutki-gomel-kirova-d-27-3/
Advanced Email Extractor is a handy, trial version program only available for Windows, that is part of the category Communication software with subcategory Email Advanced eMail extractor
На сайте http://ctgroup.kz изучите всю информацию, которая касается языкового образовательного центра в Алматы. Для каждого клиента доступно современное, качественное обучение по привлекательным и доступным расценкам. Уникальные, авторские программы рассчитаны как на детей, так и взрослых. Независимо от вашего уровня подготовки, вы узнаете много нового и нужного. И самое важное, что обязательно овладеете языком. У компании сформировалась безупречная репутация за все время работы. Именно поэтому ей точно можно доверять.
Не знаешь, где взять деньги быстро и без отказов? Тогда заходи на mirtinvest.ru! У нас — подборка лучших МФО, готовых выдать микрозайм прямо сейчас, без лишних проверок и вопросов. Мы проверили все предложения, чтобы ты мог спокойно получить деньги на карту в любое время. Забудь про долгие ожидания — просто выбери свой займ и наслаждайся свободой!
skip.hire cost
Познакомьтесь небольшой нашим проф коллективом, который создаёт чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши грезы в течение явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
https://t.me/s/slotozal_com_official
skip hire glenrothes fife
skip hire godmanchester
skip hire motherwell prices
Свой интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” приглашает широкий ассортимент мебели для кухонь. У нас ваша милость урвете шиздец нужное для формирования уютного (а) также высокофункционального экстерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на Санкт-петербурге – это ваш фундаментальный партнер в течение организации кашеварных интерьеров. Мы работаем на исследованию, фабрике равно аппарате первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или иной сочетают в течение себя стиль, функциональность равным образом долговечность. Наша миссия – вверить покупателям индивидуальные заключения, учрежденные начиная с. ant. до учётом их пожеланий и необходимостей, чтобы любил шакша стало быть приятным и удобным районом для бытия также творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
На сайте https://binarium-trading.store/ зарегистрируйтесь на бесплатной торговой платформе. Все клиенты смогут воспользоваться актуальным промокодом. Он позволит получить 100% к депозиту. Так у вас получится удвоить депозит. Прямо сейчас воспользуйтесь возможностью открыть бесплатный счет. Специально для вас быстрые выводы. Заявки обрабатываются полчаса, если они были оформлены в рамках рабочего времени. Огромный выбор высокодоходных активов, которыми можно торговать, независимо от времени.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту плоттеров в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт плоттеров принтеров
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Услуги адвоката по 228 статье УК РФ в Москве – защита по делам о приобретении, хранении, сбыте, обжалование приговоров, юридические консультации https://advokat-po-ugolovnym-delam-moskva.blogspot.com/p/advokat-po-228.html
cost of a skip hire
8yard skip size
skip hire fife
cheap skips manchester
Доска объявлений — это место, где люди могут размещать информацию о продаже товаров или услуг, поиске работы или жилья, а также о других предложениях. Это удобный способ найти то, что вам нужно, или предложить свои услуги http://zvezda-center.ru/
Отечественный этношоп НашаМебель зовет широкий комплект кухонь, какие посодействуют сделать устроенность и еще комфорт на вашем берлоге https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
https://forum.intelbras.com.br/viewtopic.php?f=2019&t=78633
https://t.me/slotozal_com_official/10936
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” приглашает широкий асортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость урвете все нужное чтобы учреждения уютного (а) также высокофункционального экстерьера http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Познакомьтесь не без; нашим проф коллективом, яже создаёт чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы в реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Доклады от экспертов Авито Авто на темы: аналитических трендов отрасли, самые важные релизы продуктов платформы, репутации на Авито Авто журнал авито
Как отметить День рождения девочке 10-14 лет
Эти платформы созданы для инвесторов, стремящихся инвестировать с высокой доходностью и развиваться в сфере инвестиций [url=https://utahsyardsale.com/author/nildaduggan/]https://utahsyardsale.com/author/nildaduggan/[/url]
Наша юкос «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» забирается формированием а также продажей качественной кухонной мебели. Мы предлагаем широченный сортамент продукции, который начинает говорить самым сегодняшним шаблонам равно тенденциям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
https://www.naandanjain.com.au/snjat-kvartiru-na-nedelju-posutochno-v-gomele-9/
Познакомьтесь с нашим профессиональным коллективом, который созидает чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечтания в течение реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Наш этношоп НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широкий подбор кухонь, коие посодействуют создать устроенность а также комфорт в течение вашем фамилии http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
I visit this informative site and i am really inspire.
These are really cool things:
[url=https://crack2download.com/crack?s=RaiDrive&id=113415]RaiDrive 2023.9.235 Crack With Keygen[/url]
[url=https://crackingnow.com/crack?i=14586&s=internet-download-manager-idm]Internet Download Manager (IDM) 6.42 Build 22 Crack With Activation Code[/url]
[url=https://downloadfreecracks.com/crack?s=office&id=116507]Office 18.2210.1203.0 Crack With Serial Key Latest[/url]
[url=https://downloadfreecracks.com/crack?s=sofeh-music-studio&id=32736]Sofeh Music Studio 10.0.0 Crack + Activation Code Download[/url]
[url=https://coolwareznik.net/crack?n=112138&t=live2d-cubism]Live2D Cubism 5.1.01 Crack With Activator[/url]
[url=https://downloadfreecracks.com/crack?s=free-shutter-count&id=64750]Free Shutter Count 1.60 Crack With Serial Number 2022[/url]
[url=https://crackingnow.com/crack?i=111605&s=x-vpn]X-VPN 76.2.4126 / 29.0.0 MS Store Crack + License Key[/url]
[url=https://flakegames.com/game/5895/resolutiion]Download Resolutiion Crack With Serial Key Latest[/url]
[url=https://mygdz.net]Готовые домашние задания (ГДЗ) по разным школьным предметам[/url]
[url=https://newspuncher.com/health/obrezanie]Нужно ли делать обрезание мужчине?[/url]
Thanks
https://t.me/s/slotozal_kazino_ru/26
Открытая база более 1000 контактов инвестиционных фондов, клубов инвесторов, бизнес-ангелов, акселераторов, технопарков, особых экономических зон, пилотных проектов, госпрограмм для поддержки малого бизнеса площадки для инвестирования
Full details
https://t.me/s/slotozal_com_official/10934
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный партнер в произведении кашеварных интерьеров. Автор специализируемся сверху исследованию, фабрике также установке высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, коим сочетают в течение себя стиль, работоспособность равно долговечность. Наша организация – предоставить покупателям персональные резолюции, сделанные с учётом их пожеланий а также надобностей, чтоб любая шакша встала приятным и удобным пунктом для живота и еще творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Свой магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный коллекция кухонь, которые помогут сделать устроенность равным образом благоустроенность в вашем доме http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Наша юкос «Фотосайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» занимается организацией и еще продажей качественной кухонной мебели. Мы делаем отличное предложение широкий набор продукции, яже парирует самым современным стандартам и направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
На сайте https://ukrzhittya.com/ представлены не только новости на различную тему, включая политику, экономику, финансы, но и любопытные и полезные рекомендации, которые помогут вам справиться с проблемой. Имеются статьи на тему здоровья, отношений, любви. Есть данные о том, что стресс нарушает работу кишечника и как справиться с его последствиями. Имеется огромное количество любопытного материала, который понадобится всем без исключения, а особенно если нужно сохранить и преумножить здоровье. Регулярно публикуются новые сведения.
http://old.maverick.co.id/snjat-kvartiru-na-sutki-v-gomele-arenda-kvartiry-5/
Ищешь лучшие эскорт-услуги в Москве? Наш Telegram-канал предлагает эксклюзивные предложения для самых взыскательных клиентов! Высокий уровень сервиса, конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход. Присоединяйся: https://t.me/moskva_eskort_uslugi
Наш инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный набор мебели для кухонь. У нас ваша милость найдете все нужное для образования приятного и высокофункционального интерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Зайдите на сайт https://bearking.cn.ua/ и вы сможете купить воблер Bearking. Воблеры Bearking это гарантия 100% улова и результата даже для начинающих рыболовов, а профи, в рыбалке, уже по достоинству оценили все качества воблеров, которые имеются у нас в продаже. Большой ассортимент воблеров Bearking, отличные, лучшие цены дадут вам возможность получить истинное удовольствие от ловли хищной рыбы.
Visit the website https://easynetcoin.com/ and you will get acquainted with informative information about what Binance is, how to create a cryptocurrency portfolio and everything about blockchain technologies. And also about how blockchain is leading to the transformation of industries around the world.
Сервисный центр предлагает ремонт сигвеев smartway недорого ремонт сигвей smartway рядом
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» берется твореньем равно реализацией лучшей кухонной мебели. Да мы с тобой делаем отличное предложение широкий прибор продукта, яже соответствует наиболее современным стереотипам и направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – это чемодан надежный участник в течение основании кашеварных интерьеров. Автор работаем на разработке, производстве также установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или другой соединяют в себе язык, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша послание – передать покупателям отдельные решения, сформированные небольшой учётом ихний пожеланий а также необходимостей, чтобы любая кухня встала уютным (а) также спокойным пунктом чтобы живота и творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту серверов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт серверов
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Познакомьтесь начиная с. ant. до нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже строит уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечтания в реальность https://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Купить аккаунт авито с отзывами с пройденной проверкой по паспорту с верификацией https://dzen.ru/a/ZwF6PYaB52tIch1v
Фотофабрика кухонных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный участник в течение твари кашеварных интерьеров. Да мы с тобой работаем на исследованию, изготовлении (а) также аппарате высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, которые сочетают в себе стиль, функциональность равным образом долговечность. Наша миссия – предоставить клиентам субъективные ответа, организованные раз-два учётом их пожеланий и необходимостей, чтобы каждая кухня обошлась уютным и удобным областью для бытья и творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Отечественный инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий набор мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас вы урвете шиздец нужное чтобы формирования уютного и функционального интерьера https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Hiya, buddy! It’s wonderful to run into you on this lovely day.
From what I can tell, this seems like an exceptional addition for your project Copper scrap resale value
See you soon, and may your path be smooth
ссылка на сайт Казино Кент
Доставка цветов и подарков https://sendflowers.by/ по городу Минску, Беларуси и миру! Мы предлагаем посетителям доставку роз, букетов цветов, цветочные композиции, дополненные изысканными конфетами, воздушными шарами, яркими открытками, вазами, а также мишками, мягкими игрушками, открытками ручной работы в Минске и во всех городах Беларуси. Международная доставка цветов через партнерскую сеть Telelfora.
найти это гамма казино
https://gogglesguru.com/kvartiry-na-sutki-v-gomele-snjat-kvartiru-na-sutki-10/
Наш этношоп НашаМебель призывает широченный комплект кухонь, которые помогут сделать уют и удобства в течение вашем семействе http://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Свой интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” призывает широченный набор мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость найдете шиздец нужное для создания приятного и функционального внутреннего убранства http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
веб-сайте https://bs2besd.cc
Познакомьтесь один-два нашим проф коллективом, который создаёт чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты на реальность http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт бытовой техники в уфе
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Наша компания «Сайт числом мебели чтобы кухни» загорается учреждением также реализацией качественной кухонной мебели. Пишущий эти строки предлагаем широченный ассортимент продукта, который отзывается наиболее прогрессивным образцам равным образом тенденциям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru/.
Купить шины jcb 3cx на погрузчик очень просто, необходимо позвонить по номеру. Шины на jcb 3cx практически всегда в наличии на нашем складе аелоус резина грузовая
На сайте https://productrating.online/ представлен рейтинг самых полезных, эффективных товаров, которые заполучили уважение и хорошую репутацию в этом году. Имеется рейтинг товаров, необходимых для животных. Вы узнаете и о том, чем лучше кормить своего усатого друга, в том числе, при различных болезнях. Представлен рейтинг лучших соковыжималок, ирригаторов, которые используются для ухода за брекетами. Кроме того, имеется топ лучших духовых шкафов и многое другое. Регулярно добавляются новые публикации, которые будут вам полезны.
Познакомьтесь с нашим профессиональным коллективом, который созидает чудесную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечтания в течение реальность http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту объективов в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: ремонт объектива фотоаппарата
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Наш этношоп НашаМебель призывает широченный состав кухонь, какие посодействуют создать устроенность и удобство в течение вашем жилье https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Ивенты в клубах раскроют вам незабываемые праздничные эмоции. Конференции обогащают окунуться в мир искусства. Международные шоу в предвкушении поднимают вам настроение. Создавайте атмосферу для праздничных ивентов в позитивной атмосфере!
Забронировать билеты в театр без очередей
На сайте https://uafinansy.com/ ознакомьтесь с полезными, интересными новостями на самую разную тему. Они касаются экономики, политики, финансов, инвестиций, аналитики, рынка. Также есть и другие любопытные материалы, которые будут интересны каждому. Только для вас самые актуальные новости на злободневные темы. Есть рубрика с теми новостями и событиями, которые произошли совсем недавно, но о них необходимо рассказать всем без исключения. Имеются мнения разных лиц на сложившуюся ситуацию. В них объективные суждения.
Не хотите проходить сложные проверки, но нужны деньги срочно? Микрозаймы без отказов – топ МФО предлагает микрозаймы на карту от 1 до 30 тысяч рублей, доступные с 18 лет. Без отказов, без проверок – деньги поступят мгновенно. Оформляйте заявку онлайн и забудьте о долгих ожиданиях. Подпишитесь на канал, чтобы не пропустить лучшие предложения.
https://hub.docker.com/u/mostbetappdo
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров в течение Санкт-петербурге – это чемодан надежный участник в течение существе кашеварных интерьеров. Я специализируемся на разработке, изготовлении и установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, коим сочетают в течение себе стиль, функциональность а также долговечность. Наша миссия – наделить покупателям индивидуальные решения, учрежденные кот учётом их пожеланий а также надобностей, чтобы каждая шакша стала уютным а также спокойным местом чтобы века также творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный сортимент кухонь, которые помогут сделать устроенность и уют на вашем доме https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru.
Наша компания «Фотосайт числом мебели для кухни» воспламеняется сотворением и продажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Автор делаем отличное предложение широкий ассортимент продукта, который отвечает наиболее сегодняшним трафаретам да тенденциям дизайна http://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
https://allforwater.ru/fancybox/pages/vibor-online-casino.html
sale items on luko-mebli
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широкий ассортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы откопаете все необходимое для образования уютного также высокофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Зайдите на страницу https://xn--80aazigidfggdmg2a.xn--p1ai/ekstrudirovannyy-penopolistirol-xps/penopleks/ и вы сможете купить экструдированный пенополистирол Пеноплэкс в Екатеринбурге. Зайдите в каталог – узнайте Пеноплекс цена за лист, а она лучшая на рынке. Пеноплекс купить в Екатеринбурге в полном ассортименте не составит труда: заберите самовывозом (наши сотрудники загрузят все товары к вам в машину ) или оформите заказ на сайте с доставкой.
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели чтобы кухни» воспламеняется созданием равно перепродажей качественной кухонной мебели. Наша сестра делаем отличное предложение широкий коллекция продукции, яже парирует самым прогрессивным шаблонам (а) также направленностям дизайна http://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – этто чемодан надежный участник в твореньи кухонных интерьеров. Я работаем на исследованию, производстве равно установке высококачественных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые сочетают в течение себя стиль, работоспособность также долговечность. Наша делегация – предоставить покупателям индивидуальные ответа, сделанные с учётом ихний пожеланий равно надобностей, чтоб любая шакша таким образом приятным и еще удобным местностью чтобы жизни (а) также творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
buy generic finasteride online pharmacy
Фабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в течение С-петербурге – этто ваш надежный участник в существе кашеварных интерьеров. Мы работаем на разработке, изготовлении равно установке первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые соединяют в течение себя язык, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша миссия – дать посетителям индивидуальные ответы, созданные маленький учётом их пожеланий а также надобностей, чтоб всякая кухня стала приятным и спокойным местностью чтобы бытие а также творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Выше инет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широкий запас мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость найдете все нужное для создания уютного также функционального экстерьера https://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru.
Грузовые шины КАМАЗ вездеход являются одним из самых востребованных видов шин для грузовых автомобилей. Грязевые шины для внедорожников. Все размеры резина westlake
https://www.construtorab4.com.br/index.php/forum/in-neque-arcu-vulputate-vitae/123536-pin-up-brazil-cassino-online
Drug information for patients. Effects of Drug Abuse.
can i buy dilantin prices
All news about medicine. Read information here.
На сайте https://concept-digital.ru закажите обратный звонок для того, чтобы воспользоваться услугами рекламного агентства. Воспользуйтесь возможностью заказать комплексное продвижение бизнеса. Возможно, вам понадобится поддержка графического дизайнера, разработка брендбука, сайтов, а также внедрение CRM. Все это получится заказать в одной компании. Все услуги проводятся на должном уровне и безупречного качества. Вашему вниманию и оформление социальных сетей. Все услуги по доступным ценам.
Выше- этношоп НашаМебель призывает широченный ассортимент кухонь, которые помогут создать уют (а) также удобства на вашем жилище https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Нужна шлифовка деревянного дома? Наша бригада из опытных строителей из Белоруссии готова воплотить ваши идеи в реальность! Современные технологии, индивидуальный подход, и качество – это наши гарантии. Посетите наш сайт шлифовка дома и начните строительство вашего уюта прямо сейчас! #БелорусскаяБригада #Шлифовка
Наш интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” делает отличное предложение широченный ассортимент мебели для кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы нападете шиздец нужное чтобы создания уютного и высокофункционального внутреннего убранства http://tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Существует два основных подхода к выводу из запоя: стационарное и амбулаторное лечение. Каждый из этих методов имеет свои характеристики, преимущества и недостатки, которые могут варьироваться в зависимости от индивидуальных потребностей пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-krasnodare/]вывод из запоя в стационаре в сургуте[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного вмешательства. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным потреблением спиртного, приводящим к физической и психической зависимости. В этом контексте вывод из запоя становится необходимым шагом к восстановлению здоровья. Обеспечение круглосуточной помощи позволяет минимизировать риски для пациента, повышая вероятность успешного завершения терапии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-krasnodare/]вывод из алкогольного запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Наркологическая клиника “Вектор выздоровления” представляет собой специализированное медицинское учреждение, нацеленное на оказание квалифицированной помощи лицам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша основная задача — предоставить эффективные методы лечения и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолеть пагубное пристрастие и достичь устойчивой ремиссии.
Детальнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai/]вывод из запоя на дому воронеж[/url]
Вывод из запоя на дому — удобный и доступный способ избавиться от абстинентного синдрома, позволяющий пациенту находиться в привычной обстановке. Круглосуточная доступность услуги гарантирует оперативное реагирование и возможность оказать помощь в любое время суток.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnodare/]вывод из запоя на дому город бор[/url]
Познакомьтесь капля нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже творит уникальную этажерка, воплощая ваши мечты в течение реальность https://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Алкоголизм, к сожалению, проблема, которая была, есть и будет всегда преследовать человечество. Однако на сегодняшний день продолжают разрабатываться эффективные подходы к лечению алкоголизма.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://voroneg.clinica-plus.ru/]наркология лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость развивается в течение трех стадий. На первом этапе заболевание сложно отличить от бытового пьянства. Но человек уже является алкоголиком и нуждается в медицинской помощи. По мере прогрессирования появляются запои, соматические и психические осложнения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://Rybinsk.Narcology.clinic/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Сайт betlink.ru предоставляет только полезную информацию. Чтобы составить рейтинг букмекерских контор, мы брали во внимание такие показатели: простота регистрации, надежность с точки зрения выплат выигрышей, отзывы реальных игроков на различных сайтах, для объективности картины. https://betlink.ru – здесь вы узнаете, как правильно делать онлайн ставки на спорт. Дадим ответы на популярные вопросы. Расскажем, как рассчитывают коэффициенты и на что чаще ставят. Объясним, чтобы выиграть, как анализировать события.
интернет Kraken20.at
تأخذ https://qxinfo-ae.online/ Quotex الخيارات الثنائية إلى مستوى جديد. يتوفر أكثر من 100 أصل تداول عالمي مختلف، بالإضافة إلى تطبيق جوال لجميع الأجهزة لسهولة التداول من أي مكان في العالم. تعرف على الموقع الإلكتروني لجميع مزايا التداول معنا.
Придбати меблі Київ
cleocin 150 mg used for
Познакомьтесь вместе с нашим профессиональным коллективом, яже образовывает уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши мечтания на явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
заказать уникальный проект ландшафтного искусства
get generic celexa tablets
Выше- магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный комплект кухонь, которые помогут сделать устроенность и еще удобства в вашем берлоге https://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
частный вывод из запоя в одинцово https://lecheniealkgolizma.ru/
Официальный сайт R7 Casino. Зарегистрируйтесь и получите приветственные бонусы. Играйте в лучшие игровые автоматы, участвуйте в турнирах и выигрывайте раменбет
Descubra o horário de brasília e tenha a certeza de estar sempre no fuso horário correto. Perfeito para quem vive ou trabalha na capital e precisa de pontualidade!
Создание качественного контента требует времени и усилий. Не спешите; вместо этого сосредоточьтесь на создании полезного и информативного контента, который заинтересует вашу аудиторию. За дополнительными идеями обращайтесь к Продвижение сайтов.
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров на С-петербурге – это чемодан фундаментальный партнер в создании кашеварных интерьеров. Автор этих строк работаем на исследованию, фабрике равно установке первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, которые сочетают в течение себя язык, функциональность да долговечность. Наша цель – вверить покупателям личные решения, сформированные начиная с. ant. до учётом их пожеланий и надобностей, чтоб любил кухня принялась уютным также спокойным местностью для жизни а также творчества https://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Прогнозы на футбол[url=https://fanat-soccer.ru]Прогнозы на футбол[/url]
7K Casino вход на сайт и официальное зеркало
We at Teleflora https://en.teleflora.by/ are honoured to represent the international flower and gift delivery service Teleflora in the Republic of Belarus. We facilitate the delivery of flowers, gifts, and bouquets through our partner network in Minsk, the Minsk suburbs, and all cities of Belarus, ensuring that they are delivered by courier to the recipient’s door. We take pride in offering only the freshest flowers and a meticulous approach to customer care. We are delighted to provide international flower delivery.
Отечественный этношоп НашаМебель предлагает широкий гарнитур кухонь, коим помогут создать устроенность а также удобства в течение вашем доме https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Мебельная фабрика предлагает изготовление корпусных, встроенных шкафов-купе на заказ по индивидуальным размерам http://optimumreality.com/groups/%d0%b6%d0%b5%d0%bb%d0%b0%d0%b5%d1%82%d0%b5-%d0%ba%d1%83%d0%bf%d0%b8%d1%82%d1%8c-%d1%88%d0%ba%d0%b0%d1%84-%d0%ba%d1%83%d0%bf%d0%b5/
https://flseo.ru/
Нужны срочные деньги, но плохая кредитная история мешает получить займ? Срочные микрозаймы онлайн 24/7 предлагает проверенные решения. Здесь представлены микрофинансовые организации, готовые предоставить до 30 000 рублей даже при наличии просрочек. Оформление онлайн и быстрое зачисление на карту – доступно каждому, кто столкнулся с трудностями. Подписывайтесь, чтобы не пропустить лучшие предложения.
limassol nicosia
shop quality at luko-mebli
слотозал казино
узнать больше Здесь Kraken19.at
is actos safe to take
cheapest real estate in cyprus
Наша компания Baikal-Wheels также предлагает премиальные кованые диски на заказ и shogun a1 r18 купить которые славятся прочностью и легкостью, улучшающей динамические характеристики автомобиля. Приобретая продукцию в компании Baikal-Wheels, вы получаете не только проверенные изделия от лучших производителей, но и профессиональный подход с удобной доставкой прямо к двери.
інтернет магазин меблів
https://balloons-with-delivery.ru
https://taplink.cc/targetboss
вывод из запоя недорого московская область https://lecheniealkgolizma.ru/
Medicine information. Effects of Drug Abuse.
can i order generic fexofenadine pill
All information about medicine. Get information here.
it аутсорсинг
flutter разработка
Наша компания Baikal-Wheels также предлагает высококачественные кованые диски на заказ и купить литье которые известны своей прочностью и легкостью, улучшающей динамические характеристики автомобиля. Приобретая продукцию в компании Baikal-Wheels, вы получаете не только надежные изделия от лучших производителей, но и превосходное обслуживание с удобной доставкой прямо к двери.
Наша компания «Сайт по мебели для кухни» увлекается основанием и еще перепродажей лучшей кашеварной мебели. Пишущий эти строки предлагаем широченный перечень продукта, который говорит самым прогрессивным стереотипам а также направленностям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Transfer Me offers assistance in finding, choosing and planning an airport transfer to anywhere in Europe. Ensuring complete customer satisfaction is our top priority. The cars are all clean, provide safety and comfort. We guarantee fixed prices. https://transferme24.com – a website where you can find out more information about us. We strive to create a unique taxi ride experience. Evaluate the convenience of electronic payment management. If you have any questions, please call. We will be happy to help!
Фабрика кухонных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – это ваш надежный партнер в течение образовании кашеварных интерьеров. Я специализируемся на разработке, изготовлении равно установке первоклассных кухонных гарнитуров, кои сочетают на себе язык, работоспособность и долговечность. Наша предназначение – навязать клиентам личные резолюции, созданные не без; учётом ихний пожеланий также надобностей, чтобы всякая кухня стала приятным также удобным площадью чтобы жизни и творчества http://www.tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
her latest blog pro tronlink
поставить капельницу от алкоголя на дому https://lecheniealkgolizma.ru/
house for sale cyprus
SEO продвижение сайтов является ключевым инструментом для достижения видимости и привлечения целевого трафика на сайт через поисковые системы, такие как Google, Яндекс и другие. В современном digital-мире, успешное продвижение сайта поисковиках включает в себя множество аспектов, начиная с тщательного подбора ключевых слов и заканчивая созданием качественного контента. Ключевые слова помогают понять, что именно ищут пользователи, поэтому важно провести подробное исследование для выбора наиболее релевантных запросов. Следующим шагом является оптимизация заголовков, мета-тегов и URL-адресов, что улучшает индексацию страниц. Внутренняя структура сайта и качественные обратные ссылки также играют важную роль, способствуя лучшему восприятию сайта как пользователями, так и поисковыми роботами. Кроме того, в эпоху мобильных устройств, адаптивный дизайн и скорость загрузки страниц имеют первостепенное значение. Технический SEO, включающий проверку на ошибки, редиректов, дубликатов контента и других аспектов, помогает устранить проблемные места, которые могут помешать ранжированию сайта. Не стоит забывать и о поведенческих факторах: высокая конверсия и длительное время пребывания на сайте указывают поисковикам на качество контента и пользовательского опыта. Наконец, регулярный анализ статистики и корректировка стратегии на основе собранных данных позволяют постоянно улучшать позиции сайта. Таким образом, SEO продвижение сайтов не ограничивается одной лишь оптимизацией, а представляет собой комплексный подход, требующий постоянного внимания и адаптации к изменениям алгоритмов поисковых систем.
Источник
Продвижение сайта в поисковых системах – это многоуровневый и многоаспектный процесс, который требует комплексного подхода и тщательной стратегии. В основе лежит оптимизация сайта под требования поисковых алгоритмов, таких как Google и Яндекс. Начнем с внутренней оптимизации: важно позаботиться о структуре сайта, его навигации, скорости загрузки страниц и адаптивности под мобильные устройства. Контент играет ключевую роль: он должен быть уникальным, информативным и полезным для целевой аудитории, а также содержать ключевые слова, по которым пользователи ищут информацию. При этом не стоит перегружать текст ключевыми словами, чтобы избежать санкций за переспам. Метатеги, такие как title, description и h1, должны быть заполнены корректно и содержать релевантные ключевые фразы. Внешняя оптимизация включает в себя работу с обратными ссылками: необходимо, чтобы на ваш ресурс ссылались качественные и авторитетные сайты. Социальные сигналы также играют важную роль – активность в социальных сетях помогает повысить узнаваемость и доверие к ресурсу. Аналитика и постоянный мониторинг позиций в поисковой выдаче позволяют своевременно вносить корректировки в стратегию. Понимание аудитории и анализ конкурентов дают ключ к разработке эффективных методов продвижения. Не забывайте про локальное SEO, если ваш бизнес ориентирован на конкретный регион или город. Наконец, участвуйте в форумах, блогах и других сообществах, связанных с вашей сферой, чтобы укрепить авторитет и создать дополнительные каналы для привлечения трафика. Только тщательная и систематическая работа на всех уровнях обеспечит долгосрочный успех в продвижении сайта в поисковых системах.
Источник
Holiday homes in Cyprus
сюда Kraken20.at
I want to show you one exclusive program called (BTC PROFIT SEARCH AND MINING PHRASES), which can make you a rich man!
This program searches for Bitcoin wallets with a balance, and tries to find a secret phrase for them to get full access to the lost wallet!
Run the program and wait, and in order to increase your chances, install the program on all computers available to you, at work, with your friends, with your relatives, you can also ask your classmates to use the program, so your chances will increase tenfold!
Remember the more computers you use, the higher your chances of getting the treasure!
DOWNLOAD FOR FREE
Telegram:
https://t.me/btc_profit_search
Познакомьтесь мало нашим профессиональным коллективом, который создаёт уникальную мебель, воплощая ваши грезы в течение явь http://www.cehitae2kuhnishki.ru/.
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сигвеев в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: мастер по ремонту сигвеев
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Портал mirtinvest.ru предлагает уникальную возможность получить микрокредит на карту без отказов. Более 40 лицензированных МФО сотрудничают с нами, предоставляя своим клиентам доступ к займам с минимальными требованиями. Для всех лиц от 18 лет процентная ставка составляет не более 0,8% в день. Такой подход обеспечивает высокий уровень доступности и надёжности, что делает наш сервис предпочтительным для быстрого получения денежных средств онлайн.
разработка личного кабинета
разработка приложений для бизнеса
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в С-петербурге – этто ваш фундаментальный партнер в течение образовании кашеварных интерьеров. Наша сестра работаем на разработке, фабрике и аппарате первоклассных кашеварных гарнитуров, коие сочетают на себя язык, функциональность и долговечность. Наша поручение – предоставить клиентам индивидуальные вывода, основанные кот учётом их пожеланий да потребностей, чтобы любил шакша остановилась приятным а также спокойным районом чтобы житья да творчества http://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru.
Да, действительно. Всё выше сказанное правда. Давайте обсудим этот вопрос. Здесь или в PM.
El juego Ingles brag (de la antigua palabra”Bragg”) se origino claramente de “brag” e incluia un farol (“engano”, “farol”), https://alpagassologne.com/, aunque este concepto ya era conocido en varios juegos de esos anos.
Выше- интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный перечень мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас ваша милость выберете шиздец нужное чтобы формирования приятного и еще многофункционального внутреннего убранства https://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Купить резину XCENT EL891 315/80R22.5 в Рубцовск по ценe пpoизвoдитeля. Свяжитесь c нaми пo вoпрoсaм сотpyдничecтва и cpокам oтгpузки шин. Грузовая шины XCENT EL891 315/80R22.5 cоздaны нa оcнoвe мeждунаpoдных cтандaртов и имеют oтличнoе кaчество обеcпeчивaющие длитeльный экcплуатaциoнный пеpиoд пpи максимальных нaгpузках. Oтличнo зарекомендовали себя пpи кoмбинирoвaнной eздe по камню и aсфaльтy. При пpoизводствe резины испoльзyютcя мaтеpиалы выcокогo кaчеcтвo с применениeм нaтурального кaчества, чтo пoзволяет шинaм держать pабочие темпepaтуры, иметь стойкость к иcтиpaнию. Бpeнд грузовых шин XCENT oтличнo ceбя зapeкoмендoвал в стрaнах Еврoпы и нaбирaет пoпулярнocть в Poccии. Дocтупная стоимость шин oбocнoвана заинтeреcованноcтью пpoизвoдитeля в продвижении своeгo бpeндa на внутреннем рынкe Pоccии и стpанах СНГ. Пpи oтгpузкe каждая пapтия шин пpoходит контрoль качеcтвa. Мoдeль резины XCENT EL891 набиpaeт попyлярнoсть в России, что я являетcя oтличной pекомeндацией при выборе грузовых шин. Мы пpиглaшаeм к cотpудничecтвy aвтoтpанcпоpтныe пpeдпpиятия и пpeдпринимaтелeй, oбеспечивая прямыe закупки пo цeнe пpоизводитeля и oплaтe зa поставляeмые шины в pyблях c НДC. Oтгpyжaeмaя пapтия грузовых шин XCENT EL891 315/80R22.5 240 шт. По вoпpоcaм сoтрудничeствa и сpокам отгpyзки прocим cвязывaться по yказaнным контaктам на сaйте. Подpобнyю инфopмацию о шинах можeтe изучить нa нaшeм сaйте.
prednisone 20 mg price walmart
Мебель Бровары
Pills information leaflet. Short-Term Effects.
where to buy kamagra no prescription
Actual information about drugs. Get information here.
Отечественный этношоп НашаМебель предлагает широченный сортамент кухонь, которые посодействуют создать устроенность а также удобство в течение вашем доме http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Выше интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный ассортимент мебели чтобы кухонь. ЯЗЫК нас вы выкопаете все нужное чтобы образования уютного и высокофункционального интерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
1xbet Sign Up Bonus
Существуют различные медицинские учреждения, предоставляющие услуги по выводу из запоя по разумным ценам. Для пациентов важно понимать, какие факторы влияют на стоимость лечения. Прежде всего, квалификация специалистов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-krasnodare/]вывод из запоя анонимно ярославль[/url]
Цена выведения из запоя на дому может колебаться в диапазоне от 5000 до 20 000 рублей и более. Данный метод подразумевает оказание медицинской помощи пациенту в привычной домашней обстановке, что имеет свои преимущества и особенности. Выездная бригада врачей проводит осмотр и оценку состояния пациента, назначает необходимые препараты и процедуры.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-krasnodare/]безопасный вывод из запоя цены зеленоград[/url]
Алкогольная зависимость представляет собой значимую проблему, требующую специализированного вмешательства. Запойное состояние характеризуется длительным потреблением спиртного, приводящим к физической и психической зависимости. В этом контексте вывод из запоя становится необходимым шагом к восстановлению здоровья. Обеспечение круглосуточной помощи позволяет минимизировать риски для пациента, повышая вероятность успешного завершения терапии.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-krasnodare/]рехаб липецк клиника наркологический[/url]
Наркологическая клиника “Вектор выздоровления” представляет собой специализированное медицинское учреждение, нацеленное на оказание квалифицированной помощи лицам, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша основная задача — предоставить эффективные методы лечения и поддержку, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолеть пагубное пристрастие и достичь устойчивой ремиссии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://xn—-7sbbkgwmincnbet5u.xn--p1ai/]наркология дзм москва[/url]
Познакомьтесь один-другой нашим профессиональным коллективом, который формирует чудесную мебель, воплощая ваши мечты в течение явь http://cehitae2kuhnishki.ru.
Избавьтесь от алкогольной зависимости с помощью нашего комплексного лечения, разработанного для тех, кто стремится к долгосрочной трезвости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://tuapse.narcology.clinic/service/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma/]кодирование от алкоголизма цены[/url]
Если вы хотите придать уникальность своему автомобилю и обновить внешний вид, то на сайте baikalwheels.ru у вас предлагается вариант купить литые диски в томске популярных мировых брендов. В каталоге представлены такие марки, как Replika, Nitro, Legeartis и K&K, которые имеют отличную репутацию. Размеры варьируются от 16 до 22 дюймов, что дает возможность выбрать идеальные диски для любых автомобилей — от седанов до внедорожников.
Наша компания «Сайт числом мебели для кухни» забирается формированием также продажей качественной кухонной мебели. Мы предлагаем широкий гарнитур(а) продукции, яже говорит самым современным штампам да направленностям дизайна https://www.sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
Основная цель клиники — создание благоприятной среды для эффективного лечения и восстановления пациентов с зависимостью. Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы каждый человек, обратившийся за помощью, получил индивидуальный план терапии, учитывающий его уникальные потребности и особенности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/]вывод из запоя южная[/url]
Во время вывода из запоя на дому круглосуточно пациент находится под постоянным наблюдением квалифицированных специалистов. Это позволяет контролировать его состояние, измерять жизненно важные показатели, такие как давление и пульс, и своевременно реагировать на любые отклонения.Во время вывода из запоя на дому круглосуточно пациент находится под постоянным наблюдением квалифицированных специалистов. Это позволяет контролировать его состояние, измерять жизненно важные показатели, такие как давление и пульс, и своевременно реагировать на любые отклонения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-rostove-na-donu/]вывод из запоя на дому фрязино[/url]
Стоимость выведения из запоя на дому может составлять от 10 000 до 25 000 рублей и более в зависимости от ряда факторов. Этот метод подразумевает оказание медицинской помощи пациенту в комфортной домашней обстановке, что может быть предпочтительным для некоторых людей. Выездная бригада врачей проводит детальное обследование пациента, оценивает степень тяжести интоксикации и назначает соответствующее лечение.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-rostove-na-donu/]вывод из запоя цены ейск[/url]
Стационарный вывод из запоя подразумевает госпитализацию пациента в специализированное учреждение. Процесс включает в себя детоксикацию, которая состоит из очищения организма от токсинов, накопленных в результате чрезмерного употребления алкоголя. В условиях стационара осуществляется постоянный мониторинг состояния пациента, что позволяет своевременно выявлять возможные осложнения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://xn—-7sbjuigkblbdbkg0myb4b.xn--p1ai/vivod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-rostove-na-donu/]вывод из запоя витебск анонимно[/url]
1xbet bangladesh
На сайте https://automylife.ru/ ознакомьтесь с полезной и ценной информацией об автомобилях. Здесь есть увлекательные данные, которые касаются китайских, корейских, отечественных автомобилей. Также есть информация и об электромобилях, содержательные и любопытные отзывы. Они особенно помогут вам в том случае, если планируете покупку. Ознакомьтесь и с новостным блоком, где вы найдете все самое актуальное и свежее, что касается технических параметров, дизайна. Регулярно выкладываются интересные и полезные публикации.
Воздушные гелиевые шары от 120 рублей за 1 шарик. Срочная доставка от 1 часа. Круглосуточная доставка по Нижнему Новгороду. Более 4000 наборов в каталоге на сайте https://balloons-with-delivery.ru
Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту сетевых хранилищ в Москве.
Мы предлагаем: цены на ремонт сетевых хранилищ
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
Шкафы распашные – купить по выгодной цене с доставкой. 36 моделей в проверенных интернет-магазинах: популярные новинки и лидеры продаж заказать мебель
Авторитетное сообщение 🙂 , заманчиво…
And landing page is able to help you to create high-quality video that is optimized for SEO, easy to read, original, suitable for https://medium.com/@volodymyrzh/content-marketing-and-its-main-concepts-2e1ad794c007 and written in an appropriate tone.
вывод из запоя на дому в ростове вывод из запоя на дому в ростове .
ростов вывод из запоя ростов вывод из запоя .
Выше- магазин НашаМебель зовет широченный гарнитур кухонь, коим посодействуют создать уют и уют в течение вашем жилье https://notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Это ценное мнение
29 de abril de 2010 https://allecleats.com/ fue reconocido/ coronado Por la asociacion internacional de deportes intelectuales (imsa) como intelectual competencia.
great furniture at luko-mebli
лечение алкоголизма домашними средствами https://lecheniealkgolizma.ru/
снять квартиру на сутки Гомель
Yesterday, while I was at work, my sister stole my iphone and tested to see if it can survive a 40 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is totally off topic but I had to share it with someone!
вован казино
gomelsutochno.ru
снять квартиру на сутки в Гомеле
Фотофабрика кашеварных гарнитуров в Санкт-петербурге – этто ваш надежный партнер в течение основании кухонных интерьеров. Мы специализируемся на разработке, производстве также установке высококачественных кухонных гарнитуров, тот или другой сочетают в себя стиль, функциональность равно долговечность. Наша послание – передать посетителям отдельные резолюции, сделанные кот учётом их пожеланий да потребностей, чтобы каждая кухня стала уютным а также спокойным помещением для жизни равно творчества https://tivokya0kuhnishki.ru/.
Если ты поиски вариант купить оружие, не покидая из квартиры, мы предлагаем тебе обратить внимание к специализированный канал. Здесь вы обнаружите широкий выбор огнестрельного или колюще-режущего оружия, а также дополнительных предметов.
Что может предложить данный канал:
Актуальные акции и специальные предложения Транспортировка в городу Советы а поддержка покупателей Присоединяйтесь в нашему каналу и получите возможность к эксклюзивным эксклюзивным предложениям! купить пистолет недорого В современном веке вопрос защищённости делается всё более важным. Обладание оружия при человеке может оказаться ключевым условием в обстановке, когда необходимо защитить человека и родных.
Прежде всего, оружие выступает надежным средством самозащиты. Оно позволяет не только отпугнуть возможных преступников, но и защитить вас в обстоятельстве непосредственной угрозы. Чувство уверенности в том, что у человека есть возможность оборониться, может существенно повысить уровень личной защиты.
Во-вторых, присутствие оружия может произвести эмоциональное воздействие на людей вокруг. Окружающие, которые понимают, что вы способны вас защитить, в большинстве случаев воспринимают к вам с осторожностью и осторожностью.
Наконец, в некоторых моментах вооружение может являться единственным средством устранения насилия. Необходимо учитывать, что с большой силой связано и весомая ответственность. Корректное использование и осознание законодательства об оружии — важные аспекты, которые необходимо учитывать.
В итоге, наличие вооружения способно выполнить ключевую функцию в гарантии персональной охранности, однако, его использование требует обдуманного отношения и соблюдённости всех важных правил.
Выше- магазин НашаМебель делает отличное предложение широченный сортамент кухонь, коие помогут сделать уют (а) также удобство на вашем доме http://www.notahye4kuhnishki.ru/.
Наша компания «Фотосайт по мебели для кухни» забирается образованием а также реализацией качественной кухонной мебели. Я делаем отличное предложение широченный перечень продукции, который отвечает самым прогрессивным эталонам и еще тенденциям дизайна https://sufebey8kuhnishki.ru.
order from luko-mebli
Меня тоже волнует этот вопрос. Подскажите, где я могу найти больше информации по этому вопросу?
в законе уточняется термин азартный бизнес, к кому относят работу по организации, проведению и представлению возможности коннекта с азартным играм в казино на игровых автоматах, компьютерных симуляторах, в бк, в интерактивных заведениях; в интернет https://1win-casino-online.shop/ вне зависимости от района расположения сервера.
Доставка воздушных шаров с гелием по цене от 115 рублей за гелиевый шарик. Круглосуточно 24/7 доставляем по Нижнему Новгороду и области, а самовывоз со скидкой 5% https://helium-balloons.ru
Отечественный интернет-магазин “Мебель-шмммммммебель” предлагает широченный набор мебели чтобы кухонь. У нас вы выкопаете все нужное чтобы тварей приятного (а) также высокофункционального экстерьера http://www.tyfapao6kuhnishki.ru/.